
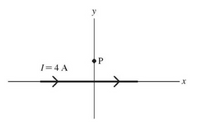
A long straight wire carrying a 4-A current is placed along the x-axis as shown in the figure. A proton is traveling in the vicinity of this wire.
(a) At the instant the proton is at point P, 4.50 cm above the wire’s center and moving with a speed of 6×104 m/s directly toward it, what is the force (magnitude and direction) that the magnetic field of the current exerts on the proton?
(b) explain how you've determined the direction of the force in part (a).
(c) What would be the magnetic force (magnitude and direction) if the proton were instead moving parallel to the wire in the same direction as the current?
(d) explain how you've determined the direction of the force in part (c).
μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A
e = 1.6 × 10-19 C
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

- The figure below shows an electric field line, at point A, draw the direction of the electric field vector Aarrow_forwardMf...arrow_forwardSee the attached picture, could you check my answers below? Answer: The magnitude of magnetic field is 2.6×10^−6 and according to right hand rule, the direction of magnetic field is outward perpendicular to the page. Which symbol (a, b, c or d) as shown in the picture is the symbol for the direction of the magnetic field at point P.arrow_forward
- The figure below shows a wire that forms a semicircle of radius R=10. 0 cm and two straight segments each of length 7.0 cm. The wire carries a current i = 42.0 mA.(a) What are the magnitude, and(b) direction of the magnetic field at point C?arrow_forward10) A proton is moving in a constant magnetic field, see figure, what is the direction of the force on the proton? Velocity proton B-Fieldarrow_forwardA rod with mass m = 0.720 kg and radius r = 6.00 cm rests on two parallel rails, as shown in the figure. The rails are separated by a distance d = 12.0 cm and have length L = 45. cm.The rod carries a current I = 48.0 A in the direction shown in the figure and rolls on the rails without slipping. There is a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B = 0.240 T perpendicular to the rails and the rod. If the rod starts from rest, what is its speed when it leaves the rails?arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





