
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Two boxes of fruit on a frictionless horizontal surface are connected by a light string as in Figure P4.65, where m1 = 10 kg and m2 = 20 kg. A force of 50 N is applied to the 20-kg box.
(a) Determine the acceleration of each box and the tension in the string.
(b) Repeat the problem for the case where the coefficient of kinetic friction between each box and the surface is 0.10.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1

arrow_forward
Step 2
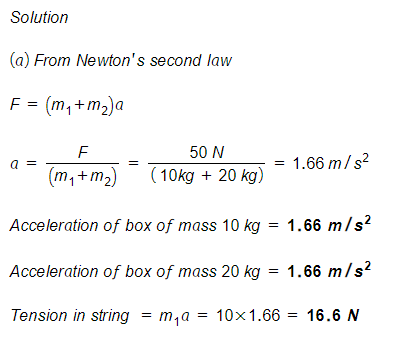
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A contestant in a winter games event pulls a 47.0 kg block of ice across a frozen lake with a rope over his shoulder as shown in the figure. F 25° The coefficient of static friction is 0.1 and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.03. (a) Calculate the minimum force F (in N) he must exert to get the block moving. N (b) What is its acceleration (in m/s2) once it starts to move, if that force is maintained? m/s²arrow_forwardA student attaches a rope to a 32 kg box, and drags it to the left with constant velocity of 1.97 m/s. The tension in the rope is 207 N at an angle of 35.7° to the ground. How much does the box weigh? Find the x and y components of the applied (tension) force: Fx = N. %3D Fy = N. How much friction must be present? How much Normal force must be present? N.arrow_forwardThe figure below shows a box with a mass of m= 3.90 kg on a ramp inclined at an angle of 35.0°. The coefficient of static friction between the box and the ramp is 0.250. Find the minimum magnitude of the force F (in N), applied to the box in a direction perpendicular to the ramp, that will prevent the box from sliding down the ramp. N m 35.0°arrow_forward
- A contestant in a winter games event pushes a 37.0 kg block of ice across a frozen lake as shown in the figure. 25°. The coefficient of static friction is 0,1 and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.03. (a) Calculate the minimum force F (in N) he must exert to get the block moving. 39.96 (b) What is its acceleration (in m/s2) once it starts to move, if that force is maintained? 0.686 xm/s2 Additional Materials O Reading Submit Answer P Type here to search DELL Esc F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 トI @ #3 $ % 3 4 Tab W R T. Y Caps Lock K Ehift V つ Aarrow_forwardA robot pushes a 20-kg box on the horizontal surface as part of the moving job. The force is 35 N to the left shown, and the box does not move. The coefficients of friction between the floor and box are µs = 0.75 and uk = 0.40. What is the minimum pushing force (magnitude only) needed to move the box, in Newtons? Useg = 10 m/s². Your answer needs to have 2 significant figures, including the negative sign in your answer if needed. Do not include the positive sign if the answer is positive. No unit is needed in your answer, it is already given in the question statement.arrow_forwardIn a movie, a stuntman places himself on the vertical front of a truck as the truck accelerates. The coefficient of static friction between the stuntman and the truck is 0.370. The stuntman is not standing on anything but can “stick” to the front of the truck as long as the truck continues to accelerate. What minimum forward acceleration will keep the stuntman on the front of the truck?arrow_forward
- A box, initially at rest, is pushed up a ramp that makes an angle of 15◦ with the horizontal as shown in the diagram. The magnitude of the pushing force is 8m newtons, where m is the mass of the box in kilograms. The force is in a direction parallel to and up the ramp. The coefficient of sliding friction between the box and the ramp is 0.25. Model the box as a particle and take the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity to be g = 9.8 m s−2 . Express the four forces in component form in terms of unknown magnitudes where appropriate and find an expression for the resultant force acting on the box. Hence find the magnitude of the acceleration of the box, in m s−2arrow_forwardA box with mass 32.5 kg rests on a frozen pond, which serves as a frictionless horizontal surface. If a fisherman applies a horizontal force of 14.0N to the box causing it to accelerate to the right. What is the acceleration produced? How far does the crate travel in 10.0 seconds?arrow_forwardYou are designing a high-speed elevator for a new skyscraper. The elevator will have a mass limit of 2400 kg (including passengers). For passenger comfort, you choose the maximum ascent speed to be 18.0 m/s, the maximum descent speed to be 10.0 m/s, and the maximum acceleration magnitude to be 5.00 m/s2. Ignore friction. What is the maximum upward force that the supporting cables exert on the elevator car?arrow_forward
- A 34.8 kg child is sitting at the top of a slide, which is inclined at an angle of 55 degrees with respect to the horizontal. Someone gives the child a quick push to get them moving, after which they slide down the incline without any further assistance. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the child and the slide is μ s = 0.44. What is the magnitude of the acceleration (in m/s2) of the child?arrow_forwardA large cube (mass = M) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force . A small cube (mass = m) is in contact with the front surface of the large cube and will slide downward unless is sufficiently large. The coefficient of static friction between the cubes is u. What is the smallest magnitude that F can have in order to keep the small cube from sliding downward?arrow_forwardA 55.0 kg block is pulled along a frictionless surface with a force P, exerted at an angle of 25.0 ̊ above the horizontal. What is the minimum force P that will lift the block off the ground? If the block is pulled with half of this force, what will its acceleration be?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON