
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
What is the value of P in the system shown in Fig. 5.9(a) to cause the motion to impend?Assume the pulley is smooth and coefficient of friction between the other contact surfaces is 0.2.
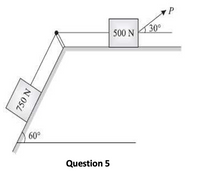
Transcribed Image Text:500 N 30°
60°
Question 5
750 N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The three flat blocks are positioned on the 30° incline as shown in Figure WDG – 3F, and a force P parallel to the incline is applied to the middle block. The upper block is pre vented from moving by a wire which attaches it to the fixed support. The coefficient of static friction for each of the three pairs of mating surfaces is shown. 1. Calculate the normal force (N) acting between 50-kg and 40-kg blocks (ANSWER: 680) and the maximum frictional resistance (N) on the surface between the 30-kg and 50-kg blocks (ANSWER: 76.5) 2. Calculate the maximum frictional resistance (N) on the surface between the 40-kg block and inclined surface (ANSWER: 459) and also determine the maximum value which P (in N) may have before any slipping takes place (ANSWER: 94).arrow_forwardPROBLEM 5: The upper block is attached to the ground as shown in the figure by a short rope. The coefficient of friction between the blocks is 0.25 while the angle of friction between the lower block and the horizontal ground is 30°. (a) Determine the tension in the rope, in N, when the lower block is about to move. (b) Determine friction force, in N, under the 900 N block when it is about to move. (c) Determine the horizontal force P, in N, required to initiate motion. 300 N P 900 N 30°arrow_forwardBlocks A and B have a masses of 150 kg and 280 kg, respectively. (Figure 2) The coefficient of static friction between A and B and between B and C is 0.290. The coefficient of static friction between the rope and peg E is 0.570. Pulley D rotates freely, and P = 27.0 N. If \theta = 60.0 degrees, what is the smallest magnitude, T, of tension, T, that causes block B to move? P A B E Tarrow_forward
- A skier stands on a 5° slope. If the coefficient of static friction is 0.1, does the skier start to slide down?arrow_forwardAn arrangement of three boxes is shown in figure below. Box A weighs 25 N and rests on an inclined plane, while box B weighs 50 N and rests on a horizontal plane. The coefficient of friction between box A and the inclined plane is 0.3, and between box B and the horizontal plane is 0.4. The pulleys are all frictionless. Determine the range of weight of box C for which no motion will occur. Consider both sliding and tipping of boxes A and B. 0.6 m 0.75 m 25 N 5 A 4 C pome 0.8 m 0.6 m 50 N B 1.2 marrow_forwardA wedge assembly, composed of wedges X and Y, is designed to lift crate W whose weight is 1CDE N, as shown in the figure below. What will be the maximum force P that can be applied before movement begins if the coefficient of friction for all surfaces of contact is 0.0875? Draw all necessary free-body diagrams and indicate the direction of impending motion. This is not your it in any way property so do not use were your own. 1CDE N W This is not your own property so do not use it in any way as if it were your own. 1C P property sol The not it in any way if your ow Parameters 1℃° 1D ° 1E ° 1CDE N 13° 14° 15° 1345 N 1Dº of use 1Eºarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY