
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Why did the average
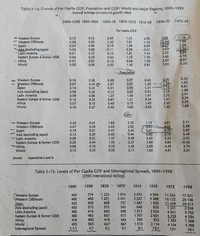
Transcribed Image Text:Table 3-1a. Growth of Per Capita GDP, Population and GDP: World and Major Regions, 1000–1998
(annual average compound growth rates)
1000-1500 1500-1820
1820-70 1870-1913 1913-50
1950-73
(1973-98
Per capita GDP
1.78
T.94
2.34
3.54
0.99
-1.10
0.01
1.33
0.95
1.42
Westem Europe
Westem Offhoots
Japan
Asia (exduding Japan)
"Lain America
Eastem Europe & former USSR
Africa
World
0.13
• 0.00
4.08
0.15
0.34
132
1.81
0.76
1.55
0.89
8.05
2.92
2.52
1.48
0.38
1.81
• 1.15
0.64
1.30.
0.03
0.09
0.19
0.05
0.00
0.15
-0.11
-0.02
0.01
0.04
-0.01
0.05
0.10
0.64
0.12
0.53
1.42
1.50.
3.49
2.07
2.93
0.10
0.01
0.05
1.02
0.91
Populabon
0.32
1.02
0.70
(155
1.15
2.19
Westem Europe
Westem Offshoots
Japan
Asia (excluding Japan)
Latin America
Eastem Europe & former USSR
Africa
World
0.16.
0.07
0.14.
0.09
0.09
0.16.
0.26
0.43
0.22
0.29
0.06
0.69
2.87
0.21
0.15
1.27
0.77
2.07
0.95
0.55
1.64
1.21
0.75
0.42
1.25
1.31
0.61
1.86
2.01
0.54
2.73
1.66
0.92
1.97
2.73
• 0.34
1.65
- 0.93
131
2.33
1.92
0.34
.0.87
0.15
0.27
0.40
0.40
0.07
0.10
0.80
GDP/
1.65
4.33
0.41
2.11
2.98
2.97
5.46
.3.02
-0.56
2.74
3.01
2.10
Westem Europe
Western Offshoots
- Japan
Asia (excluding Japan)
- Latin America
Eastern Europe & former USSR
Africa
World
4.81
4.03
9.29.
5.18
5.33
4.84
4.45
0.30
0.07
0.18
0.41
1.19
0.78
*0.31
3.92
281
2,21 .
0.90
3.43
1.84
2.69
1.85
2.44
0.13
0.09
0.20
0.06
0.15
0.29
0.21
0.44
0.16
0.32
0.03
1.37
0.94
3,48
2.37
1.40
2.11
1.52
0.52
0,93
4.91
Source
Appendices A and B. .
Table 3-1b. Levels of Per Capita GDP and Interregional Spreads, 1000-1998
1990 international dollar).
· 1000
--1500
1820 -
1870
1913
1950
1973
1998
1 232
1 201
669
575
3 473
5 257 .
1387
640
1511
1 501
• 585
1510
1 974
2 431
737
11 534
16 172
(Western Europe
Western Offshoots
Japan
Asia (exduding Japan).
Latin America
Eastem Europe & former USSR
Africa
World
Interregional Spreads
400
400
425
450
400
400
416
435
1.1:1
774
400
500
572
416
483
400
565
2:1
4 594
9 288
1 926
635
2 554
2 601
17 921
26 146
20 413
2 936
5 795
4 354
1 368
-5 709
19:1
11 439
1 231
4 531
543
665
667
418
667
3:1
698
917
5.729
1 365
444
867
5:1
852
2114
4 104
13:1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider two distinct countries, denoted as A and B. Initially, Country A had a per capita GDP of $10,000 and experienced a growth rate of 10%, while Country B had a per capita GDP of $40,000 and experienced a growth rate of 2%. Assuming that the growth rates remain unchanged, which country will have a higher per capita GDP when t = 35 time periods (years)? O Country B O Country A O All of these choices are correct. They are the samearrow_forwardSmall differences in the rate of economic growth can lead to large differences in living standards. Consider two countries: Fritolaysia and Khandibar. Currently, real GDP per person (average income) is $60,000 in Fritolaysia and $20,000 in Khandibar. Suppose you want to project what the real GDP per person will be in each country 100 years from now. The following formula shows how to compute the average income in n years, where g represents the growth rate of real GDP per person (in decimal form-that is, 1.5% is entered as 0.015): Average Income in n Years Current Average Income x (1 + g)" Use the growth formula to find the correct amounts to select to fill in the following table. Growth Rate Average Income after 100 Years (Percent) (Dollars) 1.5 1.7 4 4.2 1 1.5% 1.7% Suppose Fritolaysia is expected to grow at 1.7% for the next 100 years. Which of the following growth rates in Khandibar would cause the average income in Khandibar to exceed the average income in Fritolaysia in 100…arrow_forwardGraphically illustrate the changes over time in the table using the Lewis Model. Note that this means one assumption from the table will not be able to hold true in this model of economic development. Point out the difference on your graph.arrow_forward
- Suppose a country has a real GDP per capita of $68,000 and grows at a constant rate for the next 36 years. How much larger (in percentage terms) is this country if its growth rate is 4.33% instead of 3.13% after 36 years of growth? Answer this as a percentage and round your answer to two digits after the decimal without the percentage sign. ex. If you found the rate to be 5.125%, answer 5.13.arrow_forwardEconomic growth theories have discussed growth factors from various perspectives. Critically discuss the similarities and differences in growth factors based on Adam Smith's, David Ricardo's, and Harrod-Domar's theories.arrow_forwardConsider a numerical example using the Solow Growth Model, for 2 countries. Country A: d=0.1, s=0.3, n=0.01, z=1, F(K,L)=K0.3n0.7 Country B: d=0.1, s=0.2, n=0.01, z=1.5, F(K,L)=K0.4N0.6 Which Country has a higher level of GDP per capita in steady state? O Country A O Country B Not enough informationarrow_forward
- The table below shows real GDP, population, and real GDP per capita for the hypothetical economy of Highlands. Real GDP and Population over Time Population (thousands of people) 224 228 237 Year 1 2 Real GDP (millions of dollars) $5,847 6,666 7,541 Instructions: Round your answers to one decimal place. a. Using the information in the table, calculate the growth rates in real GDP, population, and the standard of living (real GDP per capita) between year 1 and year 2. Real GDP: Population: Standard of living: b. Now, using the information in the table, calculate the growth rates in real GDP, population, and the standard of living between year 2 and year 3. Real GDP: % % Real GDP per Capita (dollars) $26,103 29,237 31,819 % % Population: Standard of living: c. The standard of living in the economy of Highlands between year 1 and year 2 grew (Click to select) the standard of living between year 2 and year 3. %arrow_forward> Consider the data in the table below: Per capita GDP, 2017 Saving rate (%) TFP (Ā) United States 1.000 23.5 1.000 Switzerland 1.151 28.8 1.052 Answer the following questions using the Solow growth model. 9. Assuming no differences in TFP (ignore the last column) and no differences in the rate of depreciation between the U.S. and Switzerland, use the data in the table to predict the ratio of per capita GDP of Switzerland relative to that of the U.S. in the steady states. How much percent richer is Switzerland than the U.S. in steady state? 10. Now do the same exercise assuming TFP is given by the levels in the last column. Now how much percent richer is Switzerland than the U.S. in steady state? Consider the data in the table below: Per сapita GDP, 2017arrow_forwardConsider the following numerical examples for the Solow Growth Model: Economy A z=1 s=0.5 F(K,N)=K0.3N0.7 n=0.01 d=0.1 Economy B z=1 s=0.2 F(K,N)=K0.3N0.7 n=0.01 d=0.1 In which economy is GDP per capita higher in steady state? O Economy A O Economy B O Not enough Informationarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education