
PHY F/SCIENTIST MOD MASTERING 24 MO
17th Edition
ISBN: 9780137319497
Author: Knight
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1, Problem 49EAP
Problems 49 through 52 show a partial motion diagram. For each:
a. Complete the motion diagram by adding acceleration vectors.
b. Write a physics problem for which this is the correct motion diagram. Be imaginative! Don’t forget to include enough information to make the problem complete and to state clearly what is to be found.
c. Draw a pictorial representation for your problem.
49
FIGURE P1.49

50
FIGURE P1.50
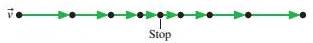
51
FIGURE P1.51
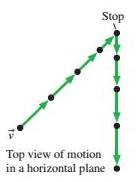
52
FIGURE P1.52
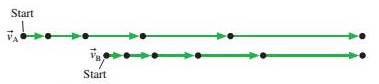
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule03:22
Students have asked these similar questions
3. Use the graph to answer the following questions.
a. What physical quantity is represented by the
Graph B
Velocity vs. Time
slope of the graph?
7
b. What physical quantity is represented by the
6
y-intercept of the graph?
c. What physical quantity is represented by the area
5
under the graph?
d. Find the area under the graph.
1
1
3
4
6
7
Time (sec)
v (m/s)
4.
onsid
the following v vs. t graph
a. What is the acceleration at:
i.
t = 11 s?
ii.
t = 15 s?
b. How far, and in which direction, did the object travel:
i.
from t = 4 to t = 11 s?
(sec)
ip
ii.
from t = 13 tot = 18 s?
c. During what time intervals is the object speeding up?
slowing down?
d. During what time intervals is the acceleration positive?
Negative? Zero?
Velocity (m/s)
a. The position of an object is given by x(t) = A + B*t + C*t³ (yes, those exponents are intentional, this is
NOT constant acceleration). Provided that x is measured in meters and t in seconds, what must be the
units for the constants A, B, and C.
b. Another position function is given by y(t) = D # E*t1 + F*t3/2). What are its velocity, and acceleration
functions with time?
c. Bonus: choose and declare your values for D, E and F, and make graphs of y(t), vy(t), and a,(t). Don't
forget appropriate units at each step.
The Nardo ring is a circular test track for cars. It has a circumference of 12.5 km. cars travel around the track at a constant speed of 100 km/h. A car starts at the easternmost point of the ring and drives for 15 minutes at this speed.
a. What distance, in km, does the car travel?
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Check Your understanding Using the three displacement vectors A , B , and F in Figure 2.13, choose a convenient...
University Physics Volume 1
What is the role of “loose” electrons in heat conductors?
Conceptual Physics (12th Edition)
56. Global Positioning System. Learn more about the global positioning system and its uses. Write a short repo...
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
The value of the charge q3 for the net force on it to be 4.00 μΝ .
Sears And Zemansky's University Physics With Modern Physics
MCAT-Style Passage Problems
Sliding on the Ice
In the winter sport of curling, players give a 20 kg stone a pus...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
25. For the combination of two lenses shown in Figure P19.25, find the position, size, and orientation of the f...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Acceleration a has the dimensions of length per time squared, speed v has the dimensions of length per time, and radius r has the dimension of length. Which of the following expressions may be correct? Explain your answer in each case. a. a = vr b. a = v/r c. a = v2/r d. a = v/r2arrow_forwardA kangaroo can jump over an object 2.7 m high. a. Calculate its vertical speed when it leaves the ground, in meters per second. b. How many seconds is it in the air?arrow_forwardAn ant travels 3.95 inches due east, then turns and travels an additional 3.35 inches south. The ant walked east for 2.25 minutes and south for 3.15 minutes. a) What is the ant's average speed over the entire trip in the given units? O 1.35 inches/minute O 1.76 inches/minute O1.06 inches/minute O 2.32 inches/minute O 3.24 inches/minute b) What is the ant's average speed over the entire trip in Sl units? 3,190 m/s 2.06 m/s O 0.000572 m/sarrow_forward
- Full formula Correct Correct Correct values answer, metric units inserted into rounded to the formula two decimal from the places word problemarrow_forward4. This table shows the speed of a car. Time (s) 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Speed (m/s) 27 36 40 36 27 169 3 a. Show the speed on a graph. b. Draw a tangent to estimate the acceleration after 10 seconds. c. Estimate the acceleration 0? d. Estimate the deceleration after 1 minute.arrow_forward1. Jack drives a distance of 160 miles at an average speed of 35 miles/hr, followed by a distance of 190 miles at 75 miles/hr. What is his average speed over the 350-mile trip? Hint: Draw a labeled sketch of the trip. V avg miles per hourarrow_forward
- A car travels with an average speed of 8.00 meter/second. A. What is the speed in km/s? B. What is the speed in mile/hour? Hint: 1km =1000.0 metersarrow_forwardA person runs 800 m at an average speed of 6 m/s and then the next 800 m at an average speed of 8 m/s.a. Calculate the total time required.b. Find the average speed.arrow_forward1. A sprinter at a track and Field event is entered in a 500 m race. The starting gun goes off, accelerating every step of the way, he runs the distance of 63.50 seconds. What is the acceleration of the sprinter in units of meters per second squared? How fast is he going as he crosses the finish line in units of meters per second? write the general form of the equation you are going use. list all given values, units, and variables they represent. solve the equation.arrow_forward
- a. You leave your home & drive 45 km in the +y direction for a job interview. They offer you the job so you decide to stop and celebrate with friends on the way home. You leave the interview and drive 22 km in the -y direction. Let your home be your reference point. - What total distance did you drive?(km) - What total distance did you drive? ____km to the a. +y, b. -y, c. +x, d. -x, c. no direction b. You are standing on a circular track that is 400 m long. You begin jogging at the start line and keep jogging until you complete 2 full lap and stop at the same point you started at. - What is the total distance you travel? (m) -What is your final displacement? (m)arrow_forward1. Problem 1: Travelling with an initial speed of 70 km/hr, a car accelerates at 6000km/hr2 along a straight road. (problem la.) How long will it take to reach a speed of 120 km/hr? (problem 1b.) Also, through which distance does the car travel during this time?arrow_forwardA. using your measured distance (35 inches) your average time of motion (drop times 2.04s,1.78,2.26,1.59,1.87 and 1.91)and the constant acceleration equation (x=1/2 at^2)calculate the acceration of the atwood machine. B. using m2-m2/m1+m2(9.8)=20/40=0.5x9.8=4.9 and the masses (60,70g) calculate the expected acceleration. C. what quanatiative compariosn is most appropriate between your results (percent difference or error)?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College
Position/Velocity/Acceleration Part 1: Definitions; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4dCrkp8qgLU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY