
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The following graph shows the historical concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide concentrations began increasing in the 1800s as humans started to rely on combustion for energy (carbon dioxide is a product of combustion). The increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide is linked to the increases in global temperatures known as global warming.
- What is the total increase in carbon dioxide between 1950 and 2007?
- What is the average yearly increase in carbon dioxide over this period?
- What is the total percentage increase in carbon dioxide over this period?
- What is the average yearly percentage increase in carbon dioxide over this period?
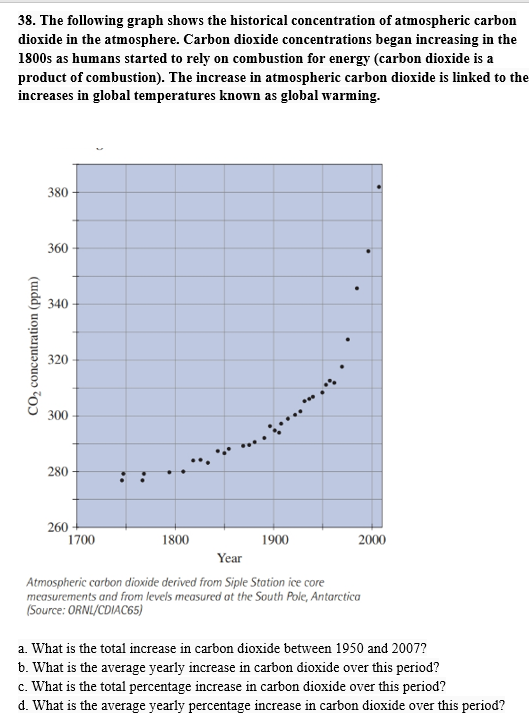
Transcribed Image Text:38. The following graph shows the historical concentration of atmospheric carbon
dioxide in the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide concentrations began increasing in the
1800s as humans started to rely on combustion for energy (carbon dioxide is a
product of combustion). The increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide is linked to the
increases in global temperatures known as global warming
380
360
340
320
300
280
260
1700
1800
1900
2000
Year
Atmospheric carbon dioxide derived from Siple Station ice core
measurements and from levels measured at the South Pole, Antarctica
(Source: ORNL/CDIAC65)
a. What is the total increase in carbon dioxide between 1950 and 2007?
b. What is the average yearly increase in carbon dioxide over this period?
c. What is the total percentage increase in carbon dioxide over this period?
d. What is the average yearly percentage increase in carbon dioxide over this period?
CO2 concentration (ppm)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Use the algebraic equation to determine the mass if the volume was 622 mL. mass (g) = (3.60 g/mL)(volume (mL)) + 11.4 g y= mass (g) m = 3.60 g/mLx= 622 mL b = 11.4 garrow_forwardSubject: chemistryarrow_forwardA chemistry student must write down in her lab notebook the concentration of a solution of potassium chloride. The concentration of a solution equals the mass of what's dissolved divided by the total volume of the solution. Here's how the student prepared the solution: • The label on the graduated cylinder says: empty weight: 1.55 g • She put some solid potassium chloride into the graduated cylinder and weighed it. With the potassium chloride added, the cylinder weighed 31.436 g. • She added water to the graduated cylinder and dissolved the potassium chloride completely. Then she read the total volume of the solution from the markings on the graduated cylinder. The total volume of the solution was 166.4 mL. What concentration should the student write down in her lab notebook? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. -1 g.mL x10 × Śarrow_forward
- The chemical formula for hydrogen fluoride is HF. A chemist measured the amount of hydrogen fluoride produced during an experiment. She finds that 119. g of hydrogen fluoride is produced. Calculate the number of moles of hydrogen fluoride produced. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forwardA chemist measures the amount of fluorine gas produced during an experiment. He finds that 3.1 g of fluorine gas is produced. Calculate the number of moles of fluorine gas produced. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Ú mol 0 x10 Xarrow_forwardA chemist measures the amount of hydrogen gas produced during an experiment. She finds that 556. g of hydrogen gas is produced. Calculate the number of moles of hydrogen gas produced. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. mol x10 Xarrow_forward
- A chemist measures the amount of chlorine gas produced during an experiment. She finds that 721. g of chlorine gas is produced. Calculate the number of moles of chlorine gas produced. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forwardAn aqueous solution of sodium chloride,NaCl , is made by dissolving 1.01 grams of sodium chloride in sufficient water in a 50.0 mL volumetric flask, and then adding enough water to fill the flask to the mark. What is the weight/volume percentage of sodium chloride in the solution? Weight/volume percentage = %arrow_forwardA chemist measures the amount of hydrogen gas produced during an experiment. He finds that 575. g of hydrogen gas is produced. Calculate the number of moles of hydrogen gas produced. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. O mol x10 ?arrow_forward
- Determine the mass of the product from the following data. Mass Aluminum Foil (g) 2.5415 Mass Filter Paper (g) 0.2777 Mass Filter Paper + Product (g) 35.6484 Mass Product (g) Group of answer choices 35.3708 g 35.3705 g 35.3707 g 35.3709 g 35.3706 garrow_forwardThe chemical formula for cesium chloride is CsCl . A chemist measured the amount of cesium chloride produced during an experiment. She finds that 9.25 g of cesium chloride is produced. Calculate the number of moles of cesium chloride produced. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY