
Concept explainers
The Experiment:
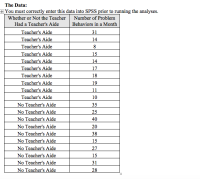
You are a researcher who studies children’s behavior in schools – your goal is to decrease problem behaviors (fighting, disrupting class, disrespecting the teacher, etc) so students can learn better. You think that part of the problem is that students aren’t getting enough one-on-one attention, so you set out to see if placing a teacher’s aide in each classroom makes a difference in the number of problem behaviors. You hypothesize that more adults in the classroom will lead to better behaved classrooms.
You recruit a total of 20 teachers. You split the teachers into two groups of 10 teachers each. For 10 of the teachers, you place a teacher’s aide in the classroom to help the teacher. The other 10 teachers do not get a teacher’s aide during this stage of the study. For a month, you have all 20 teachers in each classroom record every time a problem behavior occurred. At the end of the month, you have the teachers report to you the tally of the number of problem behaviors that occurred that month.
1. Enter and label the data appropriately in SPSS
2. Choose the appropriate statistical test that should be used to analyze the data and explain why you chose this particular test
3. Analyze the data using the test specified
4. Describe the results
5. Make a conclusion about whether the study’s hypothesis was supported.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 4 images

- You want to compare males and females in their use of coping strategies when engaged in conflict in relationships. You send surveys to couples obtained from marriage license application at the county clerk's office. You identify several distinct coping strategies on the survey and have the respondents rate their use of each strategy on a 7-point scale. You then compare scores that come from the two members of each relationship. If testing hypotheses about the effects of gender on use of coping strategies, it would be most appropriate to calculate a ... 1) independent-samples t 2) one sample t 3) paired samples t 4) z testarrow_forwardSuppose that you wanted to design an investigation that examined the association between energy drink consumption and social interaction. You select your sample population and begin making your observations. As the research progresses, you suspect that a number of the subjects exhibit behavioral changes simply related to their knowledge of being enrolled in the study and the increased attention they are receiving as subjects. This phenomenon is known as: Group of answer choices selection bias the Hawthorne effect healthy participant effect misclassification error the Rosenthal effectarrow_forwardThe Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that the official unemployment rate for Black people was 10.4% and 4.7% for White people in February 2015. Select all correct answers for this question. O The samples of white and black people are independent. The explanatory variable is the unemployment rate. The response variable is the unemployment rate. The response variable is race.arrow_forward
- What's the difference between naturalistic observation and systematic observation?arrow_forwardANOVA. Dr. Milgramm is conducting a patient satisfaction survey, rating how well her patients like her on a scale of 1-10. Her patients tend to fall into three categories: “Like a lot”, “like somewhat”, and “dislike a lot”. She believes that she might get different satisfaction scores from people in each group, but (because she's not great at numbers) she wants you to do an ANOVA to be sure. She has collected data from 12 patients (three equal groups) with the following results. Group 1) “Like a lot” Mean: 8 SS: 2 N: df: Group 2) “Like somewhat” Mean: 5 SS: 6 N: df: Group 3) “Dislike a lot” Mean: 2 SS: 4 N: df: Grand Mean: df Within-Group:__________ df Between-Groups:___________ Estimated Variance (S21) for Group 1: _______ Estimated Variance (S22) for Group 2: ___________ Estimated…arrow_forwardA researcher is studying the effects of the college experience on attitudes, values, and behaviors and is comparing random samples of freshman and seniors at the same university. Is there a significant difference in political ideology? (On this scale, 10 means "very conservative" and 1 means "very liberal") FRESHMAN SENIORSmean=5.23 mean=5.12s=1.78 s=1.07N=145 N=105arrow_forward
- Back in April and May of 1985, the Gallup organization conducted a poll to estimate the percentage of Americans who approved of how President Reagan was handling his job. At the 5% significance level, do the data suggest that the percentage of those who approved of Reagan increased from April to May in 1985? Population 1: April p = 795/1528 = 0.5203Population 2: May p = 840/1528 = 0.5497Show all your steps, setting up your null and alternative hypothesis.arrow_forwardBullying,” according to noted expert Dan Olweus, “poisons the educational environment and affects the learning of every child.” Bullying and victimization are evident as early as preschool, with the problem peaking in middle school. Suppose you are interested in the emotional well-being of not only the victims but also bystanders, bullies, and those who bully but who are also victims (bully-victims). You decide to measure anxiety in a group of bullies and a group of victims using an 18-item, 5-point anxiety scale. Assume scores on the anxiety scale are normally distributed and that the variances of the anxiety scores are the same among bullies and victims. The group of 23 bullies scored an average of 40.1 with a sample standard deviation of 10 on the anxiety scale. The group of 28 victims scored an average of 46.8 with a sample standard deviation of 11 on the same scale. You do not have any presupposed assumptions about whether bullies or victims will be more anxious, so you formulate…arrow_forwardYou are a sales manager for a grocery store, and you want to see if the introduction of a new sales promotion will increase the sales in your store. To do so, you decided to create an experiment by giving a small sample of customers the promotion before expanding it to a larger customer base. You gave 18 people the promotion, and also observed the sales of 27 people who did not get the promotion as a control group. You found those who received the promotion to have an average monthly sales of $456.60, with a sample standard deviation of $52.23. You found those who did not receive the promotion had an average monthly sales of $361.46, with a sample standard deviation of $56.11. Suppose you want to use hypothesis testing (two-sample test) to investigate if the promotion has increased the sales of your store. Using the order promotion no promotion in your hypothesis test, what is the value of the test statistic for your analysis? Note: 1- Only round your final answer. Round your final…arrow_forward
- Need help.arrow_forwardGive me an example of a research scenario where you would use an independent samples t-test. You can set up a situation where there is an experimental group and a control group, or maybe you want to compare two other groups of people (parents and non-parents, gender, partnered and single, etc). Give us a summary of what you would want to study, who your sample participants would be, why an independent samples t-test would be the best fit, and what statistically significant results would mean. Don't forget to include your research and null hypotheses!arrow_forwardCell Phones and Crashes: Analyzing Newspaper Report In an article from the Associated Press, it was reported that researchers “randomly selected 100 New York motorists who had been in an accident and 100 who had not been in an accident. Of those in accidents, 13.7 percent owned a cellular phone, while just 10.6 percent of the accident-free drivers had a phone in the car.” What is wrong with these results?arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





