
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780470458365
Author: Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Can you solve this using the flow given for determination of

Transcribed Image Text:Determination of Integrating Factor
We have already mentioned in the previous lesson the aid of integrating factor in solving a
first-order linear differential equation and that the same idea sometimes works for a nonexact
differential equation
M(x, y)dx + N(x, y)dy = 0
(1).
We mean to say that it is sometimes possible to determine an integrating factor u(x, y)
such that after multiplying it to a given nonexact equation (1), the left side of the resulting
equation
u(x, y) M(x, y)dx + u(x, y)N(x, y)dy = 0 (2)
becomes an exact differential.
To determine such integrating factor u(x, y), recall the criterion for exactness. Equation (2)
is exact if and only if
or U
U
Ə
- (UM) =
U
ду
Solving for u, u(u) = ef
ƏM
Əy
ƏM ƏN
dy дх
+ M
ƏN
əx
du ƏN
dy ?x
du
əx
du
U
=
a
da (UN)
= U + N
= N
If u satisfies (3), then u is an integrating factor for (1). Note that M, N,
ƏN
are
dy
əx
known functions of r and y. To determine such function u, from (3), we have to solve for
a partial differential equation, but were not yet ready to do that. Thus, we first make an
assumption that u is a function of only one variable.
Let us first assume that u depends on a alone. Then, =
becomes
Ju du
?х dx
ƏM
Ndu
dr
[ du = 12 (M
u
1 (ƏM ƏN
N dy Ər
du
əx
- M
ƏM ƏN
Əy ?х
ON
N ду дх
Solving for u, we have u(x) =
Similarly, if u depends on y alone, then we will have,
du
ду
It is still not easy to determine u even after taking the integral of both sides of (4) if its
right side depends on both x and y. However, if after some algebraic simplications are made,
1 (OM ON
the expression
turns out to be dependent alone on the variable y, then (4)
is now a first-order ordinary differential equation and we can finally solved for u in (4) by
separation of variables. That is,
ду Әх
ƏM ƏN
L (OM_W) dr
dx
du
1 /OM
ƏN
M ду əx
dy
du
dy
dx
(3)
dx
=-M
1
ƏN
-- (-2) dy
U
M
Əy
Əx
ƏM
, and
Ju
and = 0. Hence, (3)
Əy
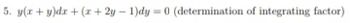
Transcribed Image Text:5. y(x + y)dx + (x+2y-1)dy = 0 (determination of integrating factor)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- the tangent to f(x) = 2x^3+ax+b has a tangent with a gradient 12 at the point (-2,33). find the values of a and barrow_forwardWhich is the quadratic parent function? A y=xy=xy=x B y=x2y=x^{2}y=x2 C y=xy=\sqrt{x}y=x D y=∣x∣y=\left| x\right|y=∣x∣arrow_forwardFind the x coordinates of all points on the curve y = (x^3 + 2)^ 1/3 where the normal to the curve has gradient −2.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY
Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,


Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780073397924
Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781118141809
Author:Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781337798310
Author:Peterson, John.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

