
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
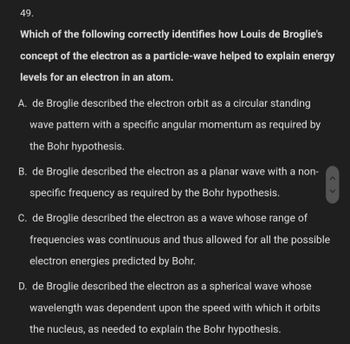
Transcribed Image Text:49.
Which of the following correctly identifies how Louis de Broglie's
concept of the electron as a particle-wave helped to explain energy
levels for an electron in an atom.
A. de Broglie described the electron orbit as a circular standing
wave pattern with a specific angular momentum as required by
the Bohr hypothesis.
B. de Broglie described the electron as a planar wave with a non-
specific frequency as required by the Bohr hypothesis.
<>
C. de Broglie described the electron as a wave whose range of
frequencies was continuous and thus allowed for all the possible
electron energies predicted by Bohr.
D. de Broglie described the electron as a spherical wave whose
wavelength was dependent upon the speed with which it orbits
the nucleus, as needed to explain the Bohr hypothesis.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- HELP!! Use this to guide you- A model of the atom which explained the atomic emission spectrum of hydrogen was proposed by Neils Bohr. Bohr suggested that an atomic spectrum is created when the electrons in an atom move between energy levels. In Bohr’s model, electrons exist in orbits around the nucleus which only exist at fixed distances from the nucleus called energy levels. According to the Bohr model electrons can orbit at many fixed distances from the nucleus. Bohr proposed electrons orbit at fixed distances from the nucleus in stationary states, such as the ground state or excited state to explain why they did not radiate energy while orbiting the nucleus.arrow_forwardDiscussion Questions 1. How well does the Bohr equation predict the line spectrum of hydrogen? 2. Which transition in table 3 emits the highest energy photon? 3. Which transition in table 3 emits the lowest energy photon? 4. Which transition in table 3 emits the highest energy photon in the visible region? 5. Which transition in table 3 emits the lowest energy photon in the visible region?arrow_forwardWhat aspect of the Bohr model is correct? (i.e. agrees with the quantum mechanical model) a. electrons have set energy levels that depend on distance from the nucleus b. energy levels are equally spaced in an atom c. the position and energy of an electron can be precisely determined simultaneously d. electrons move in circular orbits around the nucleusarrow_forward
- Which of the following should have the lowest overall energy? O a. Atin atom with one more electron O b. An iodine atom with one more electron O c. An antimony atom with one more electron O d. Atellurium atom with one more electron O e. A xenon atom with one more electronarrow_forwardIn the Bohr model for the hydrogen atom, which of the following transitions results in the emission of the highest energy photon? A. n=3 → n=4 B. n=4 → n=3 C. n=4 → n=2 D. n=1 → n=3 E. n=1 → n=4arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is incorrect? a. As the energy of a photon increases, its frequency decreases. b. As the wavelength of a photon increases, its frequency decreases. c. None of these statements are incorrect. d.The product of wavelength and frequency of electromagnetic radiation is a constant. e.As the wavelength of a photon increases, its energy decreases.arrow_forward
- Select the correct answer. Why was Niels Bohr's atomic model superior to all the earlier models? OA It proved that the atom was Indivisible and therefore the smallest unit of matter. O B. It showed how the electron could orbit the nucleus without falling Into It. C. It was the first to show that the atom had no net charge. OD. It used wave behavlor to explain the positions of electrons around the nucleus. Reset Nextarrow_forwardof the velocity in (c) to the speed of light? 2. In 1913 Neils Bohr proposed a model for the hydrogen, now known as the Bohr atom, that explained the emission spectrum of the hydrogen atom as well as one-electron ions like Het. The model permits the electron to orbit the nucleus by a set of discrete orbits where each orbit is associated with an integer value n, known as the principal quantum number. Depending upon the orbital occupied by the electron, the energy of the hydrogen atom (or one-electron ions) can only assume the following discrete values 1terd 30 tF aconstant En n2 prineiple 2 S1 where RH 2.18x10-18 J is the Rydberg constant and Z is the number of protons in the nucleus.(a) List the energies of the hydrogen atom for the first three orbits (n-1, 2, and 3).*(b) Compute the energy absorbed by the hydrogen atom when the electron is excited from the lowest orbit (n 1) to the third lowest orbit (n 3). (c) Calculate the frequency v of the photon E = y absorbed by the hydrogen…arrow_forwardWhich rule states that in filling out the electron configuration of an atom, you start with the lowest energy level? A. Hunds Rule B. Aufbau Principle C. Paul Exclusion Principle D. Bohr's Rulearrow_forward
- Which is a true statement regarding the Bohr model of the H atom? O Bohr's model stated the electron has only certain allowed energy states, not a continuous range of values. O Bohr's model did not successfully predict all the lines in the atomic emission spectrum of hydrogen. O Bohr's model correctly explained the movement of the electron about the nucleus. Onone of thesearrow_forwardWhen electrons pass through a sheet of aluminum, a pattern of high and low intensity is observed. What claim does this experimental evidence support? Electrons are particles. Light is a particle. Light is a wave. Electrons are waves.arrow_forward7. Give the Bohr orbit configurations and draw the electron dot symbol for each of the following elements. a. Ne b. Mg C. P d. Se e. Rbarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY