
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Write complete molecular equation for each observation and identify each reaction as redox or non-redox.
C1:
Observation: Zn reacts with HCl and produces a gas. Insertion of an ignited wooden splint results on an audible "pop" sound.
Equation:
Redox or Non-redox
C2a:
Observation: A reddish color rust forms on the zinc strip.
Equation:
Redox or Non-Redox
C2b:
Observation: No change in copper strip or solution color is observed.
Equation:
Redox or Non-Redox
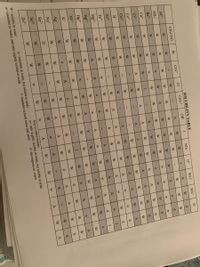
Transcribed Image Text:|ミ|ミ
>>>>E
|彡1彡
|彡
SOLUBILITY TABLE
CrO
CH,COO
Br
CO3-
OH
NO,
O-
PO
SO
AP
W
A
W
W
A
a
NH,*
W
W
W
W
W
W
W
W
W
--
Ba
W
W
W
W
W
W.
a
d
Ca2+
W
W
Cr
W
W
W
W
d.
--
a
Co+
W
W
W
A
A
W
W
A
A
W
A
Cu
W
W
W
A
a
W
A
W
H*
W
W
W
W
W
W
W
Fe
W
W
W
A
W
A
Fe+
W
W
W
A
W
A
d
A
W
d.
Mg
A
W
W
W
W
Hg"
A
W
A
A
W
A
a
W.
A
W
A
I
Hg*
W
W
W
Ni
W
W
W
W
A
W
W
W
W
W
W
W
W
K
W
W
W
A
Ag
a
--
W
a
10
W
W
W
W
d.
W
W
Na*
W
W
W
W
A
W
d.
A
A
W
A
Sn2+
D
W
W
A
A
A
Sn+
W
W
W
W
W
W
A
W
A
W
A
Zn
W
W
Key to abbreviations:
w= only slightly soluble in water, but soluble in acids
W= soluble in water
A= insoluble in water, but soluble in acids
I= insoluble in both water and acids
d= decomposes in water
a= insoluble in water, and only slightly soluble in acids

Transcribed Image Text:In this type of metathetical reaction, heat is given off and a molecular species such as water is formed. If the solutions are
dilute, the heat effect may not be noticeable and no visible change occurs. Thus, we use an indicator like phenolphthalein to indicate
that a reaction has occurred. Phenolphthalein is pink in basic solution and clear in acid solution. Strong acids and strong bases are
completely ionized in solution.
Carbonates are basic and the
addition of an acid will result
HNO, (aq) + KOH(aq) → KNO, (ag) + H:00)
in the formation of bubbles of carbon dioxide gas:
2HCI(aq) + CaCo, → CaCl:(aq) + H:0(0) + CO:(g)t
PROCEDURES: Perform
each of the following reactions. Write your observations in your notebook and write the equation for each reaction.
1.
Add a dropperful of 0.1 M NaOH and one drop of phenolphthalein to a test tube. Note the color. Add 0.1 M HCI drop by drop
until the color changes. Feel the test tube. Can you detect the evolution of heat?
Place a spatulaful of sodium carbonate in a test tube. Add a dropperful of 1M hydrochloric acid.
2.
PART II - REDOX REACTIONS
Redox reactions are reactions in which elements are oxidized and reduced, i.e. some of the elements involved undergo a change
in oxidation number. There are many types of redox reactions - combination reactions, decomposition reactions, replacement reactions
and combustion reactions. In this experiment, you will perform some combination, decomposition, and replacement reactions. Not all
combination and decomposition reactions are redox reactions.
А.
COMBINATION REACTIONS
Combination reactions are those in which two or more substances combine to form a more complex substance. The general
formula for a combination reaction is
A + B →C
Many combination reactions
involve the reaction of two
elements to fom a compound
and these are all redox reactions.
C + 0; → CO;
Many elements react with oxygen to form oxides.
4Na + 0, → 2 Na,0
Some combination reactions
involve the reaction of two
compounds to form another compound. These are often not redox reactions. Metal oxides react with water to form metal hydroxides.
The presence of the hydroxide ion is detected with phenolphthalein.
Na,0 + H,0 → 2NAOH
PROCEDURES: Perform
each of the following
reactions. Write your observations in your notebook and write the equation for each reaction. Identify each reaction as redox or non-
redox.
Work under the hood! With a pair of tongs, hold a strip of magnesium in a bunsen burner flame. Do not look directly at the
flame. Save the ash in a small beaker for the next procedure. If magnesium is substance "A" in the general equation, what is
"B"?
1.
Add a dropperful of distilled water and a drop of phenolphthalein. The phenolphthalein is only an indicator for the presence of
hydroxide ion and does not enter into the equation.
DECOMPOSITION REACTIONS
2.
В.
A decomposition reaction is the reverse of a combination reaction. It involves the breakdown of a complex substance into
simpler substances. It is often necessary to heat the substance being decomposed. The general equation for a decomposition reaction is
C - A + B
Metal oxides decompose to
the metal and oxygen gas.
This is a redox reaction.
Metal hydroxides decompose
to the metal oxide and water.
2Hg0 → 2Hg + O:
This is not a redox reaction.
PROCEDURES: Perform
each of the following
reactions. Watch for evidence
Mg(OH ), → Mgo + H;0
of the decomposition products. Write your observations in your notebook and write the equation for each reaction. Identify each
reaction as redox or non-redox.
1.
Work under the hood! Weigh out exactly 0.1 g of ammonium dichromate and add to a test tube. Clamp and warm gently with
a Bunsen burner. Two of the products of this reaction are chromium (III) oxide and nitrogen gas. Watch for evidence of the
third product.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. iron metal and oxygen gas react to form solid iron (lll) oxide. type of reaction? 2. copper metal, when added to aqueous silver nitrate produces silver metal and copper (ll) nitrate. type of reaction?arrow_forwardWhich one of the following statements is not correct? Select one: a. Oxidation refers to a chemical reaction in which a substance loses electrons. b. Reduction refers to a chemical reaction in which a substance gains electrons. c. The oxidation number represents the charge an atom would have if all its bonds to other atoms were ionic. d. An oxidizing agentis a substance that is oxidized in a chemical reaction. e. Statements A-D are all correct.arrow_forwardd. For the unbalanced redox reaction i. ii. i. Br + MnO4 → Br2 + Mn²+ e. For the unbalanced redox reaction ii. Which is oxidizing agent (oxidant)? Write the balanced redox net ionic equation when the reaction is conducted in an acidic solution. Cr³+ + MnO4 → Cr₂O7²- + MnO2 Which is oxidizing agent (oxidant)? Write the balanced redox net ionic equation when the reaction is conducted in a basic solution.arrow_forward
- With their states, please.arrow_forwardIs formation of rust a burning reaction. Explain your answerarrow_forwardBalance the following 1⁄2 reactions so there are the same number of atoms on both sides of the reaction, then add electrons to the correct side of the equation to balance the 1⁄2 reactions, Finally classify them as oxidation or reduction.arrow_forward
- A student mixes two clear, colorless solution and the test tube becomes warm. Had a reaction occurred? It may be possible to argue in favor of yes or no. Defend your answer.arrow_forwardWrite obervation and the complete molecular equation for each reaction. Identify each reaction as redox or non-redox. A1: Mg will burn with a bright color and turn into ash. redox or non-redox: Observation: Equation: A2: Dissolving collected ash from Al in water and then adding phenolpthalein to the solution result in a pink color solution. redox or non-redox: Observation: Equation:arrow_forwardH2O2, oxidation number of Oxygen is?arrow_forward
- D. The oxidation of phosphine (PH,) to phosphorus pentoxide (P,O,) is given by the chemical equation: PH, +O, P,O, +H,O Rel.arrow_forwardIn a redox reaction: electrons are created there is a transfer of protons from one species to another electrons are transferred between two species the reaction always moves in a reverse directionarrow_forwardtrue or falsearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY