
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
While doing Histogram Stretching, we established that we go pixel by pixel through whole image and apply Histogram Stretching Formula for each pixel. So, for example in the following image, if there are 100 pixels, we would do Histogram Stretching Formula 100 times. Do you think we could do Histogram Stretching for whole image and calculate this formula fewer times ? If no why ? If yes, how ?
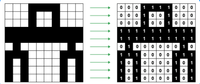
Transcribed Image Text:000 1 1 1
000 1
1000
1000
0 1
1 000
1 1 1 1
1 1
1 1 1 1
1 11 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
i1
o 1
0 00000 10
1 1 10000 1 1 1
10 100 0 0 10 1
10 100 0 0 10 1
000
1 0
1
1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Show how an approximation to the first derivative of an image can be obtained by convolving the image with the kernel [1 −1] where the image is defined as [56 64 79 98 115 126 132 133]. Ignore computing a value for the first and last image pixels (in other words, your result will be 6 values). In addition to showing the result of the convolution, indicate where edges would be detected and why.arrow_forward... A centered dataset with n = 116 observations and p = 9 variables was analysed to reduce its dimensionality. The following is a list of singular eigenvalues of X in decreasing order, that is d₁, d2, . . . , dg: 399.1338, 192.1412, 173.0043, 161.6635, 158.0541, 146.6826, 140.0039, 134.1633, 121.1941. A) Compute and write the numerical value of the eigenvalue 4 of Σ. This eigenvalue is located in the position (4, 4) of the matrix A and is simultaneously the sample variance of the score PC4: B) Compute and write the percentage of total variability explained by the Principal component PC4. The number you write should be between 0 and 100 and you should include decimals in your answer. C) A threshold of total variability explained has been set at 80%. How many principal components must you select? Write your answer (integer value).arrow_forwardPick one million sets of 12 uniform random numbers between 0 and 1. Sum up the 12 numbers in each set. Make a histogram with these one million sums, picking some reasonable binning. You will find that the mean is (obviously?) 12 times 0.5 = 6. Perhaps more surprising, you will find that the distribution of these sums looks very much Gaussian (a "Bell Curve"). This is an example of the "Central Limit Theorem", which says that the distribution of the sum of many random variables approaches the Gaussian distribution even when the individual variables are not gaussianly distributed. mean Superimpose on the histogram an appropriately normalized Gaussian distribution of 6 and standard deviation o = 1. (Look at the solutions from the week 5 discussion session for some help, if you need it). You will find that this Gaussian works pretty well. Not for credit but for thinking: why o = 1 in this case? (An explanation will come once the solutions are posted).arrow_forward
- Trace the Perceptron algorithm for the following input. Suppose the actual labels are with respect to a line passing through the origin with normal vector w* = (-1, 1); for example, the true label of (1,0) is '-1' and that of (0,1) is '+1'. The points are ₁ = (0, -1), x2 = (-1,0), x3 = (2,0), x4 = (√√2,1), x5 = (-3,-2). You need to follow the same assumptions as in the example in Slide 6 of Module 10. Show your work and specify the number of mistakes by the algorithm. x5: (-3,-2) 24=(√2,1) 22: (-1,0) xy: (2,0) (0,-1)arrow_forwardPlease solve it , theoretical part of digital image processing course ; - If you have the following image, apply region growing from the shaded seed point using 8-connectivity and a predicate of “the absolute difference is less than or equal 25”.arrow_forwardUsing Matlab, plot the following ultrasound pressure wave as a function of x for t =1 P(t, x) = Poe** cos(@t – kx) where a = 0.15 neper/m, where neper is a dimensionless quantity, k = 1 rad/cm, o = 1 rad/s, and Po = 15 N/m2. Submit your ".m" file as well as the resulting graph labeled appropriately.arrow_forward
- Write the code in matlab.arrow_forwardWorking with Matlab. I need to assign the points P=(4,3,0) and Q=(6,1,2) and the vector n=5i+8j-3k, and find the distance between Q and the plane containing P with normal vector n. I'm lost tho on what formula I need or how to input it.arrow_forwardRecall that the dot product of two vectors (1d matrices) produces a scalar value. The dot product is slightly confusing as the scalar value produced can have an arbitrary meaning that simply represents the mathematical operations of multiplying and summing. In other words, the dot product can simply represent the linear projection of vector onto the number line. This interpretation will be used repeatedly throughout machine learning as our main goal will be to take some features dotted with some weights/parameters. Once again, this can be though of as projecting our features onto a number line where the projection acts as our prediction! Keep this idea in mind as it might not make complete sense as of yet. It also important to know that the dot product can additionally take on other meanings such as a geometric meaning which represents how similar any two vectors are when projected onto one another. Meaning, how much one vector points in the direction of another. Given the following…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education