
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
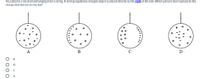
Transcribed Image Text:You observe a neutral ball hanging from a string. A strong negatively charged object is placed directly to the right of the ball. Which picture best represents the
charge distribution on the ball?
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
B
B
D
A
+++
+ +
O 0 0 O
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An electron is aligned horizontally a few nanometers apart from an unknown charge. The unknown charge is attracted to the electron due to electrical attraction. The unknown charge might be a. an electron b. a proton c. a neutron d. either a proton or a neutron e. either a proton or an electronarrow_forwardMost workers in nanotechnology are actively monitored for excess static charge buildup. The human body acts like an insulator as one walks across a carpet, collecting −50 nC per step. What charge buildup will a worker in a manufacturing plant accumulate if she walks 17 steps?arrow_forwardTwo particles having charges of 0.580 nC and 20.9 nC are separated by a distance of 1.50 m. At what point along the line connecting the two charges is the net electric field due to the two charges equal to zero? Express your answer in meters. The electric field is zero at a point = Submit Part B Request Answer VO ΑΣΦ Where would the net electric field be zero if one of the charges were negative? ? m from 0.580 nC.arrow_forward
- Answered: X https://porta x B 3.2 Explorir g x Learning ac x Learning ac x .content-service.brightspace.com ScormEngineinterface defauitui/player/modlem.html?configuration=88030417-4 3. Examine the charge distribution in the diagram below. 4.0x10:5 q3 24cm q1 q2 +) 24cm 2. 5 5. a. Determine the net force charge acting at g1 (+ 2.0 x 10 C), caused by q2 (- 4.0 x 10 C) and g3 (-4.0 x 10 C) Be sure to include a free body diagram 5. representing the force acting at q1 in your solution. b. Determine the net electric field acting at q1arrow_forwardThe charge in the bottom right corner of the figure is Q = -90 nC. What is the magnitude of the electrical force on Q?arrow_forwardIn the figure, the point charges are located at the corners of an equilateral triangle 29 cm on a side. What is the direction of the force on qa in degrees above the negative x-axis with origin at qa?arrow_forward
- Thin glass rod y Thin plastic disk In the figure shown above, a thin plastic disk of radius 0.6 m is uniformly charged with Qdisk = -3 × 10-7 C and is attached to a thin glass rod of length 2.4 m that is uniformly charged with Qrod = 5 x 10-8 C. The center of the rod and the center of disk are at the origin. The rod lies along the x axis and the disk lies in the yz plane. What is the (vector) electric field at location (0.02, 0.01, 0)m? value of €0 the Given that 8.85 x 10-12 C2/N.m². 1. (52400, -14900, 0) N/C 2. (37500, -52400,0)N/C 3. (-22600, 14900, 0) N/C 4. (-37500, 14900, 0)N/C 5. (-22600, -37500, 0)N/C 6. (-52400, 37500, 0) N/C 7. (37500, -14900, 0) N/C 8. (-14900, -22600, 0)N/C 9. (14900, -37500, 0) N/C 10. (-14900, 37500, 0) N/Carrow_forwardpts Four charges are arranged at the corners of a square of side length, L = 39.00 cm. All four charges have the same magnitude q = 3.00 nC but the lower right charge is negative. Find the magnitude of the electric field at the center of the square in N/C. Round to the nearest whole number (no decimal places). Solution: N/Carrow_forwardConsider the following sequence of events: 1. You rub a glass stirring rod with a silk cloth, giving the glass rod a positive charge. 2. Your friend holds an aluminum measuring cup in her bare hand, touching the metal. 3. Your friend puts the aluminum cup down on a rubber mat. 4. You bring the glass rod near the right side of the aluminum cup, but not close enough to touch. 5. While you hold the glass rod near the right side of the aluminum cup, your friend touches the left side of the cup with her finger, then moves her finger away. 6. You move the glass rod away from the cup. Which statements about the process are true? O In step 4, protons flow from the aluminum cup onto the rubber mat. O At the end of step 2 the cup may have been strongly charged. O After step 6, the aluminum cup has a net negative charge. O Since the glass rod does not touch the cup in steps 4 thorough 6, the cup is still neutral after step 6. O At the end of step 4 the aluminum cup is polarized. O In step 5…arrow_forward
- Two positive charges, each of magnitude q, are on the y-axis at points y= ta and y=-a Where would a third positive charge of the same magnitude be located for the net force on the third charge to be zero? a. at the origin b. at y= 2a c. at y=-2a d. at y= -aarrow_forwardPlease Asaparrow_forwardB7arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON