
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
|
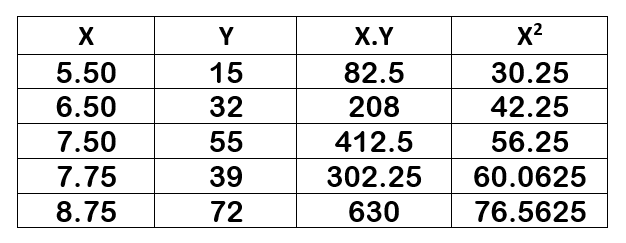
x |
5.50 |
6.50 |
7.50 |
7.75 |
8.75 |
|
y |
15 |
32 |
55 |
39 |
72 |
a) Find a for the equation of the least-squares line y = ax+b: choose one:
–75.923
42.698
–42.068
–42.698
75.923
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- . Find the equation for the least-squares line for the following table: x 6 20 0 14 25 16 28 18 10 18 y 15 31 10 16 28 20 40 25 12 15 Also calculate the coe cient of determinationarrow_forwardIn the least-squares line = 5 – 9x, what is the value of the slope?When x changes by 1 unit, by how much does y change? When x increases by 1 unit, y decreases by 9 units. When x decreases by 1 unit, y decreases by 9 units. When x increases by 1 unit, y decreases by −9 units. When x increases by 1 unit, y increases by 9 units.arrow_forwardThe cost of a leading liquid laundry detergent in different sizes is given below. Size (ounces) Cost ($) 16 3.59 32 4.39 64 5.19 200 10.19 Calculate the least squares line. Put the equation in the form of: ŷ = a + bx. (Round your answers to three decimal places.)ŷ = + xarrow_forward
- Consider the data points (2, 1), (0, –4) and (−2,−3). Given that the least squares line of best fit is y = x − 2 ,which one of the following is the least squares error? √38 +√6 √6arrow_forwardWe use the form ŷ = a + bx for the least-squares line. In some computer printouts, the least-squares equation is not given directly. Instead, the value of the constant a is given, and the coefficient b of the explanatory or predictor variable is displayed. Sometimes a is referred to as the constant, and sometimes as the intercept. Data from a report showed the following relationship between elevation (in thousands of feet) and average number of frost-free days per year in a state. A Minitab printout provides the following information. Predictor Coef SE Coef T P Constant 315.27 28.31 11.24 0.002 Elevation -31.812 3.511 -8.79 0.003 S = 11.8603 R-Sq = 96.8% Notice that "Elevation" is listed under "Predictor." This means that elevation is the explanatory variable x. Its coefficient is the slope b. "Constant" refers to a in the equation ŷ = a + bx. (a) Use the printout to write the least-squares equation. ŷ = + x (b) For each 1000-foot increase in elevation,…arrow_forwardWe use the form ŷ = a + bx for the least-squares line. In some computer printouts, the least-squares equation is not given directly. Instead, the value of the constant a is given, and the coefficient b of the explanatory or predictor variable is displayed. Sometimes a is referred to as the constant, and sometimes as the intercept. Data from a report showed the following relationship between elevation (in thousands of feet) and average number of frost-free days per year in a state. A Minitab printout provides the following information. Predictor Coef SE Coef T P Constant 316.62 28.31 11.24 0.002 Elevation -30.516 3.511 -8.79 0.003 S = 11.8603 R-Sq = 96.2% The printout gives the value of the coefficient of determination r2. What is the value of r? Be sure to give the correct sign for r based on the sign of b. (Round your answer to four decimal places.) What percentage of the variation in y can be explained by the corresponding variation in x and the least-squares…arrow_forward
- In the least-squares line ŷ = 5 − 4x, what is the value of the slope?arrow_forwardTest the following data table to see whether the data are quadratic. x 0 4 16 32 44 y 4 12 16 12 20 Calculate the first-order and second-order differences.arrow_forwardI need the right answer to d, e, and f ASAP, please.arrow_forward
- The height (sidewalk to roof) of notable tall buildings in America is compared to the number of stories of the building (beginning at street level). Stories (x) Height (y) 59 1050 29 428 25 362 40 529 60 790 22 401 38 380 110 1454 100 1127 46 700 Calculate the least squares line. Put the equation in the form of: y = a + bx. (Round your answers to three decimal places.) ŷ = + Xarrow_forward2. The Mach number of a moving object is the ratio of its speedto the speed of sound. The following table shows the speeds of a jet aircraft, in terms of Mach numbers, and the time tafter it starts to accelerate. Find the least- squares line of s as a function of t. t(min) 0.00 s(Mach Number) 0.88 0.60 0.97 1.20 1.03 1.80 1.11 2.40 1.19 3.00 1.25arrow_forwardWe use the form ý = a + bx for the least-squares line. In some computer printouts, the least-squares equation is not given directly. Instead, the value of the constant a is given, and the coefficient b of the explanatory or predictor variable is displayed. Sometimes a is referred to as the constant, and sometimes as the intercept. Data from a report showed the following relationship between elevation (in thousands of feet) and average number of frost-free days per year in a state. %3D A Minitab printout provides the following information. Predictor Сoef SE Coef P Constant 315.54 28.31 11.24 0.002 Elevation -28.950 3.511 -8.79 0.003 S = 11.8603 R-Sq = 96.2% Notice that "Elevation" is listed under "Predictor." This means that elevation is the explanatory variable x. Its coefficient is the slope b. "Constant" refers to a in the equation ŷ = a + bx. (a) Use the printout to write the least-squares equation. = 315.54 X x (b) For each 1000-foot increase in elevation, how many fewer frost-free…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman