
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
You are the manager of a firm that charges customers $16 per unit for the first unit purchased, and $12 per unit for each additional unit purchased in excess of one unit. The accompanying graph summarizes your relevant demand and costs.
a. What is the economic term for your firm’s pricing strategy?
multiple choice
-
Third degree
price discrimination -
Fourth degree price discrimination
-
First degree price discrimination
-
Second degree price discrimination
b. Determine the profits you earn from this strategy.
$
c. How much additional profit would you earn if you were able to perfectly price discriminate?
Instructions: In solving this problem, assume the firm cannot sell fractions of a unit.
$
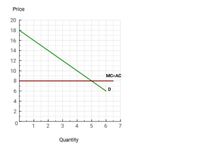
Transcribed Image Text:The image is a graph illustrating the relationships between price and quantity. The graph is plotted on a grid with 'Price' on the vertical y-axis and 'Quantity' on the horizontal x-axis.
1. **Axes and Labels**:
- The y-axis (Price) ranges from 0 to 20.
- The x-axis (Quantity) ranges from 0 to 7.
2. **Lines on the Graph**:
- The green line represents market demand (D) and has a downward slope, starting at a price of 18 when the quantity is 0 (the y-intercept) and decreasing steadily as quantity increases.
- The brown horizontal line indicates the point where marginal cost equals average cost (MC = AC) and remains constant at a price of about 8 across different quantities.
3. **Intersection Point**:
- The intersection of the green demand line and the brown MC = AC line occurs at approximately quantity 5 and price 8.
This graph can be used to illustrate concepts such as equilibrium price and quantity, as well as how costs influence market behavior.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Edison's Fire Engines is the sole seller of fire engines in the fictional country of Pyrotania. Initially, Edison produced eight fire engines, but he has decided to increase production to nine fire engines. The following graph shows the demand curve Edison faces. As you can see, to sell the additional engine, Edison must lower his price from $80,000 to $60,000 per fire engine. Note that while Edison gains revenue from the additional engine he sells, he also loses revenue from the initial eight engines because he sells them all at the lower price. Use the purple rectangle (diamond symbols) to shade the area representing the revenue lost from the initial eight engines by selling at $60,000 rather than $80,000. Then use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to shade the area representing the revenue gained from selling an additional engine at $60,000. 100 90 PRICE (Thousands of dollars per fire engine) 8 80 70 60 50 40 30 10 0 Edison 0 1 O True 2 O False + 6 3 4 5 7 QUANTITY (Fire…arrow_forwardWhich of these statements is most CORRECT about real world pricing strategies? Select one: a. Two part pricing is only beneficial when groups of customers have homogeneous demand b. Two part pricing should not be combined with price discrimination c. Price discrimination is used to separate customers into groups with heterogeneous demand d. Selling many substitute products is never a successful strategyarrow_forwardIf a company successfully advertises its product, do we expect the price elasticity of demand for this firms perceived demand curved to increase, decrease or remain the same? Explain how advertising can cause this effect.arrow_forward
- The Taco Bus Low Price High Price The Fajita Wagon Low Price Taco Bus: $1,000 Taco Bus: $500 Fajita Wagon: $1,000 Fajita Wagon: $6,000 High Price Taco Bus: $6,000 Taco Bus: $4,000 Fajita Wagon: $500 Fajita Wagon: $4,000 Refer to the table above, which describes the payoffs to different pricing strategies for a duopoly. What set of strategies would be the Nash equilibrium for this game? The Fajita Wagon adopts a high price, and the Taco Bus adopts a high price. The Fajita Wagon earns $1,000 profit, and the Taco Bus earns $1,000 profit. The Fajita Wagon earns $4,000 profit, and the Taco Bus earns $4,000 profit. The Fajita Wagon adopts a low price, and the Taco Bus adopts a low price. There is no Nash equilibrium in this game.arrow_forwardOmari's HookNLadder is the only company selling fire engines in the fictional country of Alexandrina. Omari initially produced four trucks, but then decided to increase production to five trucks. The following graph gives the demand curve faced by Omari's HookNLadder. As the graph shows, in order to sell the additional fire truck, Omari must lower the price from $105,000 to $90,000 per truck. Notice that Omari gains revenue from the sale of the additional engine, but at the same time, he loses revenue from the initial four engines because they are all sold at the lower price. Use the purple rectangle (diamond symbols) to shade the area representing the revenue lost from the initial four engines by selling at $90,000 rather than $105,000. Then use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to shade the area representing the revenue gained from selling an additional engine at $90,000. PRICE (Thousands of dollars per fire engine) 165 150 135 120 105 Omari 90 75 60 45 30 15 Revenue Lost Demand…arrow_forwardThe following graph shows the daily demand curve for bippitybops in Chicago. Use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to compute total revenue at various prices along the demand curve. Note: You will not be graded on any changes made to this graph. Total Revenue 0 8 16 24 32 40 48 56 64 72 80 200 180 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 PRICE (Dollars per bippitybop) QUANTITY (Bippitybops per day) Demand A B Area: 1280 Calculate the daily total revenue when the market price is $180, $160, $140, $120, $100, $80, $60, and $40 per bippitybop. Then, use the green point (triangle symbol) to plot the daily total revenue against quantity corresponding to these market prices on the following graph. Total Revenue 0 8 16 24 32 40 48 56 64 72 80 3840 3520 3200 2880 2560 2240 1920 1600 1280 960 640 320 0 TOTAL REVENUE (Dollars) QUANTITY (Bippitybops per day) According to the midpoints formula, the price elasticity of demand between points A and B on the initial graph is approximately . Suppose the…arrow_forward
- I pretty sure I got the first part right. I am struggling with bottom parts.arrow_forwardCould companies implementing two pricing strategies at the same time? For instance, cost based pricing and competition based pricingarrow_forwardDefine price discrimination. Give two examples of price discrimination. How does perfect price discrimination affect consumer surplus, producer surplus and total surplus?arrow_forward
- Macmillan Learning You have been appointed head of marketing for Barry's Younique Yachts. Barry, the CEO, is interested in determining whether offering his yachts at a lower price would increase the firm's revenue. He asks you for advice. Using your knowledge of elasticity, you should tell Barry that he should increase his prices. Demand for yachts is perfectly inelastic, so a price increase will cause total revenue to increase. that he should reduce his prices. Yachts are luxury goods and therefore exhibit a high price elasticity of demand. Thus, reducing prices would increase revenue. that he should increase his prices. Demand for yachts is likely to be elastic because they are so much fun to drive. Thus, increasing prices would increase revenue. that he should reduce his prices. Yachts are a necessity and therefore have a low price elasticity of demand. Thus, reducing prices would increase revenue.arrow_forwardYou are the manager of a monopolistically competitive firm, and your demand and cost functions are given by Q = 36 – 4P and C(Q) = 124 + 16Q + Q2.a. Find the inverse demand function for your firm’s product b. Determine the profit-maximizing level of production and price. Quantity: ? Price: ? c. Calculate your firm's maximum profits. d. I expect profit to (blank), price to (blank), and quantity to (blank).arrow_forwardYou are the manager of a monopolistically competitive firm, and your demand and cost functions are estimated as Q = 48 − 2P and C(Q) = 6 + 3Q + Q2. a. Find the inverse demand function for your firm’s product. P = − Q b. Determine the profit-maximizing price and level of production. Instructions: Round your response to the nearest penny (two decimal places). Price: $ Instructions: Round your response to one decimal place. Quantity: c. Calculate your firm’s maximum profits. Instructions: Round your response to the nearest penny (two decimal places). $ d. What long-run adjustments should you expect? Explain. multiple choice Entry will occur until profits are zero. Exit will occur until profits rise sufficiently high. Neither entry nor exit will occur.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education