
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:What is AG° for the conversion of glucose into lactic acid?
CH1206(aq)
2CH,CH(OH)COOH(aq)
->
kJ
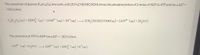
Transcribed Image Text:The conversion of glucose (C6H1206) into lactic acid (2CH3CH(OH)COOH) drives the phosphorylation of 2 moles of ADP to ATP and has a AG° =
%3D
-135 kJ/mol.
CH1206laq) +2HPO (aq) +2ADP3- (aq) +2H* (aq)
2CH,CH(OH)COOH(aq) +2ATP4- (aq) +2H,0(1)
The conversion of ATP to ADP has a AG° = -30.5 kJ/mol.
ATP4- (aq) +H,0(1) ADP (aq) +HPO (aq) +H*(aq)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The standard reaction free energy AG = 890. kJ for this reaction: ALO3(s) + 3H₂(g) 2 Al(s) + 3H₂O(g) Use this information to complete the table below. Round each of your answers to the nearest kJ. reaction — Al(s) + H₂O(g) → = ALO, (-) – È F¹₂ (3) –Al₂O; (3) + H₂(g) — — Al(s) – H₂O(g) 2Al(s) + 3H₂O(g) → ALO₂ (s) + 3H₂(g) 4 AG 0 OKJ Xarrow_forwardPLS HELP ME WITH THE FOLLOWING ASAP !!arrow_forwardCalculate AG° at 595 K for H20(g) + 1/2 O2(g) S H2O2(g) using the following data: H2(g) +O2(g) H2O2(g) K = 3.7 x 1037 at 595 K 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(g) K= 2.6 x 10° at 595 K AGO kJ/molarrow_forward
- What is AG° for the reaction CH;OH(g) → CO(g) + 2 H2(g) at 25°C? AH° = +90.7 kJ/mol AS° = +221 J/mol•K kJ/mol 1 2 3 4 C 7 8 9. +/- x 10 0 LOarrow_forwardA student determines the value of the equilibrium constant to be 2.33×1016 for the following reaction.Ca(OH)2(aq) + 2HCl(aq) ----> CaCl2(s) + 2H2O(l)Based on this value of Keq:ΔG° for this reaction is expected to be (greater, less) ____ than zero.Calculate the free energy change for the reaction of 2.34 moles of Ca(OH)2(aq) at standard conditions at 298K.ΔG°rxn = _______ kJarrow_forwardWhat is AG° for the reaction CH₂OH(g) → CO(g) + 2 H₂(g) at 25°C? AH° = +90.7 kJ/mol kJ/molarrow_forward
- The standard reaction free energy AG = -311. kJ for this reaction: P4(s) + 20 HF (g) 4 PF 5(g) + 10 H₂(g) → Use this information to complete the table below. Round each of your answers to the nearest kJ. reaction 2PF, (g) + 5H₂(g) → P₁ (s) + 10HF (g) 2 4 4PF, (g) + 10H₂(g) 3P (s) + 60HF (g) P(s) + 20HF (g) 4 12PF, (g) + 30H₂(g) 2 AGⓇ KJ kJ kJ x10 X 5arrow_forwardThe standard reaction free energy AGO= == -910. kJ for this reaction: 6 C(s) + 6H₂(g) + 3O₂(g) →C6H12O6(s) Use this information to complete the table below. Round each of your answers to the nearest kJ. AGⓇ reaction x10 1 C₂H₁2O6 (s) → 2C (s) + 2H₂ (g) + O₂ (g) kJ 3 C6H₁2O6 (s). 6C (s) + 6H₂(g) + 30₂ (g) kJ 12 3 1 3C (s) + 3H₂(g) + - 12/0₂ (8) → — C₂H₁2 06 (8) kJ 6 12 X ?arrow_forwardAt constant pressure and 25°C, the ΔrH° for the following reaction is –1560 kJ/mol C2H6(g) + 3.5O2(g) → 2CO2(g) +0.5 H2O(l) What is the enthalpy change for the oxidation of 5 g of C2H6?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY