
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
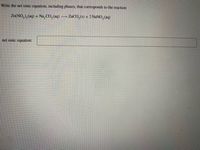
Transcribed Image Text:Write the net ionic equation, including phases, that corresponds to the reaction
Zn(NO,),(aq) + Na,CO,(aq)
ZNCO, (s) + 2 NANO,(aq)
net ionic equation:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- What is the balanced net ionic equation for this reaction. Pb(NO,),(aq) + 2HCI(aq) PBCI, (s) + 2HN0,(aq) HCl and HNO, are both strong acids.arrow_forwardWrite net ionic equations for the following reactions:arrow_forwardAssume that an aqueous solution of a cation, represented by shaded spheres, is allowed to mix with a solution of an anion, represented by unshaded spheres. Three possible outcomes are represented by boxes (a)-(c). cation anion rvey (a) (b) (c) Which outcome corresponds to the combination of copper and sulfide ions: Cu* (aq) +S2 (aq) ? O box (c) O none of these O box (b) O box (a) can harm your computer. Do you maoosoakmda.PN.url anyway? Keep Discard Address Lere to searcharrow_forward
- Balance the following equation, classify the reaction as combination, decomposition, single displacement, or double displacement, and write the total ionic equation and net ionic equation.arrow_forwardA sample of a chloride salt weighing 484.6 mg is titrated with AgNO3 using K2CrO4 as indicator. To reach the end point a 52.3 mL of 0.1475 M of AgNO3 solution is required. The net ionic equation for the reaction of titration is: Ag+ (aq) + Cℓ- (aq) → AgCℓ (s) How many moles of Ag+ (aq) ions are used to reach the end point? How many moles of Cℓ- (aq) have reacted in the titration? How many grams of chloride are present in the sample? What is the mass percent of chloride in the sample?arrow_forwardThe reaction of hypothetical elements: A, B, C, D, and E, follows the molecular equation: AB2(aq) + CDE(aq) -> AE(s) + CB(aq) + DB(aq) Assuming that all aqueous compounds would fully dissociate, indicate the element/s that would form spectator ions in the subsequent total ionic equation.arrow_forward
- Use the activity series to predict which of the following reactions will occur. Complete and balance the equations. If no reaction occurs, write “no reaction” as the product. (a) Cu(s) + NiCl2(aq) ------> (b) Rb(s) + H2O(l) ------> (c) I2(s) + CaCl2(aq) ------>arrow_forward1. (a) Write balanced molecular equations for the following potential precipitation reactions. Indicate the states of reactants and products [(aq) or (s)]. (b) In those cases where a precipitate forms, write the net ionic equation. If there is no reaction, state "No reaction." (i) Na₂S (aq) + Pb(NO3)2 (aq) → (iii) MgCl₂ (aq) + Pb(NO3)2 (aq) → (ii) FeSO4 (aq) + Na3PO4 (aq) → (iv) K₂SO4 (aq) + Ni(NO3)2 (aq) →arrow_forward?arrow_forward
- The amount of I, (aq) in a solution can be determined by titration with a solution containing a known concentration of S,O, (aq) (thiosulfate ion). The determination is based on the net ionic equation 2 S,0 (aq) + 1, (aq) → S,0 (aq) + 31-(aq) Given that it requires 38.6 mL of 0.470 M Na, S,O, (aq) to titrate a 10.0 mL sample of I, (aq), calculate the molarity of I, (aq) in the solution. [5] = Marrow_forwardHow much water (in mL) should you add to 50.0 mL of 0.300 M H,SO, (ag) to get a solution of 0.130 M H2SO4 (aq)? Write just the numerical answer with proper sig figs (no units) and do not put it in scientific notation. Make sure to record and submit the full work with units and sig figs in the separate file labeled 4 work.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY