
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
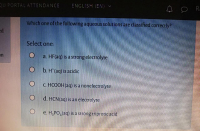
Transcribed Image Text:Which öne of the following aqueous solutions are classified correctly?
Select one:
a. HF(aq) is a strong electrolyte
b. H (aq) is acidic
C. HCOOH(aq) is a nonelectrolyte
d. HCN(aq) is an electrolyte
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 8. A student adds 22.36 mL of 1.366 x 10¹ M Mg(OH), in order to completely neutralize 25.00 mL of H₂PO acid. Calculate the original concentration of the acid solution.arrow_forwardThe dilution equation, rearranged to solve for ?1 is ?1=?2?2?1 where ?1 and ?1 are the initial concentration and volume, respectively, and ?2 and ?2 represent the final concentration and volume, respectively. A student needs to prepare 50.0 mL of 1.10 M aqueous H2O2 solution from 4.8 M H2O2 stock solution. Set up an equation to solve for the volume of stock solution needed by plugging the given values into the equation.arrow_forwardsentences. 3. Virtual Lab Questions a. A student prepares a solution of hydrochloric acid that is approximately 0.1 M and wishes to determine its exact concentration. A 25.00 mL portion of the HCI solution is transferred to a flask, and after a few drops of indicator are added, the HCI solution is titrated with 0.07575 M NaOH solution. The titration requires exactly 38.92 mL of the standard NaOH solution to reach the end point. What is the molarity of the HCI solution? b. It takes 46.22 mL of a 1.021 M NaOH solution to neutralize a solution of 4.4567 g of an unknown monoprotic acid in 80.00 mL of water. Calculate the molecular weight of the acid. 4(D) 5arrow_forward
- Determine whether each compound is soluble or insoluble. Forthe soluble compounds, list the ions present in solution.a. AgI b. Cu3(PO4)2 c. CoCO3 d. K3PO4arrow_forwardSuppose 31.0 mL of 0.510 M CoCl2 solution is added to 72.0 mL of 0.180 M NiCl2 solution. Calculate the concentration, in moles per liter, of each of the ions present after mixing. Assume that the volumes are additive. Concentration of Co2+ = mol/L Concentration of Ni2+= mol/L Concentration of Cl- = mol/Larrow_forwardWhich set of reactants forms a solid precipitate when mixed? O NANO3(aq) and KCI(aq) O Na2CO3(aq) and KOH(aq) O Na2CO3(aq) and CuCl2(aq) O CuCl2(aq) and NaC2H3O2(aq)arrow_forward
- 4. When a solutions of aluminum sulfate and potassium hydroxide are mixed, a precipitate forms. a. Write a balanced net ionic equation for the reaction. b. Calculate the mass of the precipitate when 3.89 g of aluminum sulfate in 100mL of solution is combined with 50 mL of the o.300 M KOH. c. What is the molarity of the ion in excess? (Ignore the spectator ions and assume that volumes are additive)arrow_forwardWhat volume of a 0.325 M hydrochloric acidsolution is required to neutralize 25.4 mL of a 0.192 M potassium hydroxide solution?mL hydrochloric acidarrow_forwardWhich of the following mixtures will result in a precipitate? O A. NH4CO3(aq) + KCl(aq). O B. CaBr2(aq) + NaOH(aq) O C. Sr(C2H3O2)2(aq) + NaNO3(aq) O D. Cal2(aq) + AgNO3(aq)arrow_forward
- Use the rules (in order) to assign oxidation numbers to each of the elements in the compounds below. copper hydroxide H Cu Cu(OH)2 sulfate ion S so,?- cadmium hydroxide Cd Cd(OH)2arrow_forward3. In order to perform a chemical reaction, 225 mL of 0.500 M lead (II) nitrate is required. How much 5.00 M stock solution is required to make the proper solution? mL 4. How much water needs to be added to an 18.0 M stock solution of sodium hydroxide in order to make 450.0 mL of 0.250 M sodium hydroxide solution? mL of waterarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY