
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
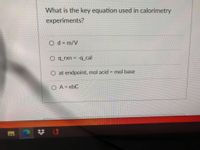
Transcribed Image Text:**Title: Key Equation Used in Calorimetry Experiments**
**Question:** What is the key equation used in calorimetry experiments?
**Options:**
1. \( d = \frac{m}{V} \)
2. \( q_{\text{rxn}} = -q_{\text{cal}} \)
3. At endpoint, mol acid = mol base
4. \( A = \epsilon b C \)
**Explanation:**
1. **Option 1: \( d = \frac{m}{V} \)**
- This equation is used to calculate the density of a substance, where \( d \) is density, \( m \) is mass, and \( V \) is volume.
2. **Option 2: \( q_{\text{rxn}} = -q_{\text{cal}} \)**
- This is the key equation used in calorimetry. It states that the heat of the reaction (\( q_{\text{rxn}} \)) is equal to the negative of the heat absorbed by the calorimeter (\( q_{\text{cal}} \)). This principle is based on the law of conservation of energy, implying that the energy lost by the system must be gained by the surroundings.
3. **Option 3: At endpoint, mol acid = mol base**
- This statement is relevant to titration experiments and not specific to calorimetry. It indicates that at the endpoint of a titration, the amount of moles of acid equals the amount of moles of base.
4. **Option 4: \( A = \epsilon b C \)**
- This equation is known as Beer's Law in spectroscopy, where \( A \) is absorbance, \( \epsilon \) is molar absorptivity, \( b \) is path length, and \( C \) is concentration.
**Correct Answer:**
- The correct answer is **Option 2: \( q_{\text{rxn}} = -q_{\text{cal}} \)**.
This equation is essential for understanding and calculating the energy changes occurring during chemical reactions in calorimetry experiments.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How many grams of sodium chloride can be formed from 6.8 g sodium carbonate and excess calcium chloride? Use proper dimensional analysisarrow_forwardFor the following reaction, 6.61 grams of benzene (C6H6) are mixed with excess oxygen gas. The reaction yields 18.6 grams of carbon dioxide.benzene (C6H6) (l) + oxygen (g) carbon dioxide (g) + water (g) What is the ideal yield of carbon dioxide? grams What is the percent yield for this reaction? %arrow_forwardSketch an energy diagram graph representing an endothermic reaction and label the following.arrow_forward
- Considering the amount of energy absorbed or released, what type of reaction occurs when gasoline is consumed in a car?arrow_forwardInterpret the following equation for a chemical reaction using the coefficients given: H2(g) + F2(g) → 2 HF(g) On the particulate level: of H2(g) reacts with of F2(g) to form of HF(g). On the molar level: of H2(g) reacts with of F2(g) to form of HF(g).arrow_forwardMethane (CH4) reacts with chlorine gas (Cl2) to form carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and hydrochloric acid (HCl).a) Write a balanced equation for this chemical reaction. b) What is the coefficient for chlorine gas?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY