
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
What is your predicted average population growth rate from this method, in terms of lambda AND % per year? Does that predict an increasing or decreasing population, on average?
| Year (t) | Nests at time t | Nests at t + 1 | N(t+1)/N(t) |
| 1983 | 746 | 780 | 1.046 |
| 1984 | 780 | 702 | 0.900 |
| 1985 | 702 | 744 | 1.060 |
| 1986 | 744 | 729 | 0.980 |
| 1987 | 729 | 843 | 1.156 |
| 1988 | 843 | 905 | 1.074 |
| 1989 | 905 | 992 | 1.096 |
| 1990 | 992 | 1180 | 1.190 |
| 1991 | 1180 | 1275 | 1.081 |
| 1992 | 1275 | 1241 | 0.973 |
| 1993 | 1241 | 1566 | 1.262 |
| 1994 | 1566 | 1930 | 1.232 |
| 1995 | 1930 | 1915 | 0.992 |
| 1996 | 1915 | 2219 | 1.159 |
| 1997 | 2219 | 3482 | 1.569 |
| 1998 | 3482 | 3365 | 0.966 |
| 1999 | 3365 | 5834 | 1.734 |
| 2000 | 5834 | 4927 | 0.845 |
| 2001 | 4927 | 5525 | 1.121 |
| 2002 | 5525 | 7601 | 1.376 |
| 2003 | 7601 | 6446 | 0.848 |
| 2004 | 6446 | 9258 | 1.436 |
| 2005 | 9258 | 10899 | 1.177 |
| 2006 | 10899 | ||
| average | 1.142 |
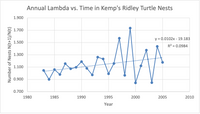
Transcribed Image Text:Annual Lambda vs. Time in Kemp's Ridley Turtle Nests
1.900
1.700
y = 0.0102x - 19.183
1.500
R2 = 0.0984
1.300
1.100
.....
...
....
0.900
0.700
1980
1985
1990
1995
2000
2005
2010
Year
Number of Nests N(t+1)/N(t)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Can you show an example similar to this problem part A - but not this problem - of how to calculate an exact percentage change?arrow_forward- GROWTH OF TABLET AND SMARTPHONE USERS The number of tablets and smartphones in use worldwide (in millions) in year t from 2010 through 2012 can be approximated by f(t) = 128.111.94 (1Si 3) %3D where t = 1 corresponds to 2010. a. How many tablets and smartphones were in use in 2011? b. How fast was the number of tablets and smartphones changing in 2011?arrow_forward= 1 W = 2 % Continue = 3 Integrating Evide....docx = 4 Type here to search = 5 X Suppose that the number of bacteria in a certain population increases according to a continuous exponential growth model. A sample of 1500 bacteria selected from this population reached the size of 1693 bacteria in three hours. Find the hourly growth rate parameter. Note: This is a continuous exponential growth model. Write your answer as a percentage. Do not round any intermediate computations, and round your percentage to the nearest hundredth. E S WRITING-CENTER_....pdf = 6 O = 7 PDF = 8 revised-summarizi....pdf T = 9 = 10 W C 11 12 Ⓒ2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use → 83°F Mostly clear ^ 13 Privacy Center | D Submit A 1 8.arrow_forward
- How do you calculate an exponential smoothing model using alpha = 0.5 and 0.8. What is the prediction for 7/1/2021 for each technique? Forecasts Date Day of Week Rooms Sold MA 2 MA 4 ES (0.8) ES (0.5) 6/1/2021 Tuesday 123 6/2/2021 Wednesday 109 6/3/2021 Thursday 140 116.0 6/4/2021 Friday 199 124.5 6/5/2021 Saturday 179 169.5 142.8 6/6/2021 Sunday 140 189.0 156.8 6/7/2021 Monday 117 159.5 164.5 6/8/2021 Tuesday 132 128.5 158.8 6/9/2021 Wednesday 108 124.5 142.0 6/10/2021 Thursday 151 120.0 124.3 6/11/2021 Friday 182 129.5 127.0 6/12/2021 Saturday 168 166.5 143.3 6/13/2021 Sunday 161 175.0 152.3 6/14/2021 Monday 119 164.5 165.5 6/15/2021 Tuesday 133 140.0 157.5 6/16/2021 Wednesday 139 126.0 145.3 6/17/2021 Thursday 146 136.0 138.0 6/18/2021 Friday 168 142.5 134.3 6/19/2021 Saturday 188 157.0 146.5…arrow_forwardThe logistic model P(t) = 96.0235 1+0.0455-0.1864t represents the percentage of households that do not own a personal computer t years since 1983. Complete parts (a)-(d). (a) Evaluate and interpret P(0). Evaluate P(0). P(0) = 91.8 % (Round to one decimal place as needed.) Which sentence below best describes P(0)? O A. P(0) is the year all households had a personal computer. O B. O C. O D. P(0) is the year no households had a personal computer. P(0) is the percentage of households with a personal computer in 1983. P(0) is the percentage of households without a personal computer in 1983. -Carrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman