
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
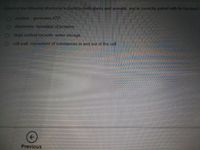
Transcribed Image Text:Which of the following structures is found in both plants and animals, and is correctly paired with its function?
nucleus- generates ATP
ribosomes- formation of proteins
large central vacuole-water storage
O cell wall- movement of substances in and out of the cell
Previous
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Cells are the smallest structural and functional unit of life. It is commonly called the building block of life. Every living thing is made up of cells. Plant cells and animals cells are similar and also different in their own ways.
Plant cells and animal cells both belong to the eukaryotic category.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following is not a cellular activity associated with microtubules? maintenance of axons mititotic spindle cilial structure cell shape orientation of cellulose microfibrils All of the following are roles of microfilaments except cell migration. muscle cell contraction. mitotic spindle formation. cytoplasmic streaming. amoeboid movement.arrow_forwardter Organelle found in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Organelle A Organelle found in animal and plant cells. Does not contain inner membranes arranged into thylakoids or cristae. Largest organelle in a eukaryotic cell. Contains DNA, RNA and enzymes. Organelle C 0101010 J K L M Organelle found in eukaryotic cells only Which one of the combinations in the table below correctly identifies organelles A, B, C and D? Organelle A Mitochondria Ribosome Mitochondria Ribosome Organelle B Ribosome Nucleus Chloroplast Chloroplast Organelle found in plant cells. Contains inner membranes arranged into flattened discs called thylakoids. Organelle B Smaller organelle, numerous the cell, has a double membrane with the inner membrane folded into cristae. Organelle D Organelle C Chloroplast Chloroplast Nucleus Nucleus Organelle D Nucleus Mitochondria Ribosome Mitochondriaarrow_forwardWhat is NOT an example of microfilament-based structures in a cell? Stress fibres Filopodia Cilia O Lamellipodium at the leading edge O Microvilliarrow_forward
- What is the structure and role of each organelle: lysosome, vacuole, mitochondria, membrane, ribosome, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, nucleus, plastidarrow_forwardMatch the cell organelle with its function. Put responses in the correct input to answer the question. Select a response, navigate to the desired input and insert the response. Responses can be selected and inserted using the space bar, enter key, left mouse button or touchpad. Responses can also be moved by dragging with a mouse. Cell membrane Cell wall Nucleus Cytoplasm Mitochondria Chloroplast Vacuole Storage Control center Shape and protection in plant cell Liquid that fills cell Powerhouse of the cell Location of photosynthesis Controls what goes in and out of the cellarrow_forwardTreating cells with a drug that breaks apart tubulin dimers would disrupt all of the following EXCEPT movement of vesicles toward the cell membrane movement using cilia movement using bacteria flagella movement of vesicles toward the centrosomearrow_forward
- Which of the following are a part of the cell theory? All of the other answers Cells can arise only by division of preexisting cells Cells contain genetic information The cell is the structural unit of life All organisms are composed of one or more cellarrow_forwardTissue boundaries are established based on the types of present of the cell membrané. fibronectin lipids integrin D) cadherin E glycolipidarrow_forwardWhich of the statements regarding plasmodesmata is true? They are channels, located in the plasma membrane of plant cells and made of transmembrane proteins, that allow ions and small molecules to pass between adjacent cells. O They are holes in the cell wall through which the plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum of adjacent cells are connected. They are channels, located in the plasma membrane of animal cells and made of transmembrane proteins, that allow ions and small molecules to pass between adjacent cells. They provide points of structural support between adjacent plant cells. They provide points of structural support between adjacent animal cells.arrow_forward
- In vertebrates, which cell-cell junction allows for direct chemical communication between adjacent cell cytoplasms, without contact with the extracellular fluid, and is composed of the transmembrane protein connexin? O Desmosome O Gap junctions O Adherens junctions O Tight junctions O Focal adhesionsarrow_forwardName the organelles on images. Then identify if they are found in Prokaryotes/Eukaryotes/Both, and lastly if they are found in plant/animal/both types of cells. Organelle Function Gives shape and support, helps plant stand upright, made of cellulose Controls what enters and exits the cell Directs activities of the cell Produces energy for the cell by cellular respiration Transports cellular materials can be rough or smooth Structure Chad Type of Cell Prokaryo... Prokaryo... Prokaryo... Prokaryo... Prokaryo... Found In Plants Plants Plants Plants Plantsarrow_forwardWhich of the following is not true for eukaryotic cells? None of these Cell wall contains peptidoglycan as one of the major components Chromosome contain histone Nucleus is bounded by nuclear membranearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education