
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
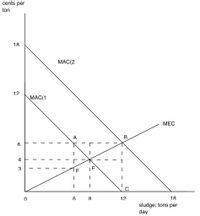
What are the estimated abatement cost
Transcribed Image Text:cents per
ton
18
MAC(2
12
MAC(1
МЕС
В
6.
4
3
F
6.
8.
12
18
sludge; tons per
day
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Can you explain why the following statement is false? The efficient level of a pollution-emitting activity (e.g., production of a good) is that at which the marginal external cost of pollution is equal to zero.arrow_forwardThe diagram to the right illustrates the market for outdoor concert tickets in a park in the middle of a residential area in a particular town. Ticket prices are measured in dollars (the grid is drawn for $2.50 increments) and ticket quantities are measured in thousands. The locals are not happy about the increased traffic congestion and noise that accompany each concert. Note that supply curve S, represents the marginal private cost of the concerts. What is the cost of the externality $55- $50- $45- per concert ticket? $40- ..... The cost of the externality is $ per concert ticket sold. $35- (Round to the nearest cent as needed.) $30.00 $30+ $25- $20.00 $20- ........ $15- $10- $5- 10 15 $0- 10 15 20 30 Q of Tickets (Thousands) 25 P. .....arrow_forwardSuppose that a local airport is near a residential neighborhood. To land at this airport, an airliner must pay $51. To soundproof the local homes, so residents do not hear airplanes all hours of the day, residents must pay $28. What is the private cost for a plane to land at this airport? What is the external cost of a plane landing at the airport? What is the social cost of a plane landing at the airport? F11 F12 F5 F6 F8 F9 F10 F7 F2 F3 F4 prt sarrow_forward
- Describe how government actions can lead to more efficient outcomes when negative and positive externalities are present.arrow_forwardThe primary source of air pollution in the small town of Smokey, Nevada is a nearby steel mill. The local environmental agency has decided that the mill needs to reduce its emissions because the town's population is located directly downwind from it. Currently the agency is considering three different approaches to reducing pollution from the mill: a technology standard, an emission standard and an emission tax. Why might the owner of the mill prefer an emission standard to a technology standard that would produce the same level of emissions? a Because with emission standards the polluter is more flexible in selecting the technology that will minimize her abatement cost Ob. Because polluters usually try to stick to their existing technology O C. Because it has been proven to be easier to implement O d. Because polluters, as all producers are suspicious about new technologiesarrow_forwardThe figure below shows the marginal benefit (demand) of polluting for two firms: Alpha and Beta. Before the introduction of a pollution tax, pollution is free, that is, MC = $0 per ton of emissions. Marginal Benefit (MB) to Firm Tax = $100 0 MB BETA MBALPHA 25 50 75 100 Emissions (tons) The government decides to impose a tax on pollution of $100 per ton of emissions. That is, the per-unit the tax is the marginal cost of polluting. Which of the follow are true? (Select all that are true.) a. As a result of the tax, the total emissions will decrease by 50 units b. The tax was intended to decrease production by 50 units for each firm. c. As a result of the tax, both firms will decrease emissions by the same amount d. After the tax is imposed, Firm Beta will emit 50 tons more pollution than Firm Alpha e. Before the tax is imposed, Firm Beta emitted more pollution than Firm Alpha f. As a result of the tax, total emissions from the two firms will be cut in half g. The amount of tax collected…arrow_forward
- Consider the market for steel. Suppose that a steel manufacturing plant dumps toxic waste into a nearby river, creating a negative externality for those living downstream from the plant. Producing an additional ton of steel imposes a constant external cost of $165 per ton. The following graph shows the demand (private value) curve and the supply (private cost) curve for steel. Use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot the social cost curve when the external cost is $165 per ton. 1100 990 Social Cost 880 770 Supply (Private Cost) 660 550 440 330 220 Demand 110 (Private Value) 1 2 4 7 QUANTITY (Tons of steel) PRICE (Dollars per ton of steel)arrow_forwardThe demand for cigarettes is given by Figure 1 P = 550 - 0.2Q. Price 650- Cigarettes are manufactured at a constant marginal cost of 100 and sold in a 600- 550 competitive market. 500여 450 What is the quantity of cigarettes sold in equilibrium? Oprivate =U 400여 350- If cigarettes generate a marginal external cost of MEC = 0.20Q, what is the socially optimal level of cigarettes? 300 250- Qsocially optimal= 200여 150 Using Figure 1 on the right that already shows the market demand curve to illustrate the private and social MC curves. Also, point out the private market quantity, the socially optimal quantity, and the social welfare cost. 100 50 D 0- 1) Using curve as 'MC'. line drawing tool, illustrate the private marginal cost curve. Label this 400 800 1200 1600 2000 2400 2800 Output 2) Using the line drawing tool, illustrate the social marginal cost curve. Label this curve as 'MSC'. (Hint: to plot this correctly you may first want to plot the socially optimal point 'B' in step 4 below)…arrow_forwardWhat is the socially optimal quantity, and how much is the social cost at this quantity?arrow_forward
- it is microeconomics If a firm does not pay for an external cost, who does? Why might there be a deadweight loss in a positive externality situation, when the amount bought and sold in the market is below the market optimal equilibrium amount? Why might private firms not want to produce certain types of goods?arrow_forwardWhy is emission mitigation is considered as a public good?arrow_forwardWhy is it socially efficient to set marginal benefits equal to marginal costs rather than abating until total benefits equal total costs?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education