
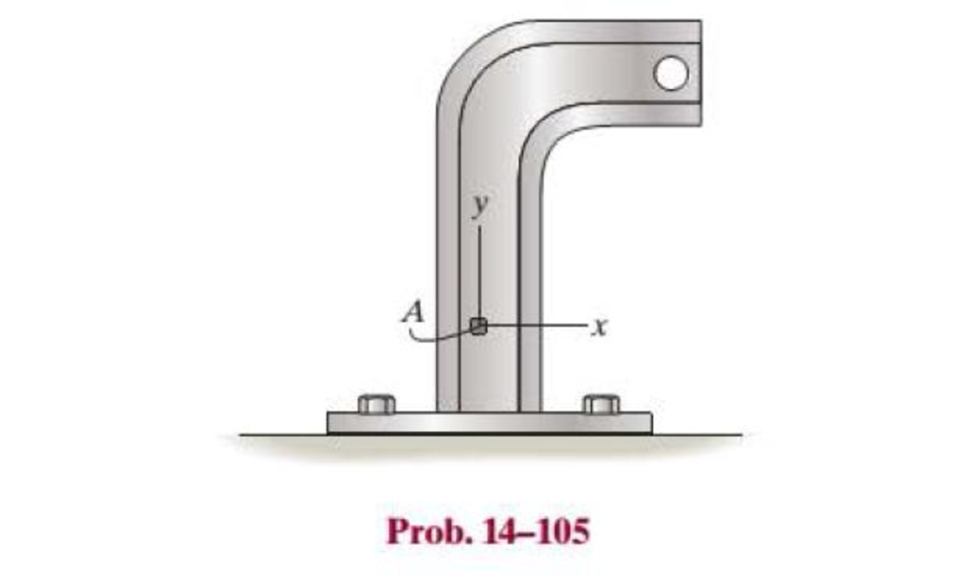
The strain at point A on the bracket has components
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Statics and Mechanics of Materials (5th Edition)
- The state of strain on an element has components Px = -300(10-6), Py = 100(10-6), gxy = 150(10-6). Determine the equivalent state of strain, which represents (a) the principal strains, and (b) the maximum in-plane shear strainand the associated average normal strain. Specify the orientation of the corresponding elements for these states of strain with respect to the original elementarrow_forwardFor the state of a plane strain with εx, εy and γxy components: (a) construct Mohr’s circle and (b) determine the equivalent in-plane strains for an element oriented at an angle of 30° clockwise. εx = 255 × 10-6 εy = -320 × 10-6 γxy = -165 × 10-6arrow_forwardThe state of strain at the point on the bracket has components Px = 350(10-6), Py = -860(10-6),gxy = 250(10-6). Use the strain transformation equations to determine the equivalent in-plane strains on an element oriented at an angle of u = 45° clockwise from the original position. Sketch the deformed element within the x–y plane due to these strains.arrow_forward
- 1arrow_forwardThe strain components Ex, Ey, and Yxy are given for a point in a body subjected to plane strain. Using Mohr's circle, determine the principal strains, the maximum in-plane shear strain, and the absolute maximum shear strain at the point. Show the angle 0p, the principal strain deformations, and the maximum in-plane shear strain distortion in a sketch. Ex = 0 μE, Ey = 310 με, Yxy = 280 μrad. Enter the angle such that -45° ≤ 0,≤ +45° Answer: Ep1 = Ep2 = Ymax in-plane = Yabsolute max. = 0p = με με urad uradarrow_forwardThe state of strain at the point on the spanner wrench has components of Px = 260(10-6), P y = 320(10-6), and gxy = 180(10-6). Use the strain transformation equations to determine (a) the in-plane principal strains and (b) the maximum in-plane shear strain and average normal strain. In each case specify the orientation of the element and show how the strains deform the element within the x–y plane.arrow_forward
- The strain at point A on the pressure-vessel wall has components Px = 480(10-6), Py = 720(10-6), gxy =650(10-6). Determine (a) the principal strains at A, in the x9y plane, (b) the maximum shear strain in the x9y plane, and (c) the absolute maximum shear strain.arrow_forwardplease solve with all stepsarrow_forwardThe state of plane strain on an element is represented by the following components: Ex =D340 x 10-6, ɛ, = , yxy Ey =D110 x 10-6, 3D180 x10-6 ху Draw Mohr's circle to represent this state of strain. Use Mohrs circle to obtain the principal strains and principal plane.arrow_forward
- The strain components e x, e y, and γ xy are given for a point in a body subjected to plane strain. Using Mohr’s circle, determine the principal strains, the maximum in-plane shear strain, and the absolute maximum shear strain at the point. Show the angle θ p, the principal strain deformations, and the maximum in-plane shear strain distortion in a sketch. Ex Ey Yxy −1,570 με -430με -950 μradarrow_forwardThe state of a plane strain at a point has the components E, = 500 (10-), ɛy = 250 (10-6) and yxy = -700 (10-5). Determine the principal strains and the maximum in plane shear strain. Select one: ɛz = -747 (10-6), ɛ2 = -3.35 (10-) and ymax in-piane = 743 (10). E1 = 747 (10-), E2 = 3.35 (10-) and ymax in-plare = 743 (10°). %3D E1 = -335 (10-), E2 = -747 (10 °) and ymax in-piane = 743 (10-°). %3D 21 = 747 (10-), E2 = 335 (10-) and ymax in-plane = 743 (10-*). E = 747 (10-), E2 = -3.35 (10-) and ymax in-plane = 743 (10-).arrow_forwardQUESTION 2: The state of plane strain on the element is e, = -300(10 ), €, = 0, and Yy = 150(10-"). Determine the equivalent state of strain which represents (a) the principal strains, and (b) the maximum in-plane shear strain and the associated average normal strain. Specify the orientation of the corresponding elements for these states of strain with respect to the original element. dy T Yay --e,dx xp-arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





