
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
What kind of reaction alters the equilibrium? What is the effect of the addition of HCl to the equilibrium?
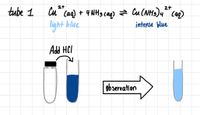
Transcribed Image Text:21
tube 1
Cu Caq) + 4 NH3 caq) z Cu(NH3)4 caq)
light blue
intense blue
Add HCI
ob servation
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Methane and hydrogen sulfide react to form hydrogen and carbon disulfide, like this: CH₂(g)+2H₂S(g) → 4H₂(g)+CS₂(g) Use this chemical equation to answer the questions in the table below. Suppose 165. mmol of CH4 and 330. mmol of H₂S are added to an empty flask. How much H₂ will be in the flask at equilibrium? Suppose 165. mmol of H, and 41.3 mmol of CS, are added to an empty flask. How much H₂ will be in the flask at equilibrium? None. O Some, but less than 660. mmol. O 660. mmol. O More than 660. mmol. O None. O Some, but less than 165. mmol. O165. mmol. More than 165. mmol. X Sarrow_forwardWhen a reaction is said to have reached equilibrium, it means A- The reaction in both directions have stopped. B- The rate of the forward reaction is higher than that of the reverse reaction. C- The concentration of reactant and product are equal. D- The concentration of reactant and products do not change over time. E- The rate of the forward reaction is lower than that of the reverse reaction.arrow_forwardPart III Short Answer 10. List 3 important factors for a reaction to reach equilibrium. Explain why these factors are necessary to reach equilibrium. 1) 2) 3)arrow_forward
- What is meant by a reaction being at equilibrium? * useing Le Chateliers Principlearrow_forwardConsider the reversible reaction. PCl5↽−−⇀PCl3+Cl2 What substances are present at equilibrium? Cl2Cl2 PCl3PCl3 PCl5PCl5 Are the concentrations of phosphorus pentachloride, PCl5,PCl5, and phosphosphorus trichloride, PCl3,PCl3, constant or changing at equilibrium? The concentrations of both PCl5PCl5 and PCl3PCl3 are changing at equilibrium. The concentrations of both PCl5PCl5 and PCl3PCl3 are constant at equilibrium. The concentration of PCl5PCl5 is constant, and the concentration of PCl3PCl3 is changing at equilibrium. The concentration of PCl5PCl5 is changing, and the concentration of PCl3PCl3 is constant at equilibrium. How does the equilibrium change if more chlorine, Cl2,Cl2, is added to the reaction? The equilibrium shifts to the left. The equilibrium shifts to the right. The equilibrium does not shift to either the left or the right. If more phosphorus pentachloride, PCl5,PCl5, is added, how does the equilibrium change? The equilibrium…arrow_forwardSuppose the reaction system: UO₂ (s) + 4HF (g) UF4 (g) + 2 H₂O (g) has already reached equilibrium. Predict the effect that each of the following changes will have on the direction of the reaction to reestablish equilibrium. Indicate whether the reaction will shift to the left, to the right, or no change. a. Additional HF is added to the system. b. The reaction is performed in a glass reaction container and the HF begins to react with the glass. c. Water vapor is added. d. The volume is increased.arrow_forward
- What are the Step to be followed to determining acidity using hybridization effects ?arrow_forwardWhich is the appropriate description to show the effect of a catalyst on the reaction rate and equilibrium in a reversible reaction: Reactants › Products O• The rate of the forward reaction is increased. • The rate of the reverse reaction is decreased 0 •The equilibrium position is displaced to the right O • The rate of the forward reaction is increased. The rate of the reverse reaction is increased The equilibrium position is unchanged. • The rate of the forward reaction is increased. 0 •The rate of the reverse reaction is unchanged • The equilibrium position is displaced to the right • The rate of the forward reaction is unchanged. The rate of the reverse reaction is unchanged The equilibrium position is unchanged. Suppose that an exothermic reaction, Reactants < › Products, is at equilibrium. According to Le Chatelier's Principle, if the reaction temperature is increased, in which direction will the equilibrium be displaced? O The equilibrium will be displaced toward the…arrow_forwardConsider the reaction. NaC2O2H3(s) <--- H2O ------> NaC2O2H3(aq), which is at equilibrium in an open flask in the lab at room temperature. You add more water to the equilibrium mixture. When the system reestablishes equilibrium, what has changed? a. the concentration of NaC2H3O2(aq) does not change b. heat is produced c. the concentration of NaC2H3O2(aq) decreases d. the concentration of the water increasesarrow_forward
- 1) When a system is at equilibrium: A) the reaction rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse B) the reaction rate of the reverse reaction is small compared to forward C) the reaction rate of the forward reaction is small compared to the reverse D) the amount of product and reactant is exactly equal 2) What will be the equilibrium expression for this reaction? (DO NOT INCLUDE SOLID PRODUCTS, THEIR CONCENTRATION IS ALWAYS EQUAL TO 1.) 4 CuO (s) + CH4 (g) = CO2 (g)+ 4 Cu (s) + 2 H2O (g) A) [CuO]/[Cu] B) [CuO]4/[Cu]4 C) [Cu]4/[CuO]4 D) [CO2][H20]2/[CH4] 3) Which K value below corresponds to the system with the highest proportion of reactants? А) К 3D25 B) K = 0.067 C) K = 1.5 x 10-3 D) K 3D 1.2 х 103arrow_forwardSelect all of the correct statements about equilibrium from the choices below. At equilibrium the rates of forward and reverse reactions are equal.Reactants are transformed into products even at equilibrium.At equilibrium the reverse rate equals zero.At equilibrium the speed of a reaction equals its rate constant.As a reaction proceeds forward toward equilibrium the reverse rate rises.At equilibrium the rate of change of product concentration is zero.arrow_forwardQUESTION 4 Adding a catalyst to an equilibrium system will: produce more products at equilibrium. produce more reactants at equilibrium. not change the amount of reactants or products at equilibrium.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY