
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
Transcribed Image Text:WLEY
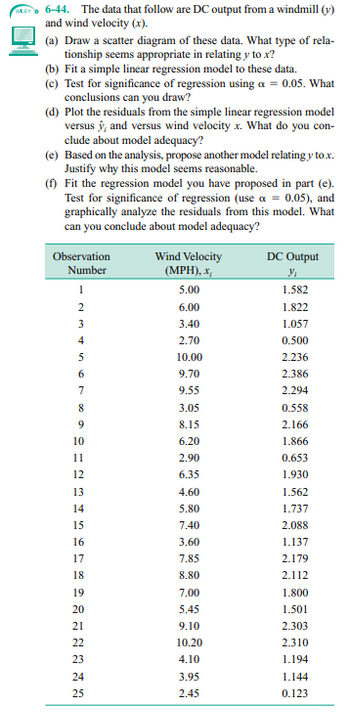
6-44. The data that follow are DC output from a windmill (y)
and wind velocity (x).
(a) Draw a scatter diagram of these data. What type of rela-
tionship seems appropriate in relating y to x?
(b) Fit a simple linear regression model to these data.
(c) Test for significance of regression using a = 0.05. What
conclusions can you draw?
(d) Plot the residuals from the simple linear regression model
versus y, and versus wind velocity x. What do you con-
clude about model adequacy?
(e) Based on the analysis, propose another model relating y to.x.
Justify why this model seems reasonable.
(f) Fit the regression model you have proposed in part (e).
Test for significance of regression (use a = 0.05), and
graphically analyze the residuals from this model. What
can you conclude about model adequacy?
Observation
Number
1
NM & in eor
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
Wind Velocity
(MPH), x
5.00
6.00
3.40
2.70
10.00
9.70
9.55
3.05
8.15
6.20
2.90
6.35
4.60
5.80
7.40
3.60
7.85
8.80
7.00
5.45
9.10
10.20
4.10
3.95
2.45
DC Output
Y
1.582
1.822
1.057
0.500
2.236
2.386
2.294
0.558
2.166
1.866
0.653
1.930
1.562
1.737
2.088
1.137
2.179
2.112
1.800
1.501
2.303
2.310
1.194
1.144
0.123
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 6 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Why did you choose one-way ANOVA to solve c) and not two-way ANOVA?
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Why did you choose one-way ANOVA to solve c) and not two-way ANOVA?
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the Thermistor given below using piecewise approximation method combined with line regression to find the best equation and value for Temperature if the system has counts =800 20 40 60 80 |ADC counts 928 785 654 420 152 T=129.7902-0.14586*Counts, T= 13.1022 T=129.7902-0.13986*Counts, T=17.9021 T=129.7902-0.12358*Counts, T= 30.9262 T=135.4745-0.14599*Counts, T= 18.68613arrow_forwardThe radius at periapsis of an Earth-orbiting spacecraft is 3R. It's apoapsis radius is 5R. Let the mean anomaly M be equal to 1 radian. Carry out three iterations of the Newton- Raphson method by hand to approximate the value of eccentric anomaly, E, corresponding to M. Remember to show your work. State your answers in radians. a. What is your initial guess for eccentric anomaly, E? Call this guess Eo. b. To five decimal places, what is your result for the first iteration, E₁? c. To five decimal places, what is your result for the second iteration, E2? I d. To five decimal places, what is your result for the third iteration, E3?arrow_forwardStatistical Inferencearrow_forward
- 4. It is determined that an experimental data taken for T as a function of time, is a first order system, following the trend line of y = yoe. The data taken for various times is shown in table below. Approximate the time constant for this experiment. Show your work. T 0.00 0.50 3.00 5.00 5.50 6.00 6.50 7.00 7.50 11.00 14.00 17.00 22.00 25.00 Y 23.00 22.43 20.13 18.81 18.54 18.29 18.05 17.84 17.63 16.57 16.01 15.64 15.31 15.20arrow_forwardFor the calibration data given in Table Q2(c), plot the calibration curve using suitable axes. Estimate the static sensitivity of the system at the midrange.arrow_forwardRegression analysis was applied between sales data (y in $1000s) and advertising data (x in $100s) and the following information was obtained. ý = 12 +1.8x n=17 SSR = 225 SSE = 75 Sb1 = .2683 The critical t value for testing the significance of the slope, at a .05 level of significance, is A) 1.753. B) 2.131. 1.746. 2.120.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY