
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:**Question 43**
You cut yourself, and the cut becomes infected. The cause of this infection is most likely a ________ cell, which is a member of domain ________.
- a. eukaryotic; Bacteria
- b. eukaryotic; Archaea
- c. prokaryotic; Bacteria
- d. prokaryotic; Archaea
- e. prokaryotic; Eukarya
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 2v
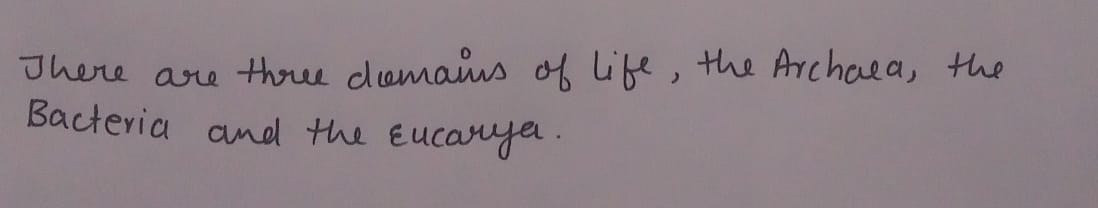
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A newly discovered unicellular organism is found to contain a cell wall, a plasma membrane, peroxisomes but no flagella. Based just on this information, the organism is most likely A. a motile prokaryote B. a nonmotile eukaryote C. a nonmotile bacterium D. a motil archea E. a motile eukaryote O F. a nonmotile archaea Reset Selectionarrow_forwardWhich of these characteristics is NOT shared by bacteria and archaea? O presence of plasma membrane O presence of peptidoglycan in cell wall O absence of a nucleus absence of membrane-bound organellesarrow_forwardArchaea cells do NOT often have: a. preferences for extreme habitats. b. specifically identifiable ribosomal RNA genes. c. Branched chains in their membrane lipids. d. Ester linkages in their phospholipids. e. Pseudomurein cell wall containing no N-acetylmuramic acid and no D-amino acids. f. circular chromosomes.arrow_forward
- Streptococcus pneumoniae is a Gram-positive bacteria, it looks like under a microscope: * chains of red rod cells O colorless spiral cells chains of purple spherical cells clusters of purple spherical cells O clusters of red rod cells Fungi are very important organisms for human because pcarrow_forwardA biologist is studying an organism that is single-celled. With only this information, we know that the organism could be only a microbial eukaryote. a bacterium, archaean, or microbial eukaryote. a bacterium or an archaean. only an archaean. only a bacterium.arrow_forwardis the process by which prokaryotic cells can acquire DNA (genes) from the environment while is when the DNA is introduced into the bacterial genome by viruses.arrow_forward
- Which description below describes viruses? acellular, made of protein capsid which protects viral genetic informaion, either DNA or RNA but not bo O acelluar, eukaryotes, Domain Archaea O cellular, eukaryotes, Domain Eukarya O acellular, prokaryotes, Domain Bacteria Question 14 Your lab partner wants to know the reasons viruses are not considered cells. You provide all the following reasons EXCEPT you make one mistake. Which statement below is FALSE with regard to why viruses are not considered cells?arrow_forwardWhich of the following answers is correct about the type of cells this organelle (where the arrow is pointing) is found in? A. prokaryote; bacteria B. eukaryote; animals C. eukaryote; bacteria D. eukaryote; plant E. prokaryote; plant F. both A and C G. both A and D H. both C and D I. All choices are correctarrow_forwardAntibiotics are medicines that are used to fight bacterialinfections. These medicines kill prokaryotic cellswithout harming human cells. What part or parts of thebacterial cell do you think antibiotics target? Why?31. Explain why not all microbes are harmful.arrow_forward
- ntibiotics are medicines used to fight bacterial infections. These drugs kill prokaryotic cells without harming human cells. What part or parts of the bacterial cell do you think the antibiotics target? Why?arrow_forwardWhich of these best demonstrates mutualism between certain types of bacteria and humans? Bacteria in improperly prepared food is consumed by humans, causing food poisoning. O Intestinal bacteria obtain nutrients from the gut and produce vitamin K used by humans. O Bacteria become resistant to antibacterial medication that humans use for treatment. Invasive bacteria at an area of injury produce toxins that damage healthy tissues of the human body. 3 4arrow_forwardA prokaryotic cell _______ contain lysosomes. A prokaryotic cell _______ contain golgi. Select one: a. will, will b. will not, will not c. will, will not d. will not, willarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education