
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
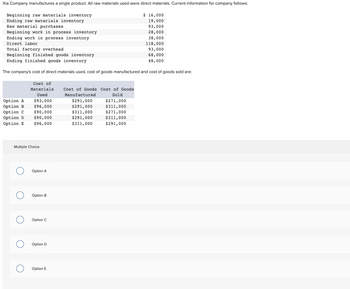
Transcribed Image Text:Xia Company manufactures a single product. All raw materials used were direct materials. Current information for company follows:
Beginning raw materials inventory
Ending raw materials inventory
Raw material purchases
Beginning work in process inventory
Ending work in process inventory
Direct labor
Total factory overhead
Beginning finished goods inventory
Ending finished goods inventory
The company's cost of direct materials used, cost of goods manufactured and cost of goods sold are:
Option A
Option B
Option C
Cost of
Materials
Used
$93,000
$96,000
$90,000
$90,000
Option D
Option E $96,000
Multiple Choice
O Option A
O Option B
O Option C
O Option D
O Option E
Cost of Goods Cost of Goods
Manufactured
Sold
$291,000
$291,000
$311,000
$291,000
$311,000
$ 16,000
19,000
93,000
28,000
38,000
118,000
93,000
68,000
48,000
$271,000
$311,000
$271,000
$311,000
$291,000
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The following data was prepared by the Sandhill Company. Total Variable Fixed $ 24/unit Sales price $ 78, 750 Direct materials used Direct labor $91,000 $ 110, 750 $ 13,850 $ 96.900 Manufacturing overhead $ 22,000 $ 12,600 $9,400 Selling and administrative expense 25,500 units Units manufactured 20, 800 units Beginning Finished Goods Inventory 9,000 units Ending Finished Goods Inventory Under variable costing, what is the unit product cost?arrow_forwardProduct Cost Flows Complete the following T-accounts: Materials Inventory 1,120 Answer Answer 18,120 250 Wages Payable 9,000 1,050 Finished Goods Inventory 1,500 Answer Answer 1,200 Manufactured Overhead 175 Answer Answer 18,000 4,500 0 Work in Process Inventory 3,500 Answer Answer 9,000 Answer 500 Cost of Goods Sold Answer Save AnswersNextarrow_forwardYouTube O Maps Estimated Income Statements, using Absorption and Variable Costing Prior to the first month of operations ending October 31, Marshall Inc. estimated the following operating results: Sales (27,200 x $96) $2,611,200 Manufacturing costs (27,200 units): Direct materials 1,572,160 Direct labor 372,640 Variable factory overhead 174,080 Fixed factory overhead 206,720 Fixed selling and administrative expenses 56,200 Variable selling and administrative expenses 68,000 The company is evaluating a proposal to manufacture 30,400 units instead of 27,200 units, thus creating an ending inventory of 3,200 units. Manufacturing the additional units will not change sales, unit variable factory overhead costs, total fixed factory overhead cost, or total selling and administrative expenses. a. 1. Prepare an estimated income statement, comparing operating results if 27,200 and 30,400 units are manufactured in the absorption costing format. If an amount box does not require an entry leave it…arrow_forward
- kk. Subject:- Accountingarrow_forwardBruce Corporation makes four products in a single facility. These products have the following unit product costs: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead. Unit product cost Additional data concerning these products are listed below. Multiple Choice Product C Product B Product D Product A Products A B C D $17.20 $ 21.10 $ 14.10 $ 16.80 19.20 22.60 17.00 11.00 6.00 7.20 29.10 16.00 $71.50 A 2.25 $ 86.70 $ 2.95 4,600 9.70 16.10 $66.90 $ 56.90 Products Grinding minutes per unit Selling price per unit Variable selling cost per unit Monthly demand in units. The grinding machines are potentially the constraint in the production facility. A total of 10,500 minutes are available per month on these machines. Direct labor is a variable cost in this company. Which product makes the MOST profitable use of the grinding machines? Note: Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places. B 1.30 $ 79.10 $ 3.65 3,600 C 0.85 $ 75.90 $4.40 3,600arrow_forwardDivision X of Bella Corporation sells Part A to other companies for $87.20 per unit. According to the company's accounting system, the costs to Division X to make a unit of Part A are: O $87.20 per unit O $62.60 per unit O $58.10 per unit O $79.95 per unit O None of the above Direct materials Direct labor $5.80 Variable Division Y of Bella Corporation uses a part much like Part A in one of its products. Division Y can buy this part from an outside supplier for $79.95 per unit. However, Division Y could use Part A instead of the part it purchases from the outside supplier. What is the most Division Y would be willing to pay the Division X for Part A? Question 21 $42.70 manufacturing $9.60 overhead Fixed manufacturing $4.50 overheadarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education