
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
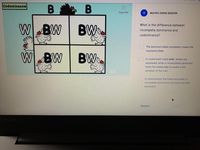
Transcribed Image Text:Codominance
B
B
Copy link
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
W BW
What is the difference between
BW
incomplete dominance and
codominance?
The dominant allele completely masks the
recessive allele.
WBW
BW.
In codominant traits both alleles are
expressed, while in incompletely dominant
traits the alleles mix to create a 3rd
Voulbbe
variation of the trait.
In codominance the traits are mixed, in
incomplete domiannce the traits are both
expressed.
Rewatch
Submit
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A set of true breeding white cows were crossed with true breeding black cows to produce all brown colored offspring. If the F2 generation yielded 113 brown, 47 black and 50 white what type of inheritance would that reflect? Full credit will only be awarded when you show your work and explain your reasoning. The type of inheritance reflected is Codominant since 50% of the offsprings doesn’t reflect the color of either parent. A single new phenotype is presented when one allele of dominance and one allele for recessive trait is paired heterozygous. This shows that for a specified gene, there are three possible phenotypes that can arise from pairing, a phenotype for homozygous dominant, homozygous recessive. For heterozygous, the allele that is dominant, W, is codominant to the allele that is recessive, w, and when paired together neither is expressed but a blended, or mixed phenotype is expressed.arrow_forwardThe gene for eye color has several alleles. The allele for brown eyes is symbolized with B and the allele for blue eyes is symbolized with b. A father has the phenotype of blue eyes (recessive trait) and a mother has a phenotype of brown eyes (dominant trait.). If they have a child, what is the most likely genotype? Bb bb BB none of thesearrow_forwardAn allelic series determines coat color in rabbits: C (full color), cch (chinchilla, gray color), c* (Himalayan, white with black extremities), and c (albino, all white). The C allele is dominant over all others, cch is dominant over c and c, ch is dominant over c, and c is recessive to all other alleles. This dominance hierarchy can be summarized as C> cch > c^ > c. The rabbits in the table are crossed and produce the progeny shown. Cross Parents Offspring А full color x albino 50% full color, 50% albino В Himalayan x albino 50% Himalayan, 50% albino C full color x albino 50% full color, 50% chinchilla D full color × Himalayan 50% full color, 25% Himalayan, 25% albino E full color x full color 75% full color, 25% albino Match the parental genotypes to the letter corresponding to the appropriate cross listed in the table. A В C D E Answer Bank Ccch x cc Cc x cc СС х сс hch x cc Сс х сс Сс х Сс chc x ccarrow_forward
- Incomplete Dominance and Codominance So far, we have been studying the inheritance of genes that show complete dominance. In other words, one allele is completely dominant over another. In some cases, such as incomplete dominance and codominance, one allele is not completely dominant over another or the alleles affect the phenotype equally. Examples of incomplete dominance include feather color in parrots (C*C* = blue, C'C = yellow, C*Cf = green) and hair texture in humans CC = curly; C'C' = straight; CC' = wavy Practice Problem 3: За. If a straight-haired man marries a curly haired woman, what are the predicted genotypes and phenotypes of their children? If a parrot with yellow feathers is crossed with a parrot with green feathers, what are the predicted genotypes and phenotypes of their offspring? 3b.arrow_forwardFor n = number of genes segregating, how many different phenotypes and genotypes are observed in the F2 generation? Assume complete dominance at each gene. 2" phenotypes and 3" genotypes 3" phenotypes and 2" genotypes n2 phenotypes and n° genotypes n3 phenotypes and n2 genotypesarrow_forwardIn the red backed vole (a small mouse-like mammal) there are two traits under investigation. The first trait is a distinct tuft of long hairs at the tip of the tail with a tufted tail being recessive to non-tufted tail. The letter T is used to represent the tail tuft gene. The second trait is a patch of red fur on the head which is known to be recessive to the more common lack of a red patch. The letter R is used to represent this trait. A female to be used in the cross was drawn from a pure breeding line that consistently has both the red patch on the head and a tufted tail. The female is to be crossed with a male from a highly variable wild population. The male used had no red head patch and a normal (untufted) tail. The results were as follows: 7 red head patch with tail tuft, 8 no red head patch with tail tuft, 8 red head patch without tail tuft, 8 no red head patch without tail tuft. What would the results be if the male was crossed with a female that was known to be…arrow_forward
- What would be the phenotypic and genotypic ratio in F2 generation of the offspring of two parents? One parent is homozygously dominant for height and the other parent is recessive or height.arrow_forwardIn a poultry breed, chickens can have black, blue or white feathers. The different feather colors are determined by interactions between genes at two loci. One locus determines the type of pigment produced by the skin cells: a dominant allele B encodes black pigment, whereas a recessive allele b encodes blue pigment. Alleles at a second locus affect the deposition of the pigment onto the feathers. Allele E allows dark pigment (black or blue) to be deposited, whereas the homozygous recessive (ee) condition prevents the deposition of dark pigment, causing the feathers to be white. In each of the following 3 crosses give the genotypes and phenotypes of the parents and their offspring: a) Two black birds that are both heterozygous for traits B and E b) Two blue birds that produce 6 blue and 2 white chicks c) A black bird that is homozygous dominant for both traits and a white bird that is homozygous recessive for both traitsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education