
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
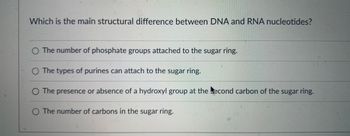
Transcribed Image Text:Which is the main structural difference between DNA and RNA nucleotides?
O The number of phosphate groups attached to the sugar ring.
O The types of purines can attach to the sugar ring.
O The presence or absence of a hydroxyl group at the econd carbon of the sugar ring.
The number of carbons in the sugar ring.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Draw an example of each of the followings: 1- a simple sugar, 2- an acid sugar, 3- an alcohol sugar, 4- a deoxy sugar, 5- a saturated fatty acid, 6- an unsaturated fatty acid, 7- a triglyceride, 8- a phospholipid, 9- a steroid, 10- an amino acid, 11- a small peptide, and lastly 12- a DNA nucleotide and 13- an RNA nucleotidearrow_forwardRNA 1 What nucleic acid is used to transport an amino acid to the site where a protein is being manufactured? Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. DNA b. TRNA MRNA TRNA Unanswered lipids 1 Fats and oils are structurally both triacylglycerols, but fats are solids at room temperature and oils are liquids at room temperature Which statement best describes the reason for their difference in physical state?arrow_forwardPlace each picture in the correct categoryarrow_forward
- What effect do restriction enzymes have on DNA? Select one: Restriction enzymes repair damaged portions of DNA. O Restriction enzymes cleave DNA at specific sequences into fragments. Restriction enzymes give a negative charge to DNA. Restriction enzymes duplicate DNA.arrow_forward"Unlike what happens in DNA replication, where both strands are copied, only one of the two strands is transcribed into mRNA. The DNA strand that contains the gene is sometimes called the sense strand, or coding strand, and the DNA strand that gets transcribed to give RNA is called the antisense strand, or noncoding strand. Because the sense strand and the antisense strand are complementary, and because the DNA antisense strand and the newly formed RNA strand are also complementary, the RNA molecule produced during transcription is a copy of the DNA sense strand... The only difference is that the RNA molecule has a U everywhere the DNA sense strand has a T." Consider the following segment of a DNA sense strand: (5') CAA-ACT-ACG-GCG-TTG-CAG (3') (a) Determine the base sequence in the antisense (non-coding) strand. Be sure to specify which end is 5' and which is 3'. (b) Determine the base sequence in the messenger RNA strand. Be sure to specify which end is 5' and which is 3'.arrow_forwardWhat is this type of molecule? HO Lipid Carbohydrate DNA Protein Ill H H WI H OHarrow_forward
- If 22% of the nucleotides in a sample of DNA contain the base adenine (A), then 22% of the nucleotides in the same sample of DNA contain the base guanine (G). True or False True Falsearrow_forwardSelect all the TRUE statements related to stability of nucleic acids. Single-stranded RNA is stabilized by base pairing that can occur between different segments of the sequence DNA fidelity is critical because DNA structure is maintained long-term in a cell Errors in mRNA sequence can be tolerated because each molecule is used for a short time and then degraded Any mutation in DNA sequence will result in a completely disrupted protein structure Both rRNA and tRNA and more stable than mRNA because they serve structural roles over a longer time frame One each new copy of the DNA genome is produced, the old DNA strands are degradedarrow_forwardDeoxyadenosine monophosphate (dAMP) and guanosine monophosphate (GMP) are nucleotides. The similarities between dAMP and GMP are that they both have? -an alpha (central) carbon.-the same R group.-a phosphate group.-a pentose (5 sided) sugar-an amino group-a nitrogenous base.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY