
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Which particle will conplete this reaction
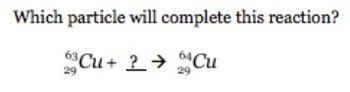
Transcribed Image Text:Which particle will complete this reaction?
Cu+ ? → Cu
29
29
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- write the solubility product equilibrium and the solubility product constant expression for beryllium fluoride?arrow_forwardThis chemical equation represents a reaction: 2 ICL (g) L (g) + 3 Cl (g) Suppose a closed flask contains only gaseous ICI,, and the concentration of ICl, is 0.10 M. How will these initial conditions affect the progress of the reaction? The concentration of the reactant will decrease, and the concentrations of the products will increase, until the concentration of each product equals 0.10 M. O The concentrations of the reactant and the products will increase until the concentration of each product equals 0.10 M. The concentration of the reactant will decrease, and the concentrations of the products will increase, until the rate of the forward reaction equais the rate of the reverse reaction. The concentrations of the reactant and the products will increase until the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reactionarrow_forwardHydrogen peroxide decomposes as shown below: 2 H2O2 → 2 H2O + O2 molar mass H2O2 = (34.0 g/mol) A sample of hydrogen peroxide solution was analyzed using the procedure from the “Enzymatic Decomposition and Analysis of Hydrogen Peroxide” experiment. A 7.54 g sample of the solution generated 0.0277 mol of oxygen gas. Calculate the mass percent of H2O2 in the solution.arrow_forward
- Page < Chem 105: Chapters 17 and 16 Homework Name: Write the equilibrium expression for each of the following reactions. a. 203(g)=30₂(g) wwarrow_forwardDo reactants that collide always react together?arrow_forward1:24 PM Sun Feb 5 ****** ******* **** Tap here or pull up for additional resources Question 15 of 31 How long will it take for the concentration of A to decrease from 0.910 M to 0.673 for the reaction A → Products? (k = 0.153 M/s)arrow_forward
- topic: molecular collision reactions A student reacts ground chalk, CaCO3(s), with HCl(aq) in an open beaker at room temperature. Explain, using collision theory, what happens to the rate of the reaction as the reaction proceeds to completion.arrow_forwardHow do I calculate k when [X]= .42 M and the rate of reaction is .0030 M/s. I can't remember exactly how to do this type of problem. Thank you for the help !arrow_forward0.0784 moles of substance A is dissolved in water to make a 2.00 L solution. Then, substance B is added, without changing the volume of the solution, and the following reaction takes place: 2A (aq) + 3B (aq) →2C (aq) During the course of the reaction, concentration of A is monitored. After 100 seconds into the reaction, it was found that 0.0570 moles of A is remaining. Calculate the rate of disappearance of A in the first 100 seconds of the reaction. Hint: Since rate is defined as the change in molar concentration (mol/L) over time, start by calculating molarity of A in the beginning of the reaction, and 100 seconds after. rate = A [A] At O 3.92x104 M.s1 O 2.14x104 MS1 O 1.07x10 M.s1 O 5.34x10 Msarrow_forward
- Scenario Consider the reaction A2+ B₂ = 2AB. If the initial concentration of both A₂ and B2 is 4.0 M, and after 10 minutes the reaction appears to stop. The concentration of [A₂] is now 2.0Marrow_forwardNitrosyl bromide decomposes according to the following equation. 2NOBR (g) 2NO (g) + Br2 (g) Asample of NOBR (0.64 mol) was placed in a 1.00-L flask containing no NO or Br2. At equilibrlum the flask contained 0.36 mol of NOB. How many moles of NO and Br2, respectively, are in the flask at equilibrium?arrow_forwardConsider the quilibrium reaction between X and Y, as shown below: X=Y AG The reaction is started with 10 mmol of X; no Y is initially present. After 48 hours, analysis reveals the presence of 10 mmol of X and 0 mmol of Y. Which is the most likely explanation? = −1 - 45 kJ mol X and Y have reached equilibrium concentrations. An enzyme has shifted the equilibrium toward X. Formation of Y is kinetically slow; equilibrium has not been reached by 48 hours. Formation of Y is thermodynamically unfavorable. Two of the above explanations are reasonable.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY