
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
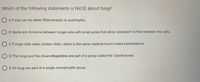
Transcribed Image Text:Which of the following statements is FALSE about fungi?
O A Fungi can be either heterotrophic or autotrophic.
O B Septa are divisions between fungal cells with small pores that allow cytoplasm to flow between the cells.
O C Fungal cells walls contain chitin, which is the same material found insect exoskeletons.
D The fungi and the choanoflagellates are part of a group called the Opisthokonts.
O E All fungi are part of a single monophyletic group.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which answer below best describes a characteristic in fungi but NOT plants? O multicellular eukaryotic cells mycelium O sporesarrow_forwardLooking at this sample of a fungus, to what main group would it belong to? The first pic is the fungus as it is seen growing on these wet walls. The second pic shows the reproductive structures. O Zygomycota Basidiomycetes O Ascomycetes O Microsporidia Pic two Pic onearrow_forwardRhizopus (bread mold) reproduces both sexually and asexually. Rhizopus' sexual reproductive structure is called? Conidia The zygosporagium The ascusarrow_forward
- Lichens are said to be composite organisms made up of two very different types of organisms: usually a fungus and an alga (or in a few lichens, a fungus and a Cyanobacterium). (Alga is the singular of algae.) How do these two types of organisms work together to become a functional composite organism? That is, what does each organism provides to the relationship to make it successful? Think about a lichen living on the face of a rock.arrow_forwardFungi are [Select ] 7. They predominately feed on [Select] [ Select * by [ Select ] enzymes and then [Select] * the organic molecules that are produced. The * aids in this process. v [ Select ] sporangia surface to volume ratio of their [Select ] low autotrophs high saprobes dead matter Ne secreting hyphae absorbingarrow_forwardPhylum Zygomycota: the molds Phylum Glomeromycota: the mycorrhizal fungus Phylum : the club fungus Phylum Ascomycota: the sac fungusarrow_forward
- Which of these is a reproductive structure found in fungi? eggs fungal spoores gametes cystsarrow_forwardFungi and animals are both part of a group called Opisthokonta. The vast majority of fungi are multicellular. However, their sister taxon consists of unicellular species. Animals also are multicellular and their closest relatives are again unicellular. Briefly describe the two hypotheses that could explain the origin of multicellularity in the Opisthokonta, and then explain which of the two is the more likely hypothesisarrow_forwardWhat traits do fungal cells share with the some bacterial cells? (Choose all that apply) the ability to secrete enzymes that break down food sources Othe ability to take up nutrients from the environment the presence of mitochondria to provide energy for the cells the ability to utilize carbohydrates and oxygen to produce ATP A cell wall that prevents lysis in hyp0tonic conditionsarrow_forward
- 1. What is an important function of fungi 2. Why is bacteria placed in a kingdom by themselvesarrow_forwardHow can fungi be defined? What is the difference between a yeast and a mold?arrow_forwardThe hyphae of fungi provide these advantages (select all that apply). O Provide large surface area to volume ratio Allow for better searching to find food The mycelium is not sensitive to dry conditions They can withstand cold and hot temperatures in certain species The mycelium can be as large as 3.4 miles in one individual O Oarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education