
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
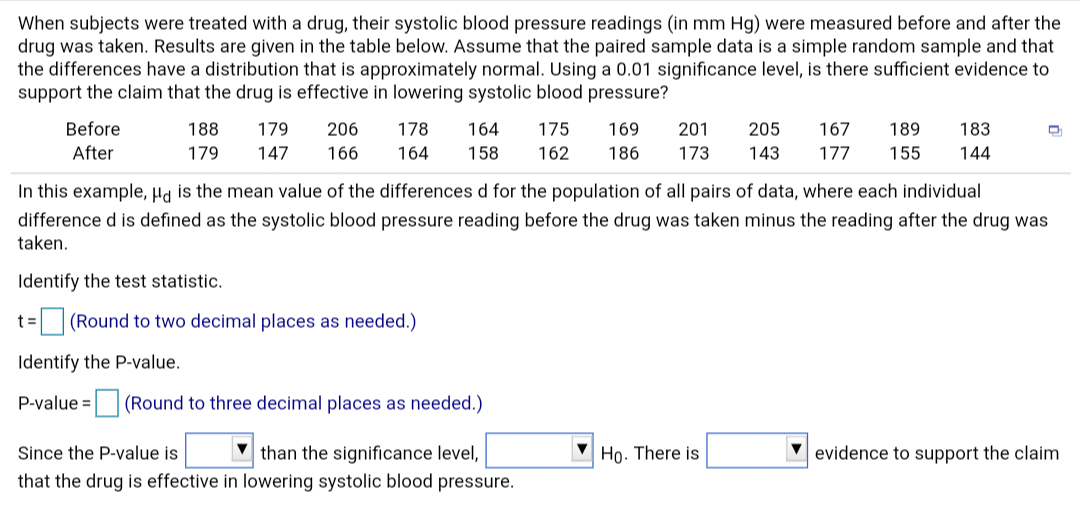
Transcribed Image Text:When subjects were treated with a drug, their systolic blood pressure readings (in mm Hg) were measured before and after the
drug was taken. Results are given in the table below. Assume that the paired sample data is a simple random sample and that
the differences have a distribution that is approximately normal. Using a 0.01 significance level, is there sufficient evidence to
support the claim that the drug is effective in lowering systolic blood pressure?
Before
178
201
205
179
206
164
175
169
167
189
183
188
After
179
173
177
147
166
164
158
162
186
143
155
144
In this example, Ha is the mean value of the differences d for the population of all pairs of data, where each individual
difference d is defined as the systolic blood pressure reading before the drug was taken minus the reading after the drug was
taken.
Identify the test statistic.
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Identify the P-value.
P-value =
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
than the significance level,
that the drug is effective in lowering systolic blood pressure.
Họ. There is
Since the P-value is
evidence to support the claim
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Use Chebyshevs rule and the empirical rule to describe the distribution of this data set. Count the actual number of observations that fall within one, two, and three standard deviations of the mean if the data set and compare these counts with the description of the the data set I developed.arrow_forwardListed in the accompanying table are heights (in.) of mothers and their first daughters. The data pairs are from a journal kept by Francis Galton. Use the listed paired sample data, and assume that the samples are simple random samples and that the differences have a distribution that is approximately normal. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that there is no difference in heights between mothers and their first daughters. ... Question content area top right Part 1 Mother 62.0 65.0 64.7 65.5 65.0 67.0 66.0 66.5 63.0 58.5 Daughter 68.0 69.0 66.5 63.0 68.0 62.0 66.5 66.7 63.5 66.5 Question content area bottom Part 1 In this example, μd is the mean value of the differences d for the population of all pairs of data, where each individual difference d is defined as the daughter's height minus the mother's height. What are the null and alternative hypotheses for the hypothesis test? H0:…arrow_forwardListed below are systolic blood pressure measurements (mm Hg) taken from the right and left arms of the same woman. Assume that the paired sample data is a simple random sample and that the differences have a distribution that is approximately normal. Use a 0.10 significance level to test for a difference between the measurements from the two arms. What can be concluded? Right arm 142 132 127 137 130 D Left arm 174 172 184 137 147 O A. Ho: Hd =0 B. Ho: Ha 0 H1: Hd =0 %3D OC. Ho: Hd = 0 H1: Hd 0 Identify the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) t= Identify the P-value. P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) What is the conclusion based on the hypothesis test?arrow_forward
- Listed below are systolic blood pressure measurements (mm Hg) taken from the right and left arms of the same woman. Assume that the paired sample data is a simple random sample and that the differences have a distribution that is approximately normal. Use a 0.10significance level to test for a difference between the measurements from the two arms. What can be concluded? Right arm 146 137 140 132 132 Left-arm 183 172 179 156 149 In this example, μd is the mean value of the differences d for the population of all pairs of data, where each individual difference d is defined as the measurement from the right arm minus the measurement from the left arm. What are the null and alternative hypotheses for the hypothesis test? Identify the test statistic. Identify the P-value.arrow_forwardDo men score higher on average compared to women on their statistics finals? Final exam scores of twelve randomly selected male statistics students and ten randomly selected female statistics students are shown below. Male: 65 94 63 85 84 72 79 80 95 79 75 84 Female: 54 60 81 72 65 66 61 77 64 77 Assume both follow a Normal distribution. What can be concluded at the the a= 0.01 level of significance level of significance? For this study, we should use Select an answer a. The null and alternative hypotheses would be: Ho: Select an answer Select an answer Select an answer (please enter a decimal) H₁: Select an answer Select an answer Select an answer (Please enter a decimal) b. The test statistic ? (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.) c. The p-value = (Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.) d. The p-value is ? a e. Based on this, we should Select an answer the null hypothesis. f. Thus, the final conclusion is that ... The results are statistically insignificant at a =…arrow_forwardWhen subjects were treated with a drug, their systolic blood pressure readings (in mm Hg) were measured before and after the drug was taken. Results are given in the table below. Assume that the paired sample data is a simple random sample and that the differences have a distribution that is approximately normal. Using a 0.01 significance level, is there sufficient evidence to support the claim that the drug is effective in lowering systolic blood pressure? Before 169 205 188 183 167 164 157 175 188 158 189 159 After 186 143 184 144 177 188 152 162 179 159 155 163arrow_forward
- A researcher would like to evaluate the effectiveness of a pain-relief patch designed for lower back pain. Prior to testing the patch, each of n = 8 patients rates the current level of back pain on a scale from 1 to 10. After wearing the patch for 90 minutes, a second pain rating is recorded. The data are as follows: Include in your responses: A. Compute the mean and variance for the sample of difference scores. B. Provide the Null and alternative hypotheses C. Calculate SSDarrow_forward7arrow_forwardWhat does the t test for the difference between the means of 2 independent populations assume? A. The sample sizes are equal. B. The sample variances are equal. C. The populations are approximately normal. D. All of the abovearrow_forward
- An article in a Journal reports that 34% of American fathers take no responsibility for childcare. A researcher claims that the figure is higher for fathers in the town of Littleton. A random sample of 234 fathers from Littleton yielded 96 who did not help with childcare. How many populations? 01 What is the parameter? O Mean O Proportion O Difference between Means O Variance Standard Deviationarrow_forwardListed below are systolic blood pressure measurements (mm Hg) taken from the right and left arms of the same woman. Assume that the paired sample data is a simple random sample and that the differences have a distribution that is approximately normal. Use a 0.05 significance level to test for a difference between the measurements from the two arms. What can be concluded? Right arm Left arm 151 136 120 134 134 181 174 180 156 138 In this example, Ha is the mean value of the differences d for the population of all pairs of data, where each individual difference d is defined as the measurement from the right arm minus the measurement from the left arm. What are the null and alternative hypotheses for the hypothesis test? O A. Ho: Hd = 0 O B. Ho: Hd 0 O C. Ho: Hd = 0 O D. Ho: Hd 0 H1: Ha>0arrow_forwardListed below are systolic blood pressure measurements (mm Hg) taken from the right and left arms of the same woman. Assume that the paired sample data is a simple random sample and that the differences have a distribution that is approximately normal. Use a 0.01 significance level to test for a difference between the measurements from the two arms. Identify the test statistic and p-value. A. T = -4.01, p-value = 0.016 B. T = -3.07, p-value = 0.037 C. T = -2.32, p-value = 0.081 D. T = -1.93, p-value = 0.127arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman