Question
Transcribed Image Text:What is the energy structure of metals, semiconductors and insulators?
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
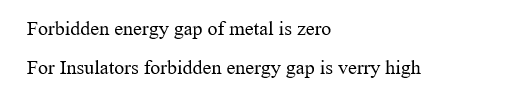
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Explain how a metal-oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) acts as a transistor. Explain how it functions as a transistor by describing its parts and how they work.arrow_forwardSpeeds of molecules in a gas vary with temperature, whereas speeds of electrons in the conduction band of a metal are nearly independent of temperature. Why are these behaviors so different?arrow_forward