
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
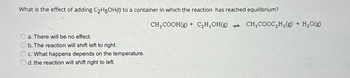
Transcribed Image Text:What is the effect of adding C₂H5OH() to a container in which the reaction has reached equilibrium?
a. There will be no effect.
b. The reaction will shift left to right.
c. What happens depends on the temperature.
d. the reaction will shift right to left.
CH₂COOH(g) + C₂H,OH(g) CH₂COOC₂H,(g) + H₂O(g)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Keq for the reaction below is 0.680. Initially the concentration of carbon monoxide is 0.500 mol/L and chlorine is 1.00 mol/L. Determine the equilibrium concentrations of all entities. (This reaction will actually proceed to the LEFT!) COCl2 <---> CO(g) + Cl2(g)arrow_forward1C. Please don't write on a paper. I can't understand handwritten.arrow_forwardConsider the following reaction at equilibrium:2SO2(g) + O2 (g) <==> 2SO3(g)Determine if the following changes will increase, decrease or not affect the partial pressure of SO2.a. Decreasing the amount of oxygen in the systemb. Decreasing the volume of the systemc. Decreasing the temperature of the systemd. Decreasing the pressure of the systeme. Adding a catalyst to the reaction systemarrow_forward
- 4. A. An important reaction in the commercial production of hydrogen is CO(g) + H2O(g) --><-- H2(g) + CO2(g) How will the system at equilibrium shift in each of the five following cases? (Use arrows or write "right" , "left" , or "no shift"). a. Gaseous carbon monoxide is removed b. In rigid reaction container, a catalyst is added. c. The temperature is decreased (the reaction is exothermic). d. The reaction container volume is doubled. e. Hydrogen gas is added. B. The equation above has a Kc value of 7.5 x 102. If 2.0 moles of each reactant and product are put into the same sealed 4.0 L container, determine the concentrations of all species present at equilibrium. Please answer A with sub parts and B.arrow_forwardAssume that the following exothermic chemical reaction is at equilibrium. CuO (s) + H2 (g) ⇌ H2O (g) + Cu (s). Which of the following statements is CORRECT? Choose one option. a. Increasing the concentration of H2 (g) will cause the reaction to proceed in the backward direction (shift to left), increasing the equilibrium concentration of H2O (g). b. Decreasing the temperature will cause the reaction to proceed in the forward direction (shift to right), increasing the equilibrium concentration of H2O (g). c. Increasing the amount of CuO(s) will cause the reaction to proceed in the forward direction, increasing the equilibrium concentration of H2O (g). d. Increasing the temperature will cause the reaction to proceed in the forward direction (shift to right), increasing the value of the equilibrium constant of this reaction. e. The value of the equilibrium constant for this reaction will stay the same after the temperature is increased.arrow_forward2C02 2 2C0+0 Consider the reaction above. If pressure was increase on this equilibrium, how would that affect the amounts of reactants? O They would decrease O They would remain the same O They would increasearrow_forward
- Which reaction, when at equilibrium, would be unaffected by a change in pressure? A. N2(g) + O2 (g) = 2NO(g) B. 2CO(g) + O2 = 2CO2(g) C. COBr2(g) = CO(g) + Br2(g) D. N2O4(g) = 2NO2 (g)arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is/are true? I. The system is in equilibrium when the reaction quotient and equilibrium constant expression are equal. II. When the reaction quotient is higher than the equilibrium constant expression, forward reaction is favored to reach equilibrium. III. When the equilibrium constant expression is higher than the reaction quotient, reverse reaction is favored to reach equilibrium. O I, Il and III O I and III only O l and Il only O Il and III only O I onlyarrow_forwardIndicate how each of the following will affect the equilibrium concentration of NH3 in the following reaction: 4NH3(g) + 5O2 ←→ 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g) + 906 kJ (since the energy is a positive value the rxn is "endo") a. Adding more O2(g) b. Increasing the temperature c. Increasing the volume of the container d. Adding more NO(g) e. Removing some H20(g)arrow_forward
- 64. Consider this reaction at equilibrium: 2 BRNO(g) = 2 NO(g) + Br2(8) Predict whether the reaction will shift left, shift right, or remain unchanged after each disturbance. a. NO is added to the reaction mixture. b. BINO is added to the reaction mixture. c. Brz is removed from the reaction mixture.arrow_forward41. Given this reaction at equilibrium: 2C0(g) + 02(g)= 2C02(g). Which statement regarding the reaction is always true? * a. the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal O b. the reaction occurs in an open system O c. the masses of the reactants and the products are equal O d. the concentrations of the reactants and the products are equal 42. Which factors must be equal in a reversible chemical reaction at equilibrium? * a. the concentrations of the reactants and products O b. the potential energies of the reactants and products c. the activation energies of the forward and reverse reactions Od. the rates of reaction of the forward and reverse reactionsarrow_forwardConsider the equilibrium, 2 NO (g) N2₂ (g) + O₂ (g), 2 for which AH = -180 kJ mol-1. How will adding more N₂ (g) affect an equilibrium mixture of the three gases? Select one: a. Reaction will proceed to the right (in the forward direction) to generate more product. b. Reaction will proceed to the left (in the reverse direction) to generate more product. C. Reaction will proceed to the right (in the forward direction) to generate more reactant. d. Reaction will proceed to the left (in the reverse direction) to generate more reactant. e. There will be no change to equilibrium mixture.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY