
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
When the car reaches point A, it has a speed of 25 m/s. After the brakes are applied, the speed is reduced by
at = (0.001s - 1) m/s2
What is the magnitude of velocity of the car just before it reaches point C?
What is the magnitude of acceleration of the car just before it reaches point C?
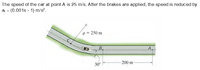
Transcribed Image Text:The speed of the car at point A is 25 m/s. After the brakes are applied, the speed is reduced by
at = (0.001s - 1) m/s?.
p = 250 m
B.
A,
- 200 m -
30°
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A skydiver jumps out of a helicopter and falls freely for 3.2 s before opening the parachute. (a) What is the skydiver's downward velocity when the parachute opens? m/s (b) How far below the helicopter is the skydiver when the parachute opens? marrow_forwardAccelerating uniformly to overtake a slow-moving truck, a car moving initially at 25.2 m/s covers 69.4 m in 2.48 s. (a) What is the final speed of the car? m/s(b) What is the magnitude of the car's acceleration? m/s2arrow_forwardAn object moving with uniform acceleration has a velocity of 10.0 cm/s in the positive x direction when its x coordinate is 3.06 cm. If its x coordinate 1.95 s later is -5.00 cm, what is its acceleration? cm/s²arrow_forward
- A snowboarder on a slope starts from rest and reaches a speed of 2.4 m/s after 7.1 s. (a) What is the magnitude (in m/s2) of the snowboarder's average acceleration? in m/s2 (b) How far (in m) does the snowboarder travel in this time? in marrow_forwardIn a test run, a certain car accelerates uniformly from zero to 16.8 m/s in 2.70 s. (a) What is the magnitude of the car's acceleration? m/s² (b) How long does it take the car to change its speed from 8.40 m/s to 16.8 m/s? S (c) will doubling the time always double the change in speed? O Yes O No Why?arrow_forwardAn object moving with uniform acceleration has a velocity of 11.0 cm/s in the positive x-direction when its x-coordinate is 3.21 cm. If its x-coordinate 2.25 s later is −5.00 cm, what is its acceleration? cm/s2arrow_forward
- A baseball is hit so that it travels straight upward after being struck by the bat. A fan observes that it takes 3.10 s for the ball to reach its maximum height. (a) Find the ball's initial velocity. m/s upward (b) Find the height it reaches. marrow_forwardA car travels in a straight line along a road. Its distance x from a stop sign is given as a function of time t by the equation x(t)=at2-Bßt3, where a = 2.25 m/s² and B = 0.0550 m/s³. Calculate the average velocity of the car for the time interval to = 0 tot = 3.00 s . %Darrow_forwardAn object moving with uniform acceleration has a velocity of 14.0 cm/s in the positive x-direction when its x-coordinate is 2.73 cm. If its x-coordinate 1.85 s later is −5.00 cm, what is its acceleration? cm/s2arrow_forward
- Assume that an MX missile goes from rest to a suborbital velocity of 3.50 km/s in 90.0 s (the actual speed and time are classified). What is its average acceleration in m/s2? What is its average acceleration in multiples of g?arrow_forwardA snowboarder on a slope starts from rest and reaches a speed of 2.9 m/s after 8.7 s. (a) What is the magnitude (in m/s2) of the snowboarder's average acceleration? m/s2 (b) How far (in m) does the snowboarder travel in this time? marrow_forwardA ball is thrown up with an initial speed of 43.0 m/s a) what is the ball's speed at its highest position? b) how long does it take the ball to reach its highest position? c) what is the magnitude of the ball"s acceleration at its highest position? d) what is the distance between the initial and highest position of the ball? e) what is the ball's speed when it comes back to its initial position?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON