
Fill in the blanks in this concept map to help you tie together the key concepts concerning elements, atoms, and molecules.
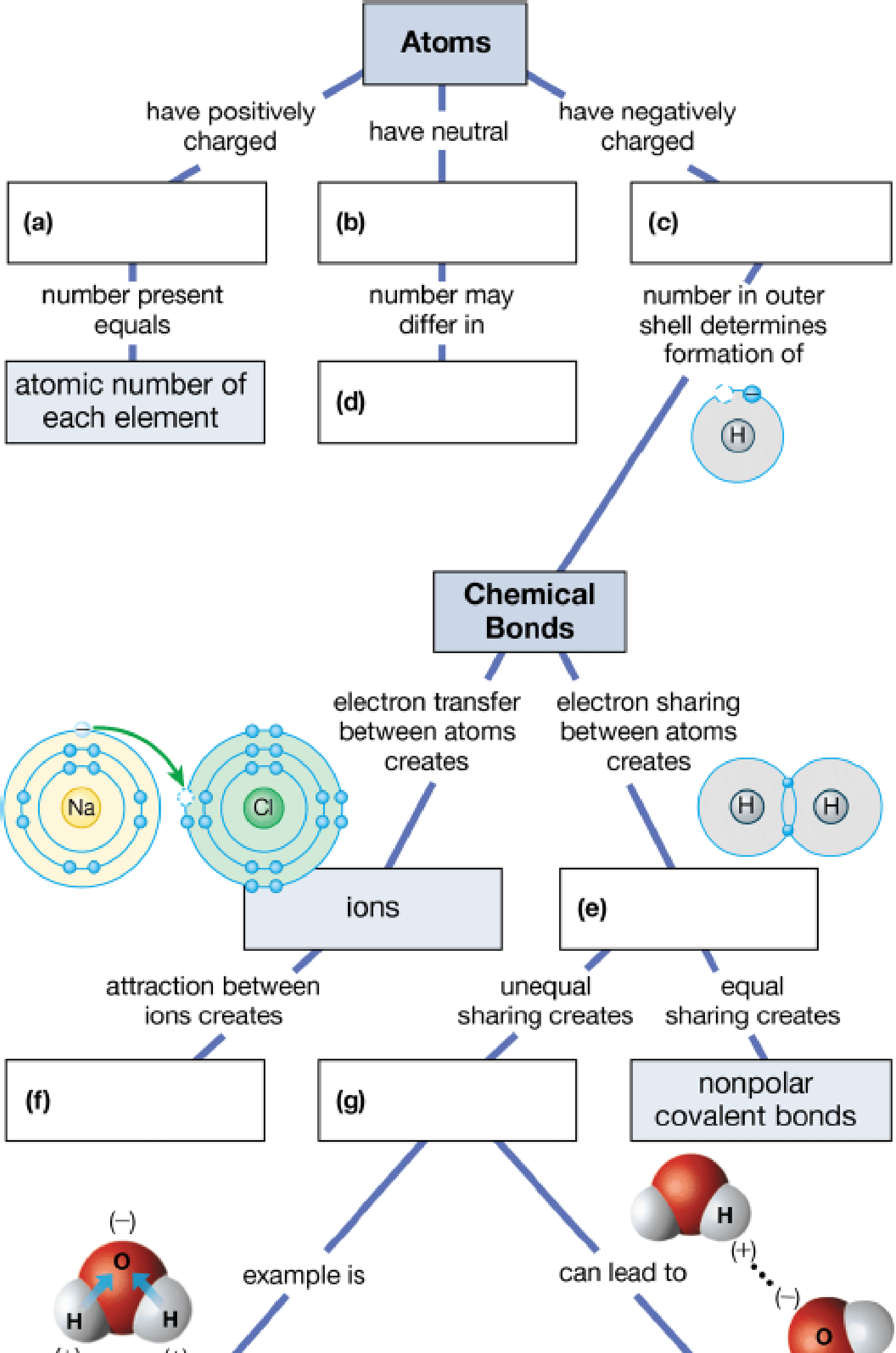

To complete: The concept map to help tie together the key concepts concerned with elements, atoms, and molecules.
Introduction:
A substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by ordinary chemical process is known as element. Every element has the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element. This smallest unit is called atom. An atom consists of electrons (e), protons (p) and neutrons (n). Different atoms have specific numbers of electrons, protons and neutrons. Nucleus of an atom contains protons and neutrons that constitute the mass of an atom. Electrons revolve around the nucleus in their orbit. The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of its atoms.
Answer to Problem 1CC
Pictorial representation: The Fig. 1 shows a concept map for hierarchy from atoms to bonding between molecules.
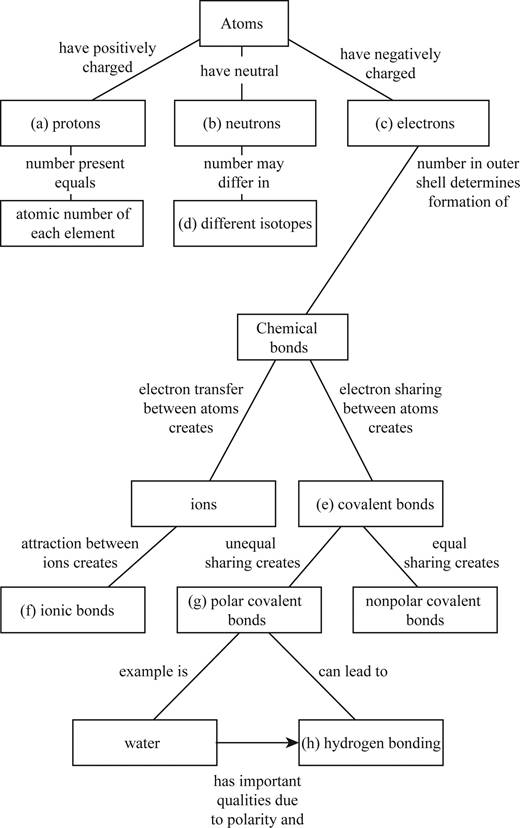
Fig.1:Concepts map of elements, atoms and molecules.
Explanation of Solution
(a)
Correct answer: Protons
Explanation: Proton is present in the nucleus of the atom and has positive charge. Hence the correct answer is proton.
(b)
Correct answer: Neutrons
Explanation: Neutron is present in the nucleus of the atom and is neutral due to no charge.
Hence, the correct answer is neutrons.
(c)
Correct answer: Electrons
Explanation: Electron revolves around the nucleus and has negative charge.
Hence, the correct answer is electrons.
(d)
Correct answer: Different isotopes
Explanation:
An isotope of an atom differs from neutron numbers and therefore by mass. Hence, the correct answer is different isotopes.
(e)
Correct answer: Covalent bond
Explanation: Electrons revolve around the nucleus in different electronic shells. The electrons present in the outermost shell are called valence electrons. The valence electron takes part in chemical bond formation by electron sharing known as covalent bond.
Hence, the correct answer is covalent bond.
(f)
Correct answer: Ionic bonds
Explanation: The transfer of electrons between two atoms creates ions and its attraction creates ionic bond. Hence, the correct answer is ionic bonds.
(g)
Correct answer: Polar covalent bonds
Explanation: Electron sharing between atoms creates covalent bond. The more electronegative atom attracts the bonded electrons towards itself. This results in unequal sharing of electrons and formation of polar covalent bond.
Hence, the correct answer is polar covalent bonds.
(h)
Correct answer: Hydrogen bonding
Explanation: Unequal sharing of electrons of covalent bond results in polar covalent bond. For example: Water molecule (H2O) consists of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Oxygen atom shares one electron to each of the hydrogen atom and forms two covalent bonds. The oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen. It attracts the bonded electron towards itself. This induces partial positive charge on hydrogen atoms and partial negative charge on oxygen atom. So, water molecule attains polarity. Oxygen atom of water molecule form a weak bond called hydrogen bond with hydrogen atom of another water molecule. This makes water molecule to have unique qualities.
Hence, the correct answer is hydrogen bonding.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (8th Edition)
- Make a connection with chemistry, biology, and physics. What do they all have in common?arrow_forwardA student created a chart to show some common compounds. Which of the following chemical formulas is wri CO2 H,0 NACL NO, CH,0 12 6C12H,0 NACL NO3 CO2arrow_forwardAdd these terms to your concept map should include these concepts and details: - the main title should be macromolecules concept of biochemistry with the following major categories: Water, Carbohydrate, Proteins, Lipids→ include cell membranes, Nucleic Acids Your concept map should include these concepts and details: Structure (functional groups, shape); Monomer; building block molecules Linkage; Properties; Functions; Key terms from the Partial List of Key functional group polarity intermolecular forces of attraction hydrogen bond essential nutrient carbohydrate monosaccharide isomer glycosidic linkage monomer polymer disaccharide oligosaccharide polysaccharide intermolecular force of attraction hydrogen bond macronutrient essential amino acid amino acid side group/R-group peptide bond polypeptide receptor neurotransmitter hormone secondary structure tertiary structure quaternary…arrow_forward
- Hello, could write me a paragraph on the importance of bonds and bonding in organisms. You could link any of these topics: • 3.1.1 Monomers and polymers • 3.1.2 Carbohydrates • 3.1.3 Lipids • 3.1.4.1 General properties of proteins • 3.1.4.2 Many proteins are enzymes • 3.1.5.1 Structure of DNA and RNA • 3.1.5.2 DNA replication • 3.1.6 ATP • 3.1.7 Water – cohesion • 3.2.2 Mitosis • 3.2.3 Transport across cell membranes • 3.2.4 Cell recognition and the immune system • 3.3.3 Digestion and absorption • 3.3.4.1 Mass transport in animals – haemoglobin • 3.3.4.2 Mass transport in plants • 3.4.2 DNA and protein synthesis • 3.4.3 Mutation and meiosis • 3.5.1 Photosynthesis • 3.5.2 Respiration • 3.5.4 Nutrient cycles • 3.6.2.2 Synaptic transmission • 3.6.3 Skeletal muscles • 3.6.4.2 Control of blood glucose concentration • 3.6.4.3 Control of blood water potential • 3.8.1 Mutations • 3.8.2.2 Regulation of transcription and translation • 3.8.2.3 Gene expression and…arrow_forwardThe fundamental unit of matter, both in living and non-living matter, is thearrow_forwardCould you write me a paragraph on the importance of bonds and bonding in organisms. Can you use only 1 of these topics: • Monomers and polymers • Carbohydrates • Lipids • General properties of proteins • Many proteins are enzymes • Structure of DNA and RNA • DNA replication • ATP • Water – cohesion • Mitosis • Transport across cell membranes • Cell recognition and the immune system • Digestion and absorption • Mass transport in animals – haemoglobin • Mass transport in plants • DNA and protein synthesis • Mutation and meiosis • Photosynthesis • Nutrient cyclesarrow_forward
- List four kinds of interactions and bonding in biological moleculesarrow_forwardUsing good details, show how the function of different proteins is connected to their structure. It's better to choose just two or three different proteins (with different functions). Remember that your connections should: • be meaningful; • be well-organized and easy-to-follow; • show your understanding of the vocabulary. Your concept map should include these concepts and details: • Structure (functional groups, shape); • Monomer; • Linkage; • Properties; • Functions; • Key terms from the Partial List of Key Terms from the Minds On section.arrow_forwardUsing good details, show how the function of two or three different nucleic acids is connected to their structure (choose among the nucleotides, dinucleotides, and chains of nucleic acids that you learned about). be meaningful; • be well-organized and easy-to-follow; • show your understanding of the vocabulary. Your concept map should include these concepts and details: ● Structure (functional groups, shape); Monomer; ● Linkage; Properties; • Functions; • And the table below nucleotide phosphodiester bond nitrogenous base ribose deoxyribose ATP NAD+ NADP+ FAD CAMP potential energy double helix autotroph heterotroph food systemarrow_forward
- 27) Draw a model that compares a solid with high density to a liquid with lower density. Be sure to label the images you draw and show the models on a molecular level (in other words you need to draw molecules or something that represents molecules).arrow_forwardChemical bonding is a fundamental concept that explains how atoms combine to form compounds. There are several types of bonds, each with distinct properties and behaviors. Ionic bonds form when electrons are transferred from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of positively and negatively charged ions. These ions are held together by electrostatic forces. Covalent bonds occur when atoms share pairs of electrons, leading to the formation of molecules. Metallic bonds, found in metals, involve a 'sea' of delocalized electrons surrounding positive metal ions. Each type of bond influences the physical properties of the substance. For example, ionic compounds typically have high melting and boiling points and conduct electricity when molten or dissolved in water. Covalent compounds can have varying physical states and usually do not conduct electricity. Metals are characterized by their malleability, ductility, and electrical conductivity. Which type of bond is responsible for…arrow_forwardname the class of large biological molecule for the following molecule. circle & label an example of each of 6 different functional groups on the molecule below. CH3 OH CH3arrow_forward

 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning


