
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
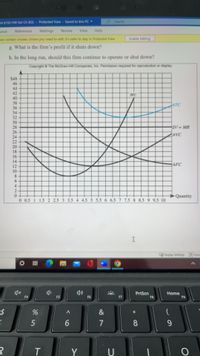
. The following graph summarizes the demand and costs for a firm that operates in a
- What level of output should this firm produce in the short run?
- What price should this firm charge in the short run?
- What is the firm’s total cost at this level of output?
- What is the firm’s total variable cost at this level of output?
- What is the firm’s fixed cost at this level of output?
- What is the firm’s profit if it produces this level of output?
- What is the firm’s profit if it shuts down?
- In the long run, should this firm continue to operate or shut down?
Transcribed Image Text:BA 6150 HW Set Ch 8(3) -
Protected View- Saved to this PC
OSearch
yout
References
Mailings
Review
View
Help
can contain viruses. Uniless you need to edit, it's safer to stay in Protected View.
Enable Editing
g. What is the firm's profit if it shuts down?
h. In the long run, should this firm continue to operate or shut down?
Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display
$48
46
44
42
40
38
36
34
32
30
28
26
24
22
20
18
16
14
12
10
8.
6.
MC
ATC
Df MR
AVC
AFC
2.
Quantity
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6 6.5 7 7.5 8 8.5 9 9.5 10
I
Oisplay Settings Focus
o 基
PrtScn
F8
Home
F9
F4
F5
F6
F7
24
&
5
7
8.
9-
T
Y
U
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider a perfectly competitive market. A firm is producing at a level where MR = MC and P > ATC.Draw the graph and clearly show the area that represents the firm’s profit or loss (and state which ofthe two it is). Describe what is likely to happen in the long run.arrow_forward9.7. A producer operating in a perfectly competitive market has chosen his output level to maximize profit. At that output, his revenue and costs are as follows: Revenue Variable costs $200 $120 $60 Sunk fixed costs Nonsunk fixed costs $40 Calculate his producer surplus and his profits. Which (if either) of these should he use to determine whether he should exit the market in the short run? Briefly explain. 9.8. Dave's Fresh Catfish is a northern Mississippi farm that operates in the perfectly competitive catfish farming industry. Dave's short-run total cost curve is STC(Q) = 400 + 2Q + 0.5Q², where Q is the number of catfish harvested per month. The corresponding short-run marginal cost curve is SMC(Q)=2+ Q. All of the fixed costs are sunk. a. What is the equation for the average variable cost (AVC)? b. What is the minimum level of average variable costs? c. What is Dave's short-run supply curve?arrow_forward9:20 Today Вack Edit 9:18 PM 9. You are given the following cost data: TFC TVC 12 1 12 5 12 9. 3 12 14 4 12 20 12 28 12 38 If the price of output is $7, how many units of output will this firm produce? What is the total revenue? What is the total cost? Will the firm operate or shut down in the short run? in the long run? Briefly explain your answers.arrow_forward
- 13. Firms in Competitive Markets The market for fertilizer is perfectly competitive. Firms in the market are producing output but are currently making economic losses. Which of the following statements is true about the price of fertilizer? Check all that apply. The price of fertilizer must be less than average total cost. The price of fertilizer must be less than marginal cost. The price of fertilizer must be equal to average variable cost. The following graphs show the cost curves faced by a typical firm, the demand for fertilizer, and possible price and supply curves. Prics and Cast MC Firm Demand Quantity Market Quantity (?) If firms in the market are producing output but are currently making economic losses, market, and indicates the corresponding supply curve. illustrates the present situation for the typical firm in the Assuming there is no change in either demand or the firm's cost curves, which of the following statements is true about what will happen in the long run? Check…arrow_forwardQ3arrow_forwardBrody's firm produces trumpets in a perfectly competitive market. The table below shows Brody's total variable cost. He has a fixed cost of $240, and the price per trumpet is $60.-Calculate the average total cost of producing 6 trumpets. Show your work. -Calculate the marginal cost of producing the 11th trumpet. -What is Brody's profit-maximizing quantity? Use marginal analysis to explain your answer. -At the profit-maximizing quantity you determined in part (c), calculate Brody's profit or loss. Show your work. -Brody also produces saxophones at a loss in a perfectly competitive market. Draw a correctly labeled graph for Brody's firm showing the following at a market price of $200. -Brody's profit-maximizing quantity of saxophones -Brody's loss, completely shaded Quantity Total Variable cost 6 $120 7 $145 8 $165 9 $220 10 $290 11 $390arrow_forward
- “That segment of a competitive firm’s marginal-cost curve that lies above its average-variable-cost curve constitutes the shortrun supply curve for the firm.” Explain using a graph and words.arrow_forwardV4arrow_forwardThe following graph shows the long-run supply curve for persimmons. Place the orange line (square symbol) on the following graph to show the most likely short-run supply curve for persimmons. (Note: Place the points of the line either on W and R or on W and M.) PRICE (Dollars per pound) 24 20 16 6 2 co 4 0 0 W 4 M R Long-Run Supply 2 6 8 10 QUANTITY (Thousands of pounds of persimmons) 12 Short-Run Supply ?arrow_forward
- Suppose the cost of renting a snowy bus were to fall from $30 per hour to $20 per hour. What do you expect would happen in the short-run (stage 1 equilibrium) to (a) the number of cones produced by each snowy bus; (b) total production of cones in the market, and (c) economic profits of snowy bus businesses? Briefly explain (you don't need to do any calculations, just explain inwords).arrow_forwardConsider the perfectly competitive market for steak (a normal good). Starting from long-run equilibrium, show graphically what happens in the short and long run to q. Q. P, and r in the market for steak (in comparison to the starting point) if income increases. Briefly explain.arrow_forward113. Subject :- Economyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education