
Essentials Of Investments
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781260013924
Author: Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill Education,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
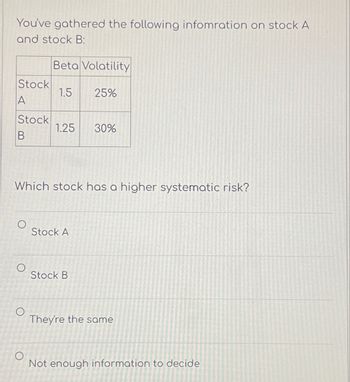
Transcribed Image Text:You've gathered the following infomration on stock A
and stock B:
Beta Volatility
Stock
1.5
25%
A
Stock
1.25
30%
B
Which stock has a higher systematic risk?
O
O
Stock A
Stock B
They're the same
Not enough information to decide
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the following information on Stocks I and II: Probability of State of Economy State of Economy Rate of Return if State Occurs Stock I Stock II Recession .22 .045 -.37 Normal .62 .355 .29 Irrational .16 exuberance .215 .47 The market risk premium is 11.7 percent, and the risk-free rate is 4.7 percent. a. Calculate the beta and standard deviation of Stock I. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter the standard deviation as a percent and round both answers to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. b. Calculate the beta and standard deviation of Stock II. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter the standard deviation as a percent and round both answers to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. c. Which stock has the most systematic risk? d. Which one has the most unsystematic risk? e. Which stock is "riskier"? a. Beta Standard deviation b. Beta Standard deviation c. Most systematic risk d. Most unsystematic risk e. "Riskier" stock 1.94 % %arrow_forwardCompute the abnormal rates of return for the following stocks assuming the following systematic risk measures (betas): Rit = return for stock i during period t Rmt = return for the aggregate market during period t Bi = beta for stock i Use a minus sign to enter negative values, if any. Round your answers to one decimal place. ARBt: ARFt: ARTt: ARct: ARET: % % % % Stock B F T C E % Rit 10.1% 9.4 13.2 11.2 15.1 Rmt 3.9% 8.5 10.0 15.6 11.2 Bi 1.00 1.10 1.45 0.65 -0.40arrow_forwardBelow are standard deviations of four stocks: M, N, O and P. Stock M N O P Standard deviation 12% 20% 15% 30% 1. Which stock is the riskest? 2. Based on the risk-return tradeoff, which stock should provide the highest 3. If stock O provides a higher return than stock P, what should happen?arrow_forward
- The beta coefficient A stock’s contribution to the market risk of a well-diversified portfolio is called Q1. ______risk. It can be measured by a metric called the beta coefficient, which calculates the degree to which a stock moves with the movements in the market. Q2. Based on your understanding of the beta coefficient, indicate whether each statement in the following table is true or false: Statement True False Over time, a stock with a beta of 1.0 produces a return that goes up and down with a 1:1 relationship with the return on the market. Beta measures the volatility in stock movements relative to the market. A stock that is more volatile than the market will have a beta of less than 1.0. Q1. Option 1 Unsystematic or Option 2 Relevant. Please provide true or false answers. Thank you!arrow_forwardK -61 =1 2 N (Expected rate of return and risk) Syntex, Inc. is considering an investment in one of two common stocks. Given the information that follows, which investment is better, based on the risk (as measured by the standard deviation) and return? Probability 0.25 0.50 0.25 Common Stock A Probability 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.25 (Click on the icon in order to copy its contents into a spreadsheet.) @ 2 a. Given the information in the table, the expected rate of return for stock A is 16.25 %. (Round to two decimal places.) The standard deviation of stock A is %. (Round to two decimal places.) b. The expected rate of return for stock B is%. (Round to two decimal places.) The standard deviation for stock B is%. (Round to two decimal places.) c. Based on the risk (as measured by the standard deviation) and return of each stock, which investment is better? (Select the best choice below.) 30² F2 W OA. Stock A is better because it has a higher expected rate of return with less risk B. Stock B is…arrow_forwardYou have the following data on three stocks: Stock Standard Deviation Beta A 20% 0.59 B 10% 0.61 C 12% 1.29 If you are a strict risk minimizer, you would choose Stock ____ if it is to be held in isolation and Stock ____ if it is to be held as part of a well-diversified portfolio. Group of answer choices A; A. A; B. C; A. B; A.arrow_forward
- The standard deviation of a stock’s return is a measure of its? Multiple Choice systematic risk correlation expected future return total riskarrow_forwardWhat is the required return for each stock? What is required return for stock B? Scenario Probability Stock A Stock B Market Risk-free rate Bust 0.25 -0.15 -0.05 Normal 0.55 0.2 0.1 Boom 0.2 0.4 0.3 Beta 1.2 0.9 Expected return 0.13 0.05arrow_forwardBased on the following information, calculate the expected return and standard deviation for Stock A and Stock B. Input area: State Probability Stock A Stock B Recession 0.15 0.04 (0.17) Normal 0.55 0.09 0.12 Boom 0.30 0.17 0.27 (Use cells A6 to D9 from the given information to complete this question.) Output area: Stock A Probability Return Product Return deviation Squared deviation Product Recession Normal Boom B э O Standard deviation Stock B 2 Recession 3 Normal 4 Boom 5 26 Standard Deviation 27 28 E(R) Variance Probability Return Product Return deviation Squared deviation Product E(R) Variancearrow_forward
- Discuss how to determine the risk or beta of a stock, the required rate of return of a stock and the value of a stock. How do you determine if a stock has high or low or average risk when compared to the S&P 500?arrow_forwardIf a stock's expected return plots on or above the SML, then the stock's return is SML, the stock's return is to compensate the investor for risk. cent to compensate the investor for risk. If a stock's expected return plots below the The SML line can change due to expected Inflation and risk aversion. If inflation changes, then the SML plotted on a graph will shift up or down parallel to the old SML. If risk aversion changes, then the SML plotted on a graph will rotate up or down becoming more or less steep if investors become more or less risk averse. A firm can influence market risk (hence its beta coefficient) through changes in the composition of its assets and through changes in the amount of debt it uses. Quantitative Problem: You are given the following information for Wine and Cork Enterprises (WCE): Tar 4%; 10 % ; RPM 6%, and beta - 1.1 What is WCE's required rate of return? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. -75 % If inflation…arrow_forwardConsider the following information for Stocks A, B, and C. The returns on the three stocks, while positively correlated, are not perfectly correlated. The risk-free rate is 5.50%. Stock A B C Expected Return 10.00% 10.90% 11.80% Standard Deviation 15% 15% 15% Beta 1.5 1.8 2.1 Let , be the expected return of stock i, ra represent the risk-free rate, b represent the Beta of a stock, and TM represent the market return. Using SML equation, you can solve for the market risk premium which, in this case, equals approximately The beta for Fund P is approximately Consider Fund P, which has one third of its funds invested in each of stock A, B, and C. You have the market risk premium, the beta for Fund P, and the risk-free rate. Hint: Recall that because the market is in equilibrium, the required rate of return is equal to the expected rate of return for each stock. This information implies that the required rate of return for Fund P is approximately Which of the following is the reason why the…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Essentials Of Investments
Finance
ISBN:9781260013924
Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,



Foundations Of Finance
Finance
ISBN:9780134897264
Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. William
Publisher:Pearson,

Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...
Finance
ISBN:9781337395250
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. Houston
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...
Finance
ISBN:9780077861759
Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education