
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
You want to move a heavy box with mass 30.0 kg across a carpeted floor. You pull hard on one of the edges of the box at an angle 30∘ above the horizontal with a force of magnitude 240 N, causing the box to move horizontally. The force of friction between the moving box and the floor has magnitude 41.5 N .
1. What is the box's acceleration just after it begins to move?
2. Draw a free body diagram for the box, assuming that the positive-x axis is to the left, and the positive-y axis is upward.
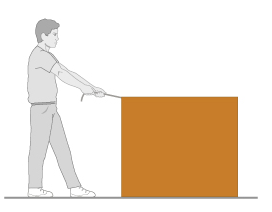

Transcribed Image Text:You want to move a heavy box with mass 30.0 kg across a carpeted floor. You pull hard on one of the edges of the
box at an angle 30° above the horizontal with a force of magnitude 240 N, causing the box to move horizontally.
The force of friction between the moving box and the floor has magnitude 41.5 N
1. What is the box's acceleration just after it begins to move?
2. Draw a free body diagram for the box, assuming that the positive-x axis is to the left, and the positive-y axis is
upward.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- ol nt... 7 2 W S 6. A mass m₁ = 4.80 kg block on a tabletop is attached by a string to a hanging block of mass m₂ = 3.00 kg, as shown in the figure. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the mass (m₁) and the surface is 0.29. The blocks are released from rest and allowed to move freely. Find the magnitude of the tension in the string. N 3 E 80 F3. 4 288 R F % 5 246 T G 6 16 ceil6 ceil6 ceil6 ceil6 cesto co B 21910291999 MacBook Air FO Y & 7 m₂ H U 8 J FB ( 9 M K 16 ceiló cerlo ceiló cel cc116 ceil6 ccilo ceiló ceilo O 4 16. cci Parrow_forwardMigo exerts a horizontal force on a 2 kg box located on an inclined plane with an angle of θ= 37 degrees. The coefficient of static and kinetic friction between the box with an inclined plane is μs = 0.4 and μk = 0.2, respectively. A. What is the minimum force for the box to move exactly B. What is the maximum force for the box to move exactly C. If the box is falling at an acceleration of 0.5 m/s^2, what is the force appliedarrow_forwardYou want to hang an object from the ceiling of an elevator that has a maximum acceleration of 4.0 m/s2. Part A If you hang the object with fishing line that supports 55 N of force, what is the maximum inertia the object can have if the line is not to break? Express your answer with the appropriate units. Part B What combination or combinations of slowing down, speeding up, going up, and going down of the elevator causes the greatest force to be exerted on the fishing line?Check all that apply. slowing down while going up speeding up while going down speeding up while going up slowing down while going downarrow_forward
- Two blocksmịand m2 connected by a rope are being pulled by a horizontalforce F equal 160 N. Suppose that mį=10 kg,20 kg, and the coefficient of kineticm 2 =20 kg10 kgfriction between each block and the surfacem1is 0.52.A. Draw free-body diagrams of both objects.B. Find the acceleration of the systemC. Find the tension in the ropeD. What is the distance that the system ( two masses) will travel if youknow that are started from rest and final velocity is 4.5 m/sec(B) a= { Farrow_forwardI need help with part barrow_forwardA 7.8 kg object undergoes an acceleration of 2.9 m/s^2 A. What is the magnitude of the resultant force acting on it? N B. If this same force is applied to a 4.7kg object, what acceleration is produced? m/s^2arrow_forward
- A student attaches a rope to a 32 kg box, and drags it to the left with constant velocity of 1.97 m/s. The tension in the rope is 207 N at an angle of 35.7° to the ground. How much does the box weigh? Find the x and y components of the applied (tension) force: Fx = N. %3D Fy = N. How much friction must be present? How much Normal force must be present? N.arrow_forwardA cardboard box rests on the floor of an elevator. The box has a mass m = 2.75 kg and the elevator has an upward acceleration of a. a. Write an expression for the sum of the forces acting on the box in the y-direction, ΣFy, given that up is the positive y-direction. Your answer should be in terms of FN, m, and g. b. Write an expression for the normal force, FN, that the block experiences in terms of the elevator's acceleration, the block's mass, and the acceleration of gravity. c. If the elevator's acceleration has a magnitude of g in the downward direction, what would the normal force, FN1 be in Newtons? d.If the elevator's acceleration had a magnitude of g in the upward direction, what would the normal force FN2 be in Newtons?arrow_forwardI need help with part a of the questionarrow_forward
- A teenager of mass m1 = 56 kg pushes backwards against the ground with his foot as he rides his skateboard. This exerts a horizontal force of magnitude F foot = = 18.5 N. The skateboard has m2 = 2.6 kg. a. Write an expression for the magnitude of the horizontal component of force that the ground exerts on the teenagers foot, F ground. b. Write an expression in terms to given quantities for the magnitude of the skateboard acceleration, a , while the teenager is pushing backwards on the ground? c. What is the numerical value of the magnitude of the acceleration, a, in m/s square?arrow_forwardYou walk into an elevator, step onto a scale, and push the "up" button. You recall that your normal weight is 625 N. Draw a free-body diagram. When the elevator has an upward acceleration of magnitude 2.50 m/s2, what does the scale read? If you hold a 2.25 kg package by a light vertical string, what will be the tension in this string when the elevator accelerates as in the previous part?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON