
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
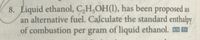
Transcribed Image Text:8. Liquid ethanol, C,H,OH(1), has been proposed as
an alternative fuel. Calculate the standard enthalpy
of combustion per gram of liquid ethanol. m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A chemist carefully measures the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of a 1.85 kg sample of C,H,,S from -0.2 °C to 10.8 °C. The experiment shows that 4.04 × 10" J of heat are needed. What can the chemist report for the molar heat capacity of C,H,S? Round your answer to 3 12 significant digits. |J•mol 1 ·K x10 ?arrow_forwardWhat is the assumption made when chemical reactions are performed which allows us to use enthalpy, ΔH, instead of energy, ΔE?arrow_forwardnuraipy changes in chemical reactions Read through pages 18-20 in your laboratory manual for information on how to calculate the enthalpy change in a solution. Part A - Calculating ms In a calorimetry experiment 5.6 g of potassium hydroxide is dissolved in 400 mL water in a thermos flask. The temperature increase in the solution is 7 °C. The effective mass of the glass in the thermos flask (mcal) is 0.040 kg. The heat capacity of the solution (Cs) is 4.04 kJkg-¹K-1¹. The heat capacity of the calorimeter (Ccal) is 0.387 kJkg-¹K-1. Remember to enter your answer using the specified number of significant figures, but keep the entire number in your calculator for use in further calculations. Calculate the total mass of solution in kilograms (ms) Give your answer to four significant figures. ▾ View Available Hint(s) Hint 1. Calculating ms mg = mass water (kg) + mass solute (kg) —| ΑΣΦ Submit Request Answer ? kg < Pear 10arrow_forward
- Calculate the standard enthalpy of reaction for the combustion of methane. Round to the nearest whole number.CH4(g) + O2 --> CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) kJ/mol Compound Hf (kJ/mole) CH4(g) -75 CO2(g) -394 H2O(l) -284 This reaction is: endothermic or exothermicarrow_forward1. A certain two-step process involves transfer of heat and work between the system and the surroundings. In the first step, the internal energy, AE, of the system increases by 115.4 J when 95.1 J of work is done on the system. In the second step, the internal energy of the system decreases by 32.2 J when 15.6 J of work is done on the surroundings. In the first step of the two-step process, how much heat, in Joules, was absorbed or released? b. How much heat, in Joules, was absorbed or released in the whole two-step process? a.arrow_forwardA calorimeter is calibrated by mixing two aqueous solutions each with a volume equal to 44.4 mL. The reaction is known to produce 1,465 J of heat, and the measured temperature rise is 4.64 K. Heat produced by the reaction is absorbed by the calorimeter and the resulting solution in it. The same calorimeter is used in a subsequent experiment where 44.4 mL of 0.430 mol L-1 HCl are mixed with 44.4 mL of 0.43 of NaOH. The temperature rises by 3.38. Calculate the heat evolved by the reacting system in J *be sure to include the correct sign in your answer*. heat evolved (J) = What is the enthalpy of the neutralization reaction in kJ/mol ? Enthalpy of Reaction (kJ/mol) = kJ/molarrow_forward
- A 77.5g piece of brass is heated so that its temperature is 98.7◦C. Next,it is quickly placed in a calorimeter containing 102.76 g of water at 18.5◦C.Knowing that the final temperature is 23.5◦C, what is the specific heat of this alloy?Note: Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc. From 98.7 to 23.5◦C, this alloy does not changeno phase, it remains in solid form.arrow_forwardWhen 1.42 g of iron reacts with 1.80 g of chlorine, 3.22 g of iron(II) chloride (FeCl2, molar mass = 126.75 g/mol) and 6.8 kJ of heat is produced. What is the enthalpy change for the reaction when 1 mole of iron(II) chloride is produced? round to sig figsarrow_forwardDetermine the change in enthalpy (kJ/mol) for the following reaction. Use significant figures CH4(g) + 2O2(g) -> CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) H=?arrow_forward
- 5. When 1.00g of NaCl (MM 58.44 g/mol) is dissolved in 50.00g of water, the temperature drops by 0.319°C. This temperature change is only detectable by the most sensitive thermometers. If this process takes place in a very well insulated calorimeter, no calorimeter constant is needed. a. Calculate the enthalpy change per gram of NaCl. b. Calculate the enthalpy change per mole of NaCl.arrow_forward3. Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction P406 (s) + 2 02 (g) → P4010 (s) given the following enthalpies of reaction: AH = -1640.1 kJ P4 (s) + 3 02 (g) P4 (s) + 5 02 (g) → P406 (s) → P4010 (s) AH = -2940.1 kJarrow_forward10 A student heats 84.17 mL of water to 95.27°C using a hot plate. The heated water is added to a calorimeter containing 73.92 mL of cold water. The water temperature in the calorimeter rises from 2.15°C to 37.48°C. The specific heat capacity of water is 4.184 J and the density of water is g. °C 1.00 mL Assuming that heat was transferred from the hot water to the cold water and the calorimeter, determine the heat capacity of the calorimeter. J Heat capacity of calorimeter = °Carrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY