
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
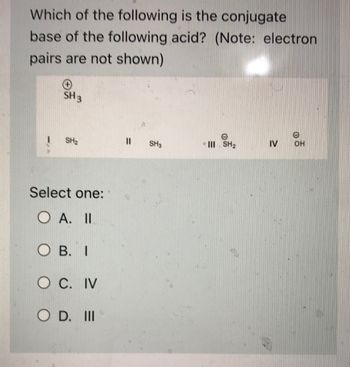
Transcribed Image Text:**Question:**
Which of the following is the conjugate base of the following acid? (Note: electron pairs are not shown)
**Chemical Structures:**
- Acid: \( \text{SH}_3^+ \)
**Options:**
- I. \( \text{SH}_2 \)
- II. \( \text{SH}_3 \)
- III. \( \text{SH}_2^- \)
- IV. \( \text{OH}^- \)
**Select one:**
- A. II
- B. I
- C. IV
- D. III
**Explanation:**
To determine the conjugate base of an acid, one hydrogen ion (H⁺) should be removed. Considering the acid \( \text{SH}_3^+ \), removal of \( \text{H}^+ \) results in the neutral \( \text{SH}_2 \) (Option III).
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Conjugate base is formed when a protone is removed from a acid.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 29 The pH of an aqueous solution at 25°℃ WAS found to be 7.30. S S The hydrodium ion concentration is The hydroxide ion concentration is in stan M. m.arrow_forward1. Calculate the hydronium ion concentration in an aqueous solution that has a hydroxide ion concentration of 7.24 x 10-4 M.arrow_forwardA solution is prepared by adding 0.10 mol of iron(III) nitrate, Fe(NO3)3, to 1.00 L of water. Which statement about the solution is correct? A. The solution is basic. B. The solution is neutral. C. The solution is acidic. D. The value of Ka for the species in solution must be known before a prediction can be made. E. The value of Kb for the species in solution must be known before a prediction can be made.arrow_forward
- Nicole and Patrick test the pH of four common kitchen substances and record the pH values in the table below. pH OF KITCHEN SUBSTANCES Substance pH Value Q 5 S 12 Which statement best compares Substance I to the other tested substances? A.O Substance T has the greatest concentration of H* ions. В. Substance T has the lowest H3O+ concentration in solution. C. Substance dissolves the fewest compounds. D.O Substance T contributes the most protons to water.arrow_forwarda. A solution of HNO3 has a pH of 3.69. What is the molarity of the solution? Molarity |M b. A solution of HNO3 has a pH of 4.34. What is the molarity of the solution? Molarity M c. A solution of HNO3 has a pH of 2.22. What is the molarity of the solution? Molarity Marrow_forwardWater (H,O) acts as a Brønsted-Lowry base in which of the following equilibrium reactions? I. HCO, + H,O= H,CO, + OH- II. HSO, + H,O*= H,0 + H,SO, III. NH, + H,O = H,O* + NH3 I a. I only b. Il only C. Il and III d. I and IIIIarrow_forward
- 46 plzarrow_forward3. Which of the following should produce the lowest pH when dissoived in water (assuming equal concentrations dissolved)? A. HCIO B. LIOH C. HC;H,O, D. HОCNarrow_forwardWhich aqueous solution has the highest pH? О 0.55 М Ba(ОН)2 O 1.0 M HCN О 1.4 МСН3СОН O 1.2 M NaHSO4arrow_forward
- For the reaction: HPO, (aq) + H,O (€) = H¿PO, (aq) + OH" (aq) Use figure 16.4 to predict if equilibrium lies to the left or to the right. If the pOH is 10.5 calculate the [OH] and [H;O*]arrow_forwardWhat are the major species present in 0.250 M solutions of each of the following acids? Calculate the pH of each of these solutions.a. HOC6 H5b. HCNarrow_forwarda. A solution of HINO, has a pH of 3.57. What is the molarity of the solution? Molarity = M b. A solution of HNO3 has a pH of 4.11. What is the molarity of the solution? Molarity = M c. A solution of HNO3 has a pH of 1.83. What is the molarity of the solution? Molarity Marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY