
Concept explainers
Fill in the blanks in the table below summarizing the interspecific interactions in a community.
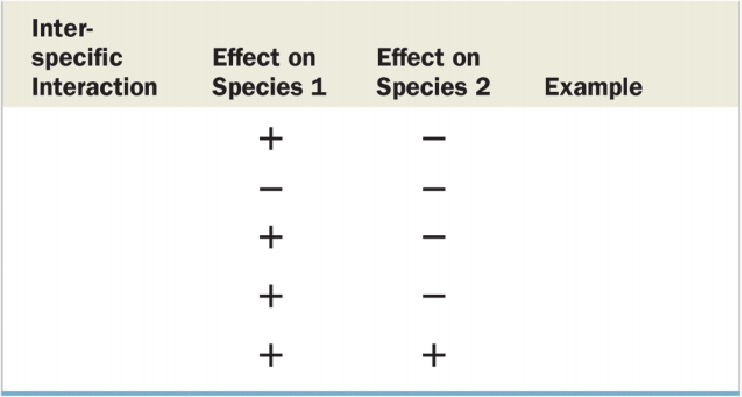
To complete: The blanks summarizing the interspecific interactions in a community.
Introduction: While surviving in an ecosystem, many species interact with each other. These interactions can be mutually beneficial or harmful for one or the other. There are five main types of interspecific interactions, namely, predation, competition, herbivory, parasitism, and mutualism.
Answer to Problem 1CC
Tabular representation: Table 1 represents the interspecific interactions in a community as follows:
| Interspecific interactions | Effect on species 1 | Effect on species 2 | Examples |
| Predation | + | - | Osprey/fish |
| Competition | - | - | Hyenas/vultures |
| Herbivory | + | - | Deer/shrub |
| Parasitism | + | - | Tapeworm/horse |
| Mutualism | + | + | Clown fish/anemone |
Table 1 Depicts the interspecific interactions in a community.
Explanation of Solution
The five types of interspecific interactions are as follows:
Predation: In predative interspecific interactions, one species preys on the other species for food or territory. It is a type of +/- interaction where one species benefits and the other species does not benefit. For example: interaction between a deer and a lion is predation.
Competition: It is the competitive interspecific interaction where two different types of species are competing for the same resource. Neither of them benefits from this, so it is a type of -/- interaction. For example: the interaction between vulture and hyenas.
Herbivory: It is the interaction between the herbivores and the plants. This interaction is a type of +/- interaction where the deer is benefited while the plant is not. For example: an interaction between deer and grass is herbivory.
Parasitism: It is parasitic form of interspecific interaction that involves one organism using the other for food and shelter. One organism such as the tapeworm inhabits the gut or any other part of the other organism such as the horse. This interaction is a +/- interactions, where only one is benefitted.
Mutualism: In this interaction, the organisms that are interacting are mutually beneficial for each other. One species provides one factor, while the other species provides another factor, for example, in the case of mycorrhiza, the fungus is in mutual interaction with the roots of the gymnosperm tree. The fungal element provides minerals and water from the soil, while the tree provides the nutrients. It is a +/+ form of interaction as both the organisms are benefitted.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 37 Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (8th Edition)
- Species within a community interact with each other in a variety of ways. Match each scenario with the type of species interaction it describes. Competition Commensalism Consumption Mutualism grass and clover both using the mice eating seeds lizards catching insects for food limited nutrients in the same patch of soil from sunflowers Answer Bank orchids growing harmlessly on branches of trees bees receiving nectar in exchange for pollinating flowers doves and cardinals eating seeds from the same limited number of plantsarrow_forwardWhich sort of interaction is harmful to one species but beneficial to the other? List at least three.arrow_forwardWhat level of disturbance allows the greatest coexistence among species? Y At what level of disturbance is interspecific competition the greatest? X Many #Species in Community Few Low X Y Level of Disturbance High Narrow_forward
- What is meant by interaction that happen among species is diffusearrow_forwardCan you please help find the answer that is reasonable base on this chart?arrow_forwardInterspecific interactions affect the survivaland reproduction of the species that engage in them. As shownin the table, these interactions can be grouped into three broadcategories: competition, exploitation, and positive interactionsarrow_forward
- Which of the following measures the relative abundance of species in a community? Species Evenness Species Diversity Species Distribution Species Richnessarrow_forwardWhy Are Community Interactions Important?arrow_forwardBackground: Define biodiversity, its ecological importance of the Squirrel that has been researched and is it endangered, extirpated, endemic etcarrow_forward
- Give examples of coevolutionary relationships in communities.arrow_forward_______________ competition occurs within a population, and _______________ competition occurs among populations of different species. (a) Interspecific; intraspecific (b) Intraspecific; interspecific (c) Type I survivorship; Type II survivorship (d) Interference; exploitation (e) Exploitation; interferencearrow_forwardA symbiotic association in which organisms are beneficial to one another is known as (a) predation (b) interspecific competition (c) intraspecific competition (d) commensalism (e) mutualismarrow_forward
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College




