
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
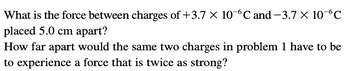
Transcribed Image Text:What is the force between charges of +3.7 x 10-6℃ and −3.7 × 10-6℃
placed 5.0 cm apart?
How far apart would the same two charges in problem 1 have to be
to experience a force that is twice as strong?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the arrangement of three point charges in a right triangle shown in the figure, which have charges q1 = 9.5 μC, q2 = -69 μC, and q3 = 25 μC. The distance between q1 and q2 is 28 cm and the distance between q2 and q3 is 61 cm. q1 = 9.5 μCq2 = -69 μCq3 = 25 μCa = 28 cmb = 61 cm 1. How much potential energy, in joules, is stored in this configuration of charges? 2. Now assume that q1 and q2 are fixed in space at the locations indicated, and q3 is brought into it's position from infinity. What is the change in potential energy of the system, in joules, during this process?arrow_forwardQuestion 1 1.0 nc 60° 60° 2.0 nC -2.0 nc In the configuration of charges shown in the figure above, a – 3.50 cm. What is the magnitude of the force on the 1.0 nC charge? Question 2 4.0 cm 2.0 cm 3.0 cm 3.0 cm In the figure above, q7 = 3.05 nC, 92= 6.10 nC, and q3 = 6.10 nC. If the net force on q, is 0, then what would q be? Answer:arrow_forwardThree equal charges are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle 0.50 m on a side. What are the magnitude of the force on each charge if the charges are each -3.1×10-9 C?arrow_forward
- Consider the following figure. (The four charges are at the corners of a square. Take q = 1.11 µC and Q = 2.07 µC.) (a) In the figure, what are the magnitude and direction of the resultant force on q1? (Take q1 as the origin of the coordinate system and measure the angle counterclockwise from the positive x-axis, which is directed towards the right.) magnitude direction (b) What is the resultant force on the center of mass of the four charges?arrow_forwardConsider the following figure. (The four charges are at the corners of a square. Take q = 1.02 µC and Q = 2.03 µC.) 92=Q 9₁ = 9 10.0 cm 93=-9 94= -Q (a) In the figure, what are the magnitude and direction of the resultant force on 9₁? (Take 9₁ as the origin of the coordinate system and measure the angle counterclockwise from the positive x-axis, which is directed towards the right.) magnitude direction O (b) What is the resultant force on the center of mass of the four charges?arrow_forwardGive the illustration of the given situation Two positive charges, when combined, give a total charge of +9.0 uC. When the two charges are separated by 3.00 m, the force they exerted to one another has a magnitude of 8.00 x 10-3 N.arrow_forward
- Three charges are located as shown in the figure, with values q1 = 4.6 × 10-16 C, q2 = -1.9 × 10-16 C, q3 = 6.75 × 10-16 C. The charges are separated by d1 = 3.4 × 10-6 m and d2 = 4.5 × 10-6 m. a. What is the force of q2 on q1 in the x direction, Fx? Give your answer in newtons, and recall k = 8.988 × 109 N m2/C2. b. What is the force of q3 on q1 in the y direction, Fy? Give your answer in newtons.arrow_forwardRank the following scenarios in terms of the strength of the force between particles A and B from strongest to weakest. QA and QB are the charges of particles A and B, and d is the distance between the particles. If two of the scenarios have forces are equal in strength, mention that. (Ranking the order of the letters is fine.) (a) QA = +2 µC, QB = +2 µC, and d = 4 m (b) QA = −4 µC, QB = −2 µC, and d = 2 m (c) QA = +2 µC, QB = +4 µC, and d = 4 m (d) QA = +1 µC, QB = +1 µC, and d = 1 m (e) QA = −1 µC, QB = +2 µC, and d = 2 marrow_forwardConsider two thin, conducting, spherical shells as shown in cross-section in the figure below. The inner shell has a radius r₁ = 19.7cm and a charge of 10.4nC. The outer shell has a radius r₂ = 30.4cm and a charge of -27.0nC. с Barrow_forward
- Consider the following figure. (The four charges are at the corners of a square. Take q = 1.08 µC and Q = 1.83 µC.) (a) In the figure, what are the magnitude and direction of the resultant force on q1? (Take q1 as the origin of the coordinate system and measure the angle counterclockwise from the positive x-axis, which is directed towards the right.) magnitude direction ° (b) What is the resultant force on the center of mass of the four charges?arrow_forwardA charge of Q creates an electric field of E= 100 N/C at a distance of r= 0.1 m. If two charges Q1 = 1.4Q and Q2 = -1.1Q are separated by a distance of { = 0.6 meters, what is the magnitude of the electric field at point P that is at the middle of the charges? Express your answer with one decimal point in units of N/C.arrow_forwardThree charges are located as shown in the figure, with values q1 = 3.3 × 10-16 C, q2 = -1.1 × 10-16 C, q3 = 6.25 × 10-16 C. The charges are separated by d1 = 2.9 × 10-6 m and d2 = 2.1 × 10-6 m. What is the force of q2 on q1 in the x direction, Fx? Give your answer in newtons, and recall k = 8.988 × 109 N m2/C2.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON