
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

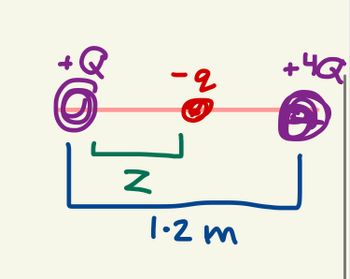
Transcribed Image Text:You have 2 positive charges, Q+ and +4Q. Ther
are fixed on the axis shown on the image.
They are 1.2 m appart. A nagative charged
particle -q, is placed gently between the two
positive charges and it remains at rest. The
distance between the particle (z) and the
other particle that's negative is? (Units are cm
for the following options)
a. 24. B. 30.
C. 40.
D. 60. E. 80
Transcribed Image Text:GO
z
-오
1·2 m
HQ
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Three point charges are aligned along the x axis as shown in the figure below. 0.500 m- (a) Ē = -4.00 nC (0, 1.90 m) -0.800 m- N/C 5.00 nC i Find the electric field at the following position. (Enter your answer as a sum of i-hat and j-hat vectors.) 3.00 nC xarrow_forwardThree point charges are aligned along the x-axis as shown in the figure below. Find the electric field at the position x = +2.7 m, y = 0. magnitude direction -0.50 m- -0.80 m- Three point charges lie along the x-axis in the xy-coordinate plane. A-4.0 nC charge is 0.50 m to the left of the origin. A 5.0 nC charge is at the origin. A 3.0 nC charge is 0.80 m to the right of the origin. 17.17 x Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. N/C +xarrow_forwardQUESTION 2 Tw stationary protons experience a repulsive force of magnitude 2.50 x 10-9 N. What is the distance between the protons? The charge of a proton is 1.602 x 10-19 С. a. 6.13 x 10-10 m b. 1.66 x 10-10 m C. 2.11 x 10-10 m. d. 3.04 x 10-10 m e. 8.20 x 10-10 m.arrow_forward
- The figure below shows three small, charged beads, all lying along the horizontal axis. Bead A, at left, has a 6.45 nC charge. Bead B has a 1.40 nC charge and is 3.00 cm to the right of A. Bead C has a-2.05 nC charge and is 2.00 cm to the right of B. 3.00 cm 9 9 -Select- 2.00 cm- Q (a) What is the magnitude (in N/C) of the electric field at a point 2.00 cm to the right of A? N/C (b) A fourth bead with a charge of -5.00 nC is placed at this point. What are the magnitude (in N) and direction of the net electric force on it? magnitude N directionarrow_forwardAn electron is aligned horizontally a few nanometers apart from an unknown charge. The unknown charge is attracted to the electron due to electrical attraction. The unknown charge might be a. an electron b. a proton c. a neutron d. either a proton or a neutron e. either a proton or an electronarrow_forwardA negatively charged particle, q1, is brought near a stationary, negatively charged particle, q2. The charge, q1, is then allowed to move freely, while q2 remains stationary. Which of the following statements is true for the moving charge? A). ΔU > 0; ΔV> 0 B). ΔU < 0; ΔV< 0 C). ΔU > 0; ΔV< 0 D). ΔU < 0; ΔV> 0 E). ΔU = 0; ΔV< 0arrow_forward
- NA 1.75-nC charged particle located at the origin is separated by a distance of 0.0825 m from a 2.88-nC charged particle located farther along the positive x axis. Both particles are held at their locations by an external agent. a. What is the electrostatic force on the 2.88-nC particle? b. What is the electrostatic force on the 1.75-nC particle? 28) NA 1.75-nC charged particle located at the origin is separated by a distance of 0.0825 m from a 2.88-nC charged particle located farther along the positive x axis. If the 1.75-nC particle is kept fixed at the origin, where along the positive x axis should the 2.88-nC particle be located so that the magnitude of the electrostatic force it experiences is twice as great as it was in Problem 27? 35arrow_forwardThree point charges are arranged as shown in the figure below. 5.00 C -3.00 w 0:300m 0.100m (a) Find the vector electric field that the q -9.50 nC and -3.00 nC charges together create at the origin. N/CI+ N/Cj Need Help? (b) Find the vector force on the 5.00 nC charge. UNI+ UN Read Itarrow_forwardQUESTION 2 A point particle with a positive charge, q, and a mass, m, is held stationary by the forces of gravity and electricity above an infinite, thin, planar sheet of positive charge with charge density o. What is the value of o? a. εomg/q b. qmɛo/gr2 O c. 2qeo/mg O d. qeo/mgr2 e. 2ɛ0mg/qarrow_forward
- An electron and a proton are fixed at a separation distance of 917 nm. Find the magnitude and the direction of the electric field at their midpoint. E = N/C The direction is perpendicular to the line of the particles. O is toward the proton. is toward the electron. cannot be determined.arrow_forwardThin glass rod y Thin plastic disk In the figure shown above, a thin plastic disk of radius 0.6 m is uniformly charged with Qdisk = -3 × 10-7 C and is attached to a thin glass rod of length 2.4 m that is uniformly charged with Qrod = 5 x 10-8 C. The center of the rod and the center of disk are at the origin. The rod lies along the x axis and the disk lies in the yz plane. What is the (vector) electric field at location (0.02, 0.01, 0)m? value of €0 the Given that 8.85 x 10-12 C2/N.m². 1. (52400, -14900, 0) N/C 2. (37500, -52400,0)N/C 3. (-22600, 14900, 0) N/C 4. (-37500, 14900, 0)N/C 5. (-22600, -37500, 0)N/C 6. (-52400, 37500, 0) N/C 7. (37500, -14900, 0) N/C 8. (-14900, -22600, 0)N/C 9. (14900, -37500, 0) N/C 10. (-14900, 37500, 0) N/Carrow_forwardFour point charges are placed at the corners of a square as shown in the figure. Each side of the square has length 1.0 m. Determine the magnitude of the electric field at the point P, the center of the square. (note Q = 0.15 C) a. no answer is correct b. 5.0 x 10 4 N/C c. 3.6 x 10 4 N/C d. 3.6 x 10 9 N/C e. 5.4 x 10 9 N/Carrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON