
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY-MASTERING BIO.ACCESS
12th Edition
ISBN: 9780136486787
Author: Urry
Publisher: SAVVAS L
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 28, Problem 10TYU
SYNTHESIZE YOUR KNOWLEDGE
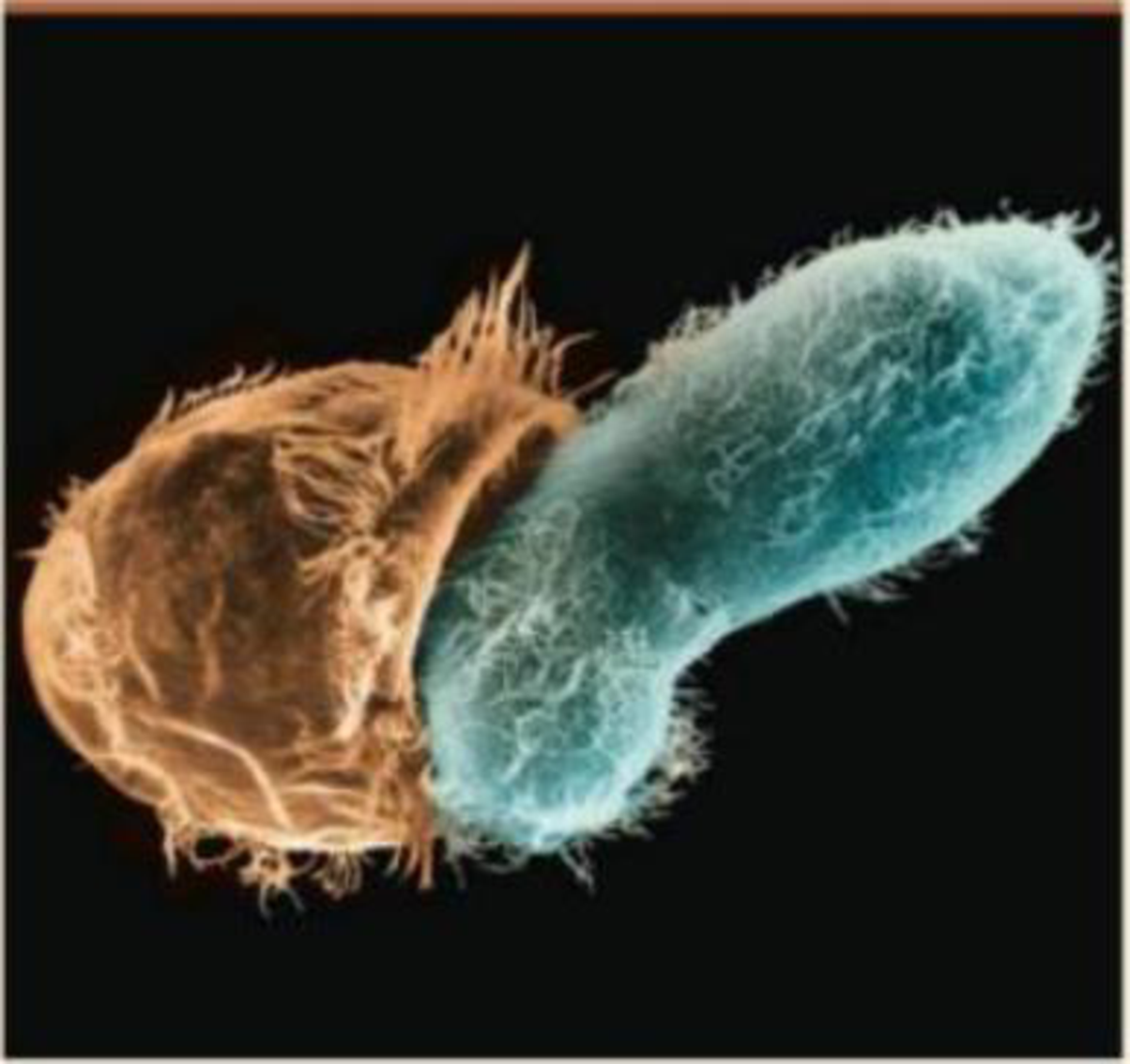
This micrograph show's a single-celled eukaryote, the cillate Didinium (left), about to engulf its Paramecium prey, which is also a ciliate. identify the eukaryotic. supergroup to which ciliates belong and describe the role of endosymbiosis in the evolutionary history of that supergroup Are these abates more closely related to all other proatists than they .are to plants,
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
DNA sequence data for a diplomonad, a euglenid, a plant, and an unidentified protist suggest that the unidentified species is most closely related to the diplomonad. Further studies reveal that the unknown species has fully functional mitochondria. Based on these data, at what point on the phylogenetic tree in Figure 1 did the mystery protist’s lineage probably diverge from other eukaryote lineages? Explain.
Differentiate the functions of the macro-and micronuclei of ciliates. What is the advantage of having dimorphic nuclei as compared to the monomorphic nucleus of other protozoans?
Apicomplexans are widespread and common parasites of worms, echinoderms, insects, and vertebrates (including humans). What characteristics do these protozoans have that make them highly infective (efficient as parasites)?
How can foram fossils provide clues about past cold and warm periods, and global temperature change?
What characteristics separate Euglenozoans from Chlorophytes (i.e., Volvox, green algae)?
The following groups of protists will be covered in lecture: Amoebazoa, Excavate-euglena,
Alveolata: ciliates, dinoflagellates, apicomplexan;
Stramenopiles: diatoms and brown algae, and
Plantae: chlorophytes.
How do these organisms compare in their
-general type of nutrition (autotroph, heterotroph),
-ecological roles (parasites, decomposers, importance in
food chains)
-general structures (cell walls, structures that help them
move and feed, single vs multicellular)
-reproduction (asexual, sexual)
-presence or absence of alternation of generations, -
degree of complexity of life cycles
-habitats that they are found in
Chapter 28 Solutions
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY-MASTERING BIO.ACCESS
Ch. 28.1 - Cite at least four examples of structural and...Ch. 28.1 - Summarize the role of endosymbiosis in eukaryotic...Ch. 28.1 - Prob. 3CCCh. 28.2 - Why do some biologists describe the mitochondria...Ch. 28.2 - WHAT IF? DNA sequence data for a diplomonad, a...Ch. 28.3 - Explain why forams have such a well-preserved...Ch. 28.3 - WHAT IF? Would you expect the plastid DNA of...Ch. 28.3 - Prob. 3CCCh. 28.3 - Prob. 4CCCh. 28.4 - Contrast red algae and brown algae.
Ch. 28.4 - Why is it accurate to say that Ulva is truly...Ch. 28.4 - Prob. 3CCCh. 28.5 - Contrast the pseudopodia of amoebozoans and...Ch. 28.5 - Prob. 2CCCh. 28.5 - Prob. 3CCCh. 28.6 - Justify the claim that photosynthetic protists are...Ch. 28.6 - Prob. 2CCCh. 28.6 - WHAT IF? High water temperatures and pollution...Ch. 28.6 - MAKE CONNECTIONS The bacterium Wolbachia is a...Ch. 28 - Describe similarities and differences between...Ch. 28 - What evidence indicates that the excavates form a...Ch. 28 - Prob. 28.3CRCh. 28 - On what basis do systematists place plants in the...Ch. 28 - Describe a key feature for each of the main...Ch. 28 - Prob. 28.6CRCh. 28 - Plastids that are Surrounded by more than two...Ch. 28 - Biologists think that endosymbiosis gave rise to...Ch. 28 - Prob. 3TYUCh. 28 - According to the phylogeny presented in this...Ch. 28 - In a life cycle with alternation of generations,...Ch. 28 - Based on the phylogenetic tree in Figure 28.2,...Ch. 28 - Prob. 7TYUCh. 28 - SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY Applying the If then logic of...Ch. 28 - WRITE ABOUT A THEME: INTERACTIONS Organisms...Ch. 28 - SYNTHESIZE YOUR KNOWLEDGE This micrograph show's a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The Phylum Animalia has some unique traits that set it apart from plants and fungi. Check all traits that animals have: [] They have teeth [] A blastula is formed shortly after fertilization [] They are all cute and furry [] Prokaryotic Cells [] Eukaryotic cells[] They are all noctumal[] Multicellular[] They are all nocturnal[] Motile at some point in their lives[] No cell wallarrow_forwardDescribe the morphology of oomycetes. Which protists are known for their cytoplasmic streaming movement? Which protists occasionally resemble tiny snails? What are the shells made of? Which group of protists have elaborate exteriors of glassy silica and are very common in the fossil record? What supergroup do land plants share a common ancestor with? What protists are common in tropical waters and are generally called “seaweeds?” Which of the algaes are the furthest living relatives to land plants? Which algaes are the closest living relatives to land plants? Which protists move using tube-like pseudopodia? Which protist group exhibits similarities to fungi as a result of convergent evolution? Which protist group takes on a slug form when nutrients are hard to come by? What protist group do animals share a common ancestor with? What are the choanoflagellates are believed to resemble? Which group contains at least one type of human parasite? Ecology of…arrow_forwardIn the pictures below, identify the arrowed reproductive structures of microscopic cyanobacteria based on the following descriptions: Akinetes are dormant structures larger than the vegetative cells, are rich in food reserves, and have thick walls. Most filamentous cyanobacteria develop akinetes in adverse conditions (e.g., winter, dry periods). When favorable conditions return, they germinate and produce new filaments. Hormogonia are short pieces of filaments consisting of 5–15 trichomes that fragment and develop into new filaments. Heterocytes (or heterocysts) are multicellular structures that have a thick and massive sheath, formed by members of the Nostocales. It is the location of the enzyme nitrogenase for nitrogen fixation, the conversion of nitrogen gas into ammonium and then amino acids. They may be intercalary or terminal in position and may germinate from either end or both the ends to give rise to new filaments. Non-filamentous cyanobacteria generally produce spores…arrow_forward
- Algae are autotrophs and can have photosynthesis, however, evolutionary evidence suggests that plants shared a common ancestor with only green algae and are closest relatives of Charophytes. What evidences support this statement? How an algal cell is different from fungal cells, even if both are eukaryotes? Why slime mold is a protist not a fungus even if it does not have chloroplast?arrow_forwardIf an ancestral protist was classified as an opisthokont, then what should be true of this protist? -They should also have given rise to the plants. -They should perform heterotrophy by secretion of exoenzymes. -Like diplomonads and parabasalids, they should bear multiple flagella. -They should be parasitic -They should be the common ancestor of the basidiomycetes and animals.arrow_forwardAmoebas and foraminferans are distantly related protists. They are however similar in the fact that; They are both encased in shells They are both photosynthetic They are both members of the Archaeplastida They both feed via psuedopodsarrow_forward
- The termite gut environment is lacking a fresh supply of oxygen O2. However, it is rich with food due to the presence of bacteria that contain enzymes capable of breaking down cellulose and lignin, the macromolecules that make wood. Use this information to determine which of following protista groups is more likely to be found in a termite gut. Diatoms Radiolaria Parabasilids O Rhodophyta O Foraminifera (Forams)arrow_forwardGive typed explanation of both questions otherwise leave itarrow_forwardProtists are(a) single-celled eukaryotes.(b) multicellular eukaryotes.(c) single-celled prokaryotes.(d) single-celled akaryote. Please try to break the solutions into as many steps as practically possible and the steps should come one by one and they should be short and crisp and plagiarism-free.arrow_forward
- Microscopic Images Examine the microscopic images of protists below. Note cell shapes, organelles, intracellular structures, locomotory structures and other distinguishing features. The species or taxonomic names are located under each photo. (a) (b) (c) (d) (0) Multicellular algae (top row A-C, left to right) and unicellular algae (D-F): A. Brown kelp (seaweed) Macrocystis B. Red algae Corallina C. Green algae Halimeda incrassata D. Bioluminescence (blue color) from dinoflagellates (flagellated unicellular algae). E. Diatoms (shelled unicellular algae) F. Colonial green algae Volvox (bottom row)arrow_forwardPlease briefly describe the idea of endosymbiosis and its role in protist evolution-relate to the idea of function of the group.arrow_forwardJr. Scientist discovers a never-before-classified protist. It contains multinucleated filaments, similar to fungal hyphae however, upon closer examination the cell walls are found to be composed of cellulose rather than chitin. They do not perform photosynthesis but instead acquire nutrients by way of parasitism or decomposition. Jr. Scientist has likely discovered a rhizarian a foraminiferan an oomycete a mycetozoanarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning
From Sea to Changing Sea | Early Life in the Oceans || Radcliffe Institute; Author: Harvard University;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ac0TmDf5Feo;License: Standard youtube license