
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
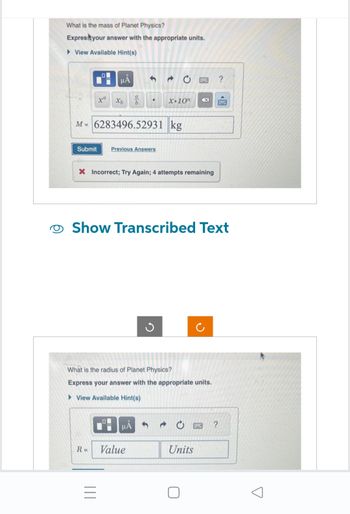
Transcribed Image Text:What is the mass of Planet Physics?
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
View Available Hint(s)
xa
μÅ
Xb
a
b
M=6283496.52931 kg
Submit Previous Answers
|||
●
X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining
HÅ
R= Value
X.10n
Show Transcribed Text
G
What is the radius of Planet Physics?
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
View Available Hint(s)
S
Units
0
C
?
?

Transcribed Image Text:While visiting Planet Physics, you toss a rock
straight up at 15 m/s and catch it 2.4 s later. While
you visit the surface, your cruise ship orbits at an
altitude equal to the planet's radius every 210 min.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A runner taking part in the 200 m dash must run around the end of a track that has a circular arc with a radius of curvature of 40 m. The runner starts the race at a constant speed. If she completes the 200 m dash in 22.2 s and runs at constant speed throughout the race, what is the magnitude of her centripetal acceleration (in m/s2) as she runs the curved portion of the track? m/s?arrow_forwardChapter 21 and 22, Problem 2arrow_forwardA planet orbiting a distant star has radius 3.54×106 m. The escape speed for an object launched from this planet's surface is 7.15×103 m/s. What is the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the planet?arrow_forward
- A planet travels in a circular orbit around a star. The radius of the circular orbit is 3.01×1011 m and the orbital period is 4.27 years. What is the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration of the planet, in m/s2?arrow_forwardA piece of space debris is travelling in an elliptical orbit around a planet. At its closest point to the planet, the debris is travelling at 5000ms. When the debris is 10000km from the planet, it travels at 5000kmhr. How close does the debris get to the planet in its orbit?arrow_forwardThe Sun orbits the center of the Milky Way galaxy once each 2.60 × 108 years, with a roughly circular orbit averaging 3.00 × 104 light years in radius. (A light year is the distance traveled by light in 1 y.) a) Calculate the centripetal acceleration of the Sun in its galactic orbit in m/s2. b) Calculate the average speed of the Sun in its galactic orbit in m/s.arrow_forward
- A race car goes around a level, circular track with a diameter of 1.00 km at a constant speed of 100 km/h. What is the car's centripetal acceleration in m/s2?arrow_forwardYou are watching a TV news program when they switch to some scenes taken aboard the space shuttle which circles 500 miles above the Earth once every 95 minutes. To allow the audience to appreciate the distances involved, the announcer tells you that the radius of the Earth is about 4000 miles and the distance from the Earth to the Moon is about 250,000 miles. When an astronaut drops her pen it floats in front of her face. You immediately wonder how the acceleration of the dropped pen compares to the acceleration of a pen that you might drop here on the surface of the Earth.arrow_forwardIf you are sitting at the equator on Earth, what would your average speed be knowing that the radius of the Earth is 6.37 x 106 m? What would your acceleration on Earth be?arrow_forward
- Suppose an object is traveling in a circle of radius 10 m. if the object has a period of 6 s, what is its orbital speed (in m/s)?arrow_forwardThe International Space Station orbits the Earth in a circle with a radius of approximately 6688185 m (which is only a few hundred miles above Earth's surface). At that distance, the acceleration due to gravity is only 8.87m / (s ^ 2) what is the velocity of the space station in this orbit? Your answer should be in units of m / sarrow_forwardA spy satellite is in circular orbit around Earth. It makes one revolution in 8.90 h. Mass of Earth is 5.974 × 1024 kg, radius of Earth is 6371 km and Gravitational constant G is = 6.674 × 10−11 N·m2/kg2. a. How high above Earth’s surface is the satellite? answer in km b. What is the satellite’s acceleration? answer in m/s^2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON