
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
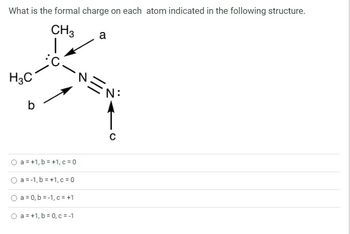
Transcribed Image Text:What is the formal charge on each atom indicated in the following structure.
CH3
H3C
O
○
O
b
a = +1,b=+1,c=0
a=-1,b=+1,c=0
a = 0,b=1,c= +1
O a = +1,b=0,c=-1
a
2
C
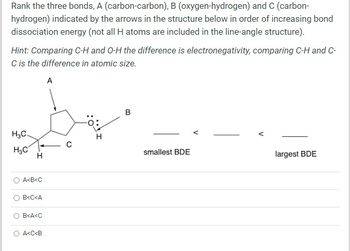
Transcribed Image Text:Rank the three bonds, A (carbon-carbon), B (oxygen-hydrogen) and C (carbon-
hydrogen) indicated by the arrows in the structure below in order of increasing bond
dissociation energy (not all H atoms are included in the line-angle structure).
Hint: Comparing C-H and O-H the difference is electronegativity, comparing C-H and C-
C is the difference in atomic size.
A
H3C.
H3C
H
A<B<C
B<C<A
B<A<C
A<C<B
B
smallest BDE
V
largest BDE
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Nhy is resonance structure A and resonance structure B not the same structure? If you rotate the molecule like a spicket handle (l. e. clockwise with the C at the center and the R group remaining in place as you look down the C - R bond) wouldn't you get the same thing? Why are these not equivalent structures? Resonance structure A t Resonance structure B Actual structurearrow_forwardConsider the reaction 2H₂ + O₂ --> 2H₂O. One way to imagine this reaction (this is NOT how it really happens) is by breaking all the bonds in H₂ and O2, and then forming new bonds in the H₂O. In the three boxes below, draw out: 2H₂ + O2 (Showing all the bonds) What it would look like if all the bonds in 2H₂ + O2 broke 2H₂O (showing all the bonds)arrow_forwardHW4arrow_forward
- Q3: Draw the Lewis structures for nitromethane (CH3NO2) and methyl nitrite (CH3ONO). Draw at least two resonance forms for each. Determine which form for each is the major resonance contributor. Page 1 of 4 Chem 0310 Organic Chemistry 1 Recitations Q4: Draw the Lewis structures for the cyanate ion (OCN) and the fulminate ion (CNO-). Draw all possible resonance structures for each. Determine which form for each is the major resonance contributor.arrow_forwardHow come there are two major resonance structure? Wouldn't the structure with the positive charge on the nitrogen be the only major structure, as it is less electronegative than oxygen?arrow_forwardExamples: Example: H▬N▬H HIN: Examples: :F Н lone pair : -bond pair (2 e-) single bond :F: Non-Polar 8+. H :F: H:Cl: HCl:o is better represented as closer to Cl due to its greater electronegativity. Thus, HCl contains a polar covalent bond. H :0: Polar lone pair 8- :S H -S= :0: 2 bond pairs (4 e-) double bond because the bond electrons are pulled F: Polaarrow_forward
- Why is it less clear to see the electrons on HBrO2 molecular electron geometry than it is on something like H2O? I know there should be 20 electrons on HBrO2, but this leads me to an incorrect drawing. And with the correct drawing, I don't see where all the electrons are. It seems like there's only 10 total. What am I missing here?arrow_forward5. Three possible resonance structures for dinitrogen monoxide (N20) are drawn below. :N=N=ö: EN: :NEN- -0: :N-NE0: a. How many total valence electrons are available in N20? b. What is the formal charge on the oxygen atom in the structure farthest to the left? Resonance structures that are considered unimportant when describing the average bonding are those that either have individual atoms bearing a formal charge greater than or equal to two for any individual atom and/or a high total absolute value formal charge for the entire molecule, calculated by adding the absolute values of each of the atoms. Which of these three structures not as important as the other two in determining the accurate structure of N20? Support your conclusion using formal charges. С.arrow_forwardWhich has a greater dipole moment? CH2Cl2 or CH2F2 The book states that a C-Cl bond has a greater dipole moment than a C-F bond, regardless of F's larger electronegativity, because the C-Cl has a larger bond length. Does the same logic apply?arrow_forward
- 3. One curved arrow shows the movement of an electron pair. o a bond (sigma or pi) involves two electrons, so each curved arrow indicates some change in bonding. Step 6: When a curved arrow starts from a o bond and points to a distant atom, the o bond breaks and a new o bond is formed. A -B A-C B* B-C A* or Note that two possible cations can be formed, depending on whether the electrons from the o bond move with atom A or B. Draw curved arrows to form the products shown. Select Draw Rings More Erase Al H. -0: + AIH, H - Al -H étv 0 hulu MacBook Pro GSearch or type URL & 5 7 T Y * 00arrow_forwardDraw the Lewis structure for formaldehyde, CH2O. Include all hydrogens and lone pairs explicitly.arrow_forward2. Rank the following C-H bonds (labeled a, b, c, d) in decreasing strength (strongest to weakest bond). Justify your answer. H a H b Harrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY