
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
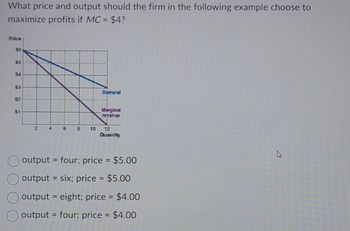
Transcribed Image Text:What price and output should the firm in the following example choose to
maximize profits if MC = $4?
Price
$0
$5
$4
$3
$2
$1
2
6
8
Demand
Marginal
revenue
10 12
Quantity
O output = four; price = $5.00
output = six; price = $5.00
output = eight; price = $4.00
output = four; price = $4.00
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A catering company producing fruit ice, in the Tandy school, has a production function q = 10min(k,l), where k is capital and 1 is labor. a. 15% If v = 81000 and w = 500 and P = 8600, where v, w, and P are as per the lecture notes, how many units of fruit ice will be produced and how much profit will be obtained? b. 10% Draw the supply curve for this catering company.arrow_forwardIn competitive markets, there are many small firms with each firm unable to influence the market price. Suppose company ABX operates in the wheat market. The company produces and markets wheats at a Price = $20 per container. The firm’s total costs are given as: TC = 50 +2Q + 3Q2 What level of output should the firm produce? Hint: Set P = MC and solve for Q. Use a graph to show your answers as wellarrow_forwardAssuming that the market for cigarettes is in perfect competition, what does allocative and productive efficiency imply in this case? What does it not imply?arrow_forward
- Suppose Rina runs a small business that manufactures frying pans. Assume that the market for frying pans is a competitive market, and the market price is $20 per frying pan. The following graph shows Rina's total cost curve. On the graph below, use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot total revenue and the green points (triangle symbol) to plot profit for the first seven frying pans that Rina produces, including zero frying pans. TOTAL COST AND REVENUE (Dollars) 200 175 150 125 100 75 50 25 0 -25 □ 0 1 U 2 ■ U 3 4 5 QUANTITY (Frying pans) n 6 Total Cost 7 8 Total Revenue Profit ?arrow_forwardCan you complete this question entirely and provide the solutions.arrow_forwardEconomists assume that by pursuing a strategy of cost minimization of production, most firms try to achieve profit maximization. Can you discuss the concept of an expansion path? If you can use a graph that would help me understand thank youarrow_forward
- do this question step by steparrow_forwardPlease help with this question If a competitive firm finds that its average variable cost is decreasing at its current profit maximizing quantity, should the firm increase or decrease output?arrow_forward“An upward – sloping demand curve doesn’t make sense in my business. All I know is that if I raise my prices, revenue doesn’t go up, it goes down. I don’t sell more products, I sell less. “Can you straighten out this business man’s thinking?arrow_forward
- In long-run equilibrium, all firms in the industry earn zero economic profit. Why is this true?arrow_forwardConsider a kettle firm A in a perfectly competitive market. Table 1 shows the quantity produced per hour (Q) and the total cost (TC) in the short run. Quantity 0 12345C70 2 6 8 Total cost 17 30 40 55 75 100 130 165 210 Fixed cost 17 17 17 17 17 17 17 17arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education