
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
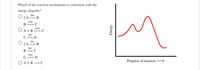
Transcribed Image Text:Which of the reaction mechanisms is consistent with the
energy diagram?
fast
2 A → B
slow
В
slow
A + B
fast
С — D
fast
2 A
fast
В
slow
D
O A + B → C
Progress of reaction
Energy
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the single step reaction: A + B -> 2C + 25 kJ If the activation energy for this reaction is 35.8 kJ, sketch an energy vs. reaction co - ordinate diagram for this reaction. Be sure to label the following on your diagram: each of the axes, reactant compounds and product compounds, enthalpy of reaction, activation energy of the forward reaction with the correct value, activation energy the backwards reaction with the correct value and the transition state. On the same sketch you drew, after the addition of a homogeneous catalyst, show how it would change the graph. Label any new line "catalyst" and label any new activation energy. Please actually draw the diagram, don't just explain how to draw it.arrow_forwardConsider the following reaction mechanism. Step 1 : W2 ⇌ 2W (fast) Step 2 : W + Z ⇌ D + F (fast) Step 3 : W + F → M (slow)Write the overall reaction.arrow_forwardIn what direction will implementing CO(g) +NO(g) - CO2(g) + NO(g) affect the rate of the reaction, decreasing the pressure of NO, from 0.50 atm to 0.250 atm?arrow_forward
- A gaseous reaction occurs by a two-step mechanism, shown below. Step 1: AX +Y2 ⇌ AXY2 fast and reversible Step 2: AXY2 + AX → 2 AXY slow Including concentration of only reactants and products, what is the rate law for this reaction?arrow_forward10. Which of the following reactions features the greatest kí/kĎ? kí is the reaction rate constant when all the hydrogen atoms in the organic reactant are 'H while kp is the reaction rate constant with all the hydrogen atoms in the organic reactant replaced by D (²H). OH OH to __ОН OH CI OH H₂SO4 heat HCI heat HCI heat Nal H₂SO4 heat CI CIarrow_forwardWe don't see the answer written with a photo or pen, give the answer using the toolarrow_forward
- At 20°C the rate of a reaction 2 H₂O₂ à 2 H₂O + O₂ is 3.0 x 10¹ M/s. What is a good estimate for the rate of this reaction at 30°C? O 9.0 x 10-2 M/s O 1.5 x 101 M/s 3.0 x 101 M/s O 5.5 x 101 M/s 6.0 x 10¹ M/sarrow_forwardA reversible reaction that occurs in a single step has AH= -26.2 kJ/mol and Ea = 25.2 kJ/mol. What is the activation energy of the reverse reaction? kJ/molarrow_forwardThe rate of a reaction is increased with the addition of a catalyst as shown in the following diagram: Praducts Reactants Reaction Coordinate Energyarrow_forward
- ⦁ 2. Explain, in terms of collision theory, why increasing the pressure on the following reaction will probably have very little effect on the reaction rate: 2Al(s)+Fe2O3(s)→2Fe(s)+Al2gO3(s)arrow_forwardConsider the following reaction and its associated rate law. A + B ----> C R = k[A]2 Which of the following will not increase the rate of the reaction? Group of answer choices adding a suitable catalyst. increasing the temperature of the reaction. increasing the concentration of reactant B. increasing the concentration of reactant A.arrow_forwardConsider the following reaction mechanism. Step 1 : W2 ⇌ 2W (fast) Step 2 : W + Z ⇌ D + F (fast) Step 3 : W + F → M (slow)What are the intermediates?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY