
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134753119
Author: Sheldon Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
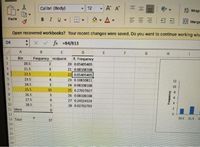
what is the relative frequency of yields in sample A that were greater than 21.5 and less than or equal to 22.5 q/ha?
i am getting the wrong one. its saying mine is incorrect.
Transcribed Image Text:Calibri (Body)
v 12
• A A
3 Wrap
Paste
BIUV
三==|E
E Merge
Open recovered workbooks? Your recent changes were saved. Do you want to continue working whe
D4
: x v fx =B4/B13
A
B
D
Bin
Frequency midpolnt
R. Frequency
20.5
2.
20 0.05405405
21.5
3.
21 0.08108108
22.5
2.
22 0.05405405
23.5
4
23 0.10810811
12
24.5
24 0.08108108
10
25.5
10
25 0.27027027
8.
26.5
3.
26 0.08108108
6.
27.5
9.
27 0.24324324
10
28.5
28 0.02702703
11 More
12
13 Total
37
20.5 21.5
14
15
16
17
18
Aouanba
234 567
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, probability and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the cumulative frequency of students that scored half of the points on the SAT? choices: 1. none of the above/can't be determined 2. 26 3. 9 4. 55.5 5. 0.35 I already tried 2(26) and 5(0.35) but it was wrong.arrow_forwardEpistasis is a phenomenon in which one gene controls the expression of another. In one case, a dihybrid cross should yield a 9:3:4 ratio. You collect the following data on mice: black coat: 138 brown coat: 46 white coat: 60 Is there any reason to doubt the ratio of 9 black : 3 brown : 4 white?arrow_forwardWhich of the following is NOT a requirement of testing a claim about the mean of the differences from dependent samples? Choose the correct answer below. O A. The degrees of freedom aren- 2. O B. The samples are simple random samples. O C. The sample data are dependent. O D. Either the number of pairs of sample data is larger than 30 or the pairs have differences that are from a population having a distribution that is approximately normal, or both.arrow_forward
- 4. A new method for cholesterol utilizing 4 - aminoantipyrine was evaluated in the laboratory. The procedure was run in on 20 separate days. The following values are given: Mean = 150 mg/dl Sum of the squared difference from the mean is 3600 Calculate the SD.arrow_forward9.13 Given a sample size of 36, how large does the population standard deviation have to be in order for the standard error to be A. 1? B. 2? C. 5? D. 100?arrow_forwardWhat percent of our campus is female? If no preliminary study is made to estimate, how large a sample is needed be 99% sure that the error will be no more than 0.03 from?arrow_forward
- You want to compare differences in prior arrests across ethnicity in your study, you measured ethnicity as white =0 black =1 hispanic=2, and other =3. Prior arrests was recorded as the number of prior arrests. which test would you perform to see if arrests differ across diffrent ethnic categories? A. ANOVA B. T-testarrow_forwardI. There are two samples with means 15 and 18. Both of those samples consist of 24 observations. Sample standard deviations are equal to 4 in both cases. If you want to test whether the difference between the mean in the first and the mean in the second population is equal to 0, what is your decision at the .01 level?arrow_forwardIn a measurement of B two results were obtained, B1 = (8.3+/- 0.78) mT and B2 = (8.81+/- 0.20) mT . The error on the weighted/arithmetic mean is (Report your answer in mT with 3 significant figures)arrow_forward
- 14.arrow_forwardSuppose a one sided test for a proportion resulted in a p-value of 0.06. What would the p-value be if the test were two tail test? Select one: A. It would still be 0.06. B. It would be 0.3. C. It would be 0.12. D. There is no way to calculate this without completely redoing the original test with a new alternative hypothesis.arrow_forward1. An experimenter feels that a population standard deviation is no larger than 17.0and would like to construct a 95% two-sided t-interval for the population mean that has alength at most 2.8. What sample size would you recommend?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON

A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:9780134753119
Author:Sheldon Ross
Publisher:PEARSON
