
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Review. A block of mass M= 0.450Kg is attached to one end of a cord of mass 0.003 20Kg: the other end of the cord is attached to fixed point. The block rotates with constant angular speed in a circle on a frictionless. horizontal table as shown in figure p16.55. Through what angle does the block rotate in the time interval during which a transverse wave along the string from the center of the circle to the block?
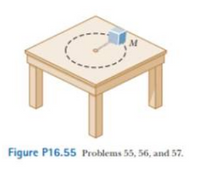
Transcribed Image Text:Figure P16.55 Problems 55, 56, and 57.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An ethernet cable is 3.90 m long and has a mass of 0.210 kg. A transverse pulse is produced by plucking one end of the taut cable. The pulse makes four trips down and back along the cable in 0.810 s. What is the tension in the cable?Narrow_forwardn.com - ClosetMaid 156 X Ebern Designs Cimino Desk & UO Home Décor + Apartment Sale X + gen/Iti/main.uni ent PRINTER VERSION ( BACK Chapter 16, Problem 025 Your answer is partially correct. Try again. = 7.19 m/s. The wave is A wave has the following properties: amplitude = 0.371 m, period traveling in the -x direction. What is the equation for the wave? = 0.770 s, wave speed %3D 0.371 У 3 1.13 8.16 rad/s *sin( *x) SHOW HINT LINK TO TEXT By accessing this Question Assistance, you will learn while you earn points based on the Point Potential Policy set by your udy instructor. Question Attempts: 2 of 6 used SAVE FOR LATER SUBMIT ANSWER Earn Maximum Points available only if you MacBook Pro Q Search or type URL %23 & 3 5 8 de т н K в N. * 00 C.arrow_forwardTuning the Waves. You and your team are designing a system that allows you to control the speed of a transverse wave on a thin tungsten wire by adjusting its tension with a spring. One end of the wire is connected to an inner wall of a large wooden crate and the other end to one side of a spring. The opposite side of the spring is then connected to a screw that is mounted on the opposite wall of the crate. The screw can then be adjusted to stretch the spring, and therefore adjust the tension in the wire. The uniform wire is 75.6 cm long and has a mass of 3.15 × 103 kg. The spring has an unstretched length of 11.0 cm and a spring In the lowest possible tension setting of the screw, that is, that which stretches from its equilibrium position. The screw can be turned to stretch it an additional attainable speeds of transverse waves that can travel on the wire with this setup? N/m. constant k = the spring the least, the spring is stretched by 0.500 cm 2.75 cm. What are (a) the highest and…arrow_forward
- A train moves along a straight track at v0=30m/s blowing its horn with frequency f0=600Hz. The stationary listener is positioned at the minimum distance from the train, d=40m, as shown in the drawing. A. what is the frequency heard by the listener as a FUNCTION of the trains POSITION. B. Evaluate this frequency if the angle between v0 and the listener's position is 30•, 45•, and 60•arrow_forwardI need help with parts e and f please. I know that a) 0.288m, b) 180 m/s, c) 162 N, and d) 125Hz.arrow_forward?arrow_forward
- The drawing shows a 21.9-kg ball being whirled in a circular path on the end of a string. The motion occurs on a frictionless, horizontal table. The angular speed of the ball is w = 14.8 rad/s. The string has a mass of 0.0230 kg. How much time does it take for a wave on the string to travel from the center of the circle to the ball? Number i Units String Ballarrow_forwardA.) The frequency of a vibrating bar is inversely proportional to the SQUARE of its length: f = constant/L2. I have two identical bars, except that one has a length of 36.8 cm and the other a length of 24.2 cm. What is the ratio of the vibrational frequency of the shorter bar to the longer bar? B.)A 0.8 meter length of string in mode number 2 vibrates with a frequency of 385 Hz. What is the velocity of the wave on the stringarrow_forwardA piece of string AB is 7 m long with end B left free to move. A is vibrated harmoniously up and down so that it travels on a string with a speed of 20 m/s. If the 5th node is 4 m from the origin of the vibration, calculate: a. the wavelength that propagates on the rope b. the frequency of the resulting wavearrow_forward
- A guitar string is vibrating in its fundam ental mode, with nodes at each end. The length of the segment of the string that is free to vibrate is 0.388 m. The maximum transverse acceleration of a point at the middle of the segment is 8100 m/s2 and the maximum transverse velocity is 3.60 m/s. a. What is the amplitude of this standing wave? b. What is the wave speed for the transverse traveling waves on this string?arrow_forwardOne end of a horizontal rope is attached to a prong of an electrically driven tuning fork that vibrates the rope transversely at 120 Hz. The other end passes over a pulley and supports a 1.50 kg mass. The linear mass density of the rope is 0.0550 kg/m. A.) What is the speed of a transverse wave on the rope? B.) What is the wavelength? C.) How would your answers to A and B change is the mass were increased to 3.00 kg?arrow_forwardA piano wire of linear density 12 g/m has a length 2 m. It is stretched with a force of 7000N. A. What is the third harmonic of vibation of this wire? Draw a diagram. B. By what factor do you have to change the tension to get a fundamental mode at the same frequency.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON